Sequence to Sequence with RNNs
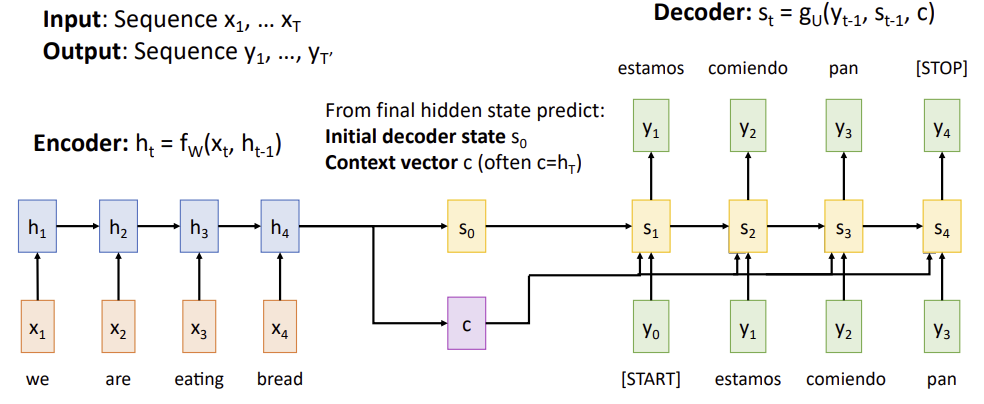
C : encoded sequence와 decoded sequence 사이의 정보를 전딜하는 과정
문제 : input sequence bottlenecked through fized-sized vector. What if T=1000?
C (context vector)는 input sequence의 모든 관련 정보를 캡처하여 decoder를 초기화하는 데 사용된다. 입력 시퀀스 T가 길어지면 single fixed size vector로 sequence의 모든 정보를 효과적으로 요약하는 것이 어려워진다.
해결 : use new context vector at each step of decoder! (provide different context vector at each decoding step)
Sequence to Sequence with RNNs and ATTENTION
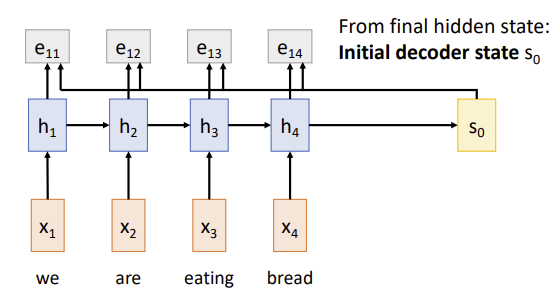
h4에만 의존하는 대신, attention mechanism은 decoder가 output sequence의 각 token을 생성할 때 encoder의 모든 hidden states(h1, h2, h3, h4)를 고려한다.
