Recurrent Neural Network
RNN은 순차적인 데이터를 처리하기 위해 개발되었으며, 이는 feedforward network의 한계를 극복
variable-length sequences 처리 가능
capturing temporal dependencies
recurrent neural networks의 역할 : process sequences
non-sequential data도 sequential processing으로 가능
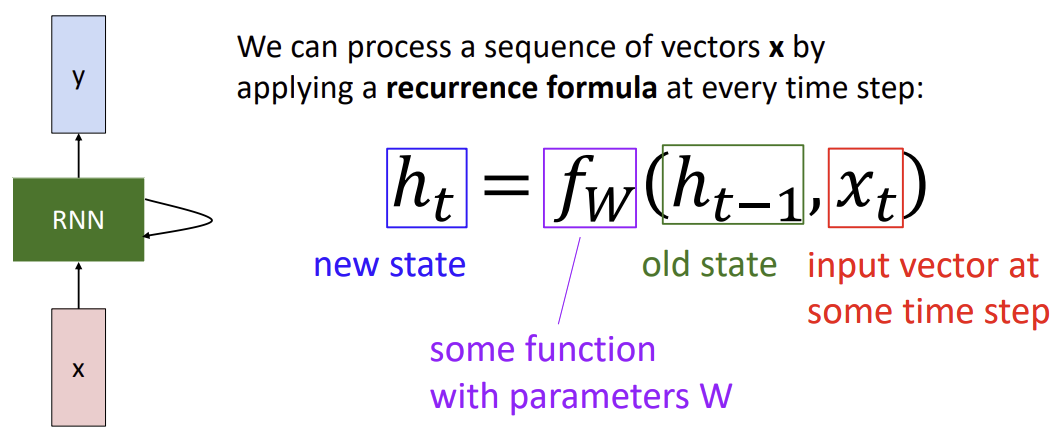