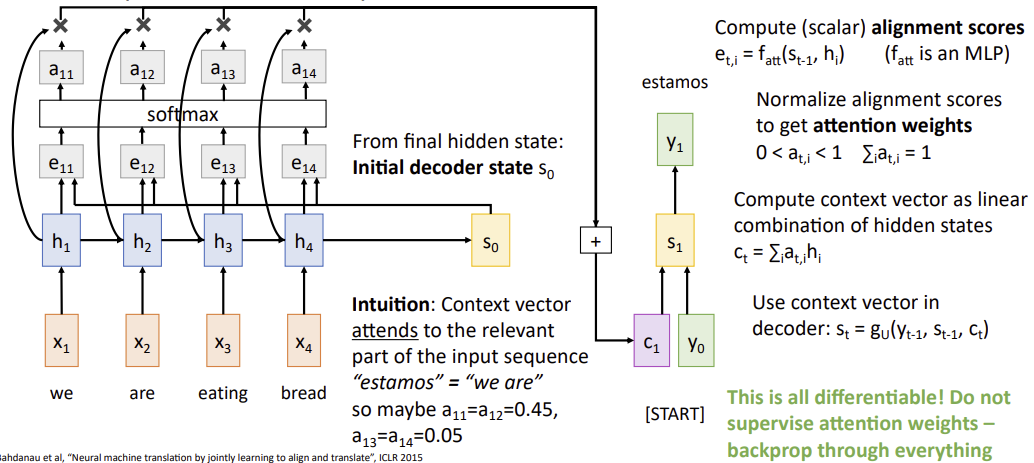
repeat : use to compute new context vector
Use a different context vector in each timestep of decoder
1. input sequence not bottlenecked through single vector
2. at each timestep of decoder, context vector "looks at" different parts of the input sequence
Image captioning with RNNs and ATTENTION
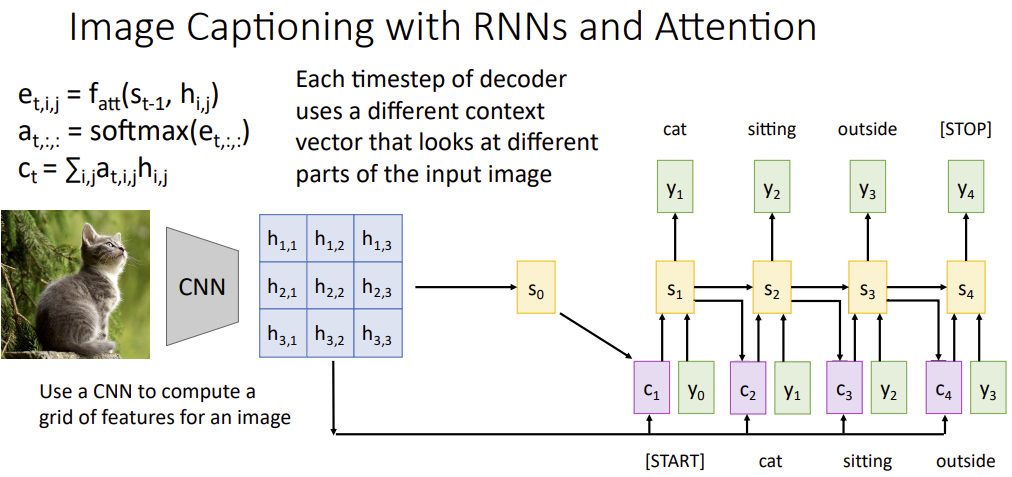
: how much do we want to emphasize the vector
: summing over all position in the image i,j
output sequence를 생성하는 각 시간 단계마다, 입력 이미지의 grid of features를 가중합하여 모델이 새로운 context vector를 생성할 수 있도록 한다.
Attention Layer
Changes :
- use scaled dot product for similarity
- multiple query vecotrs
- seperate key and value
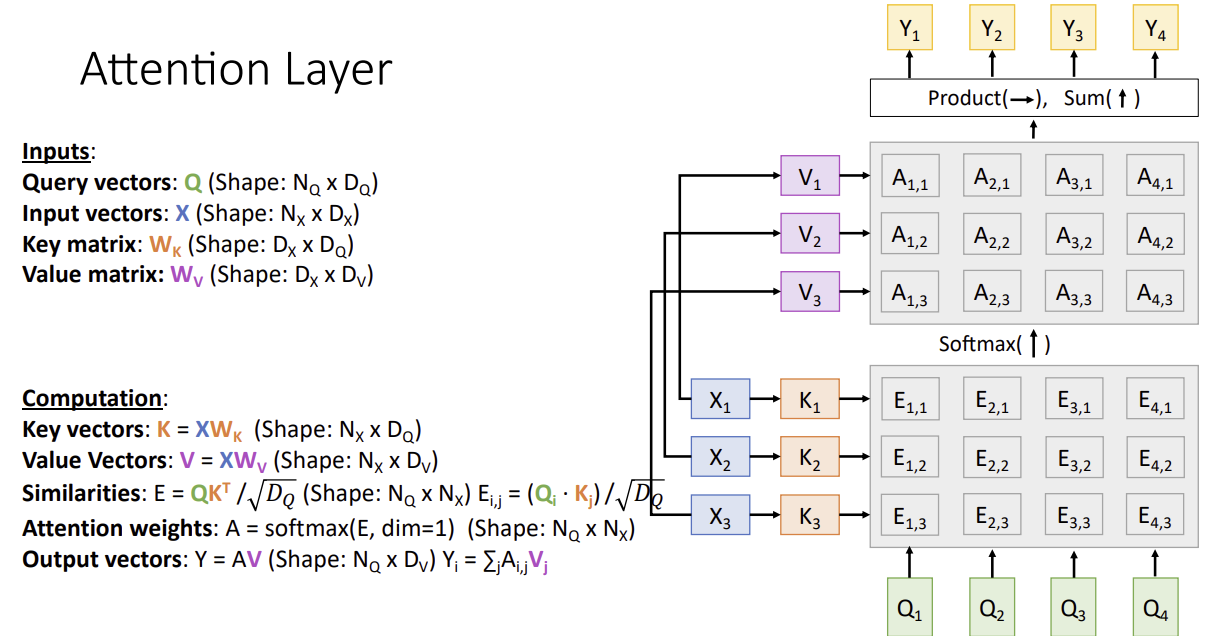
- Query vector: decoder의 현재 상태에서 생성
- Key, Value vector: encoder의 output에서 생성
- Query와 Key 벡터의 similarity를 계산하여 attention weights를 얻고, 이 weights를 Value 벡터에 적용하여 context vector 생성
Self-Attention Layer
one query for input vector
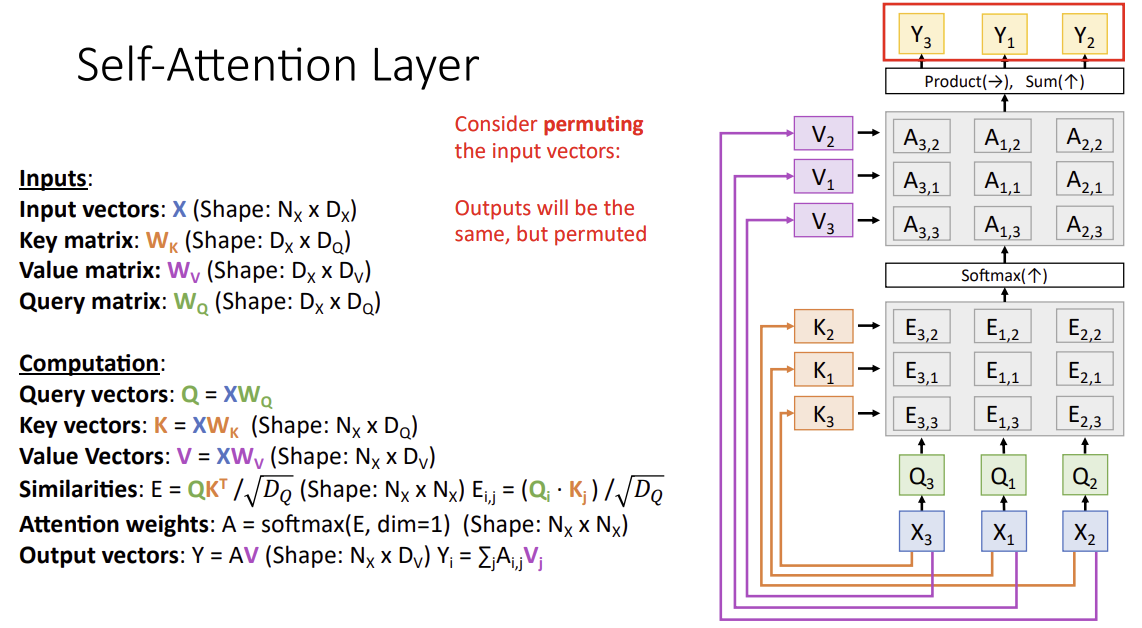
- Query, Key, Value 벡터: 모두 동일한 input sequence에서 생성
- input sequence의 각 위치에 대해 Query, Key, Value vector를 생성하고, 각 Query 벡터가 모든 Key 벡터와의 유사도를 계산하여 attention weights를 얻는다.
- 이 weights를 사용하여 Value 벡터의 가중합을 계산하고, 이를 통해 각 위치의 새로운 표현을 생성
- 이 과정은 input sequence 내의 각 위치가 다른 모든 위치와의 관계를 고려할 수 있게 한다.
-> 네트워크에 의해 결정된 비선형적인 방식으로 입력의 각 벡터를 다른 모든 벡터와 비교하는 것
근데 self-attention layer is Permutation Equivariant
따라서 positional encoding 사용
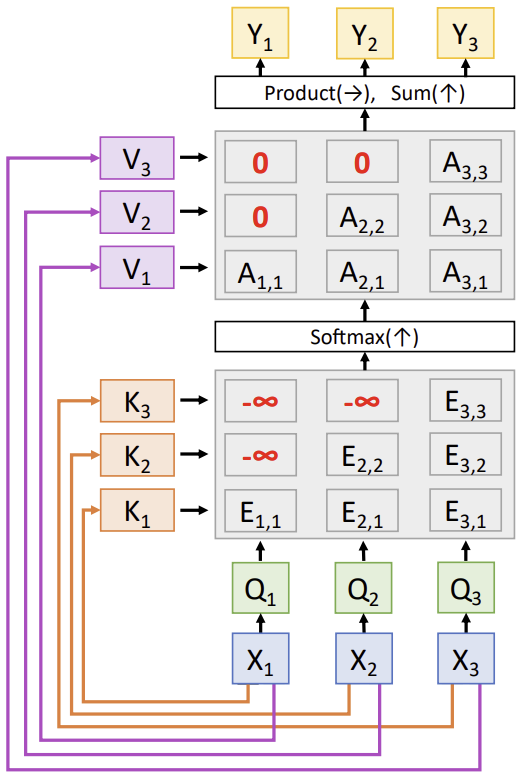
Masked Self-Attention Layer
Don't let vectors "look ahead" in the sequence
Multihead Self-Attention
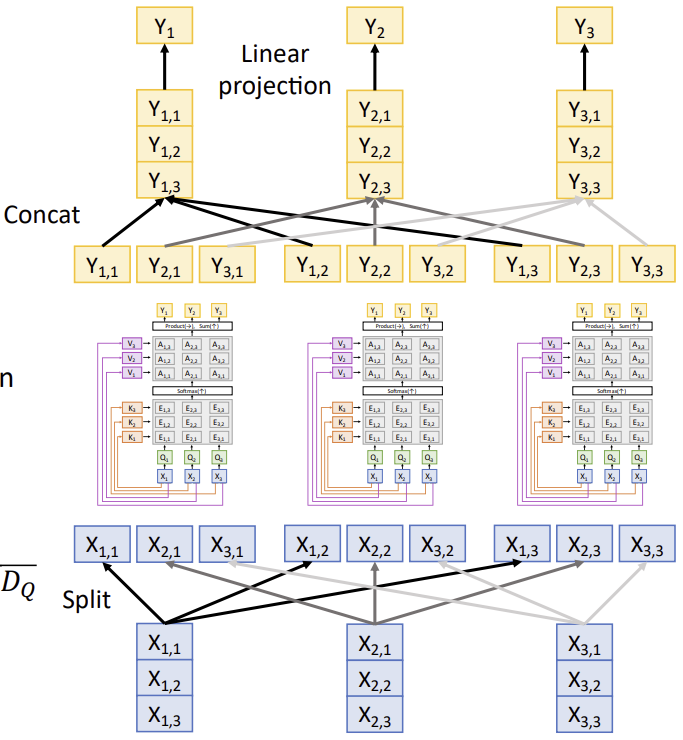 H개의 독립적인 Attention Head를 병렬적으로 사용함
H개의 독립적인 Attention Head를 병렬적으로 사용함
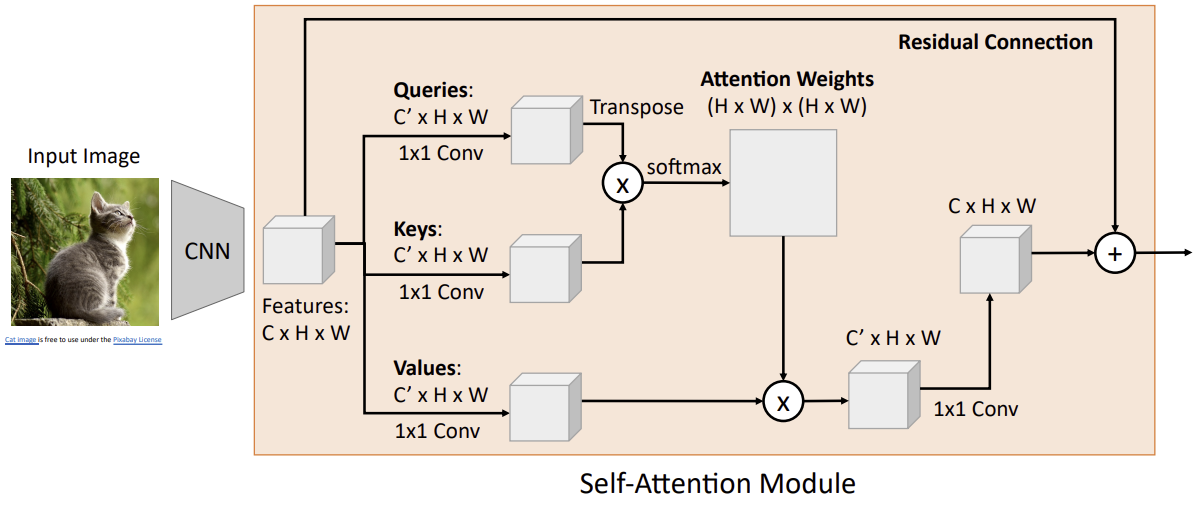
Example: CNN with Self-Attention
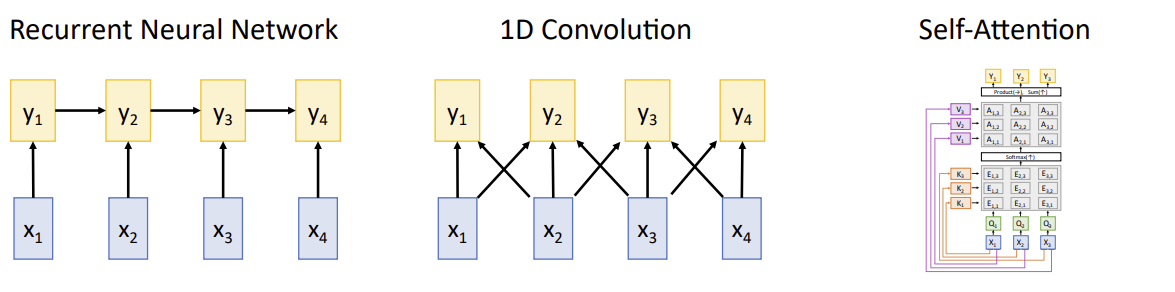
Three Ways of Processing Sequences
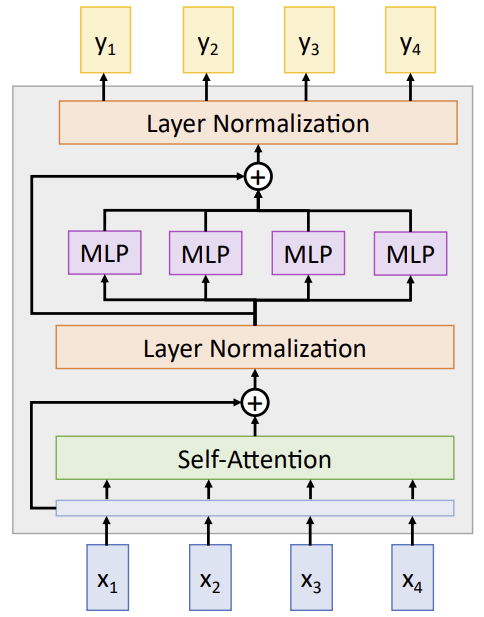
근데 "Attention is all you need"
The Transformer
self-attention : vector들 사이에 상호작용 유일함
layer norm, MLP : vector들 사이에서 독립적으로 작동함
Summary
- Adding Attention to RNN models lets them look at different parts of the input at each timestep
- Generalized self-attention is new, powerful neural network primitive
- Transformers are a new neural network model that only uses attention -> Attention is All you Need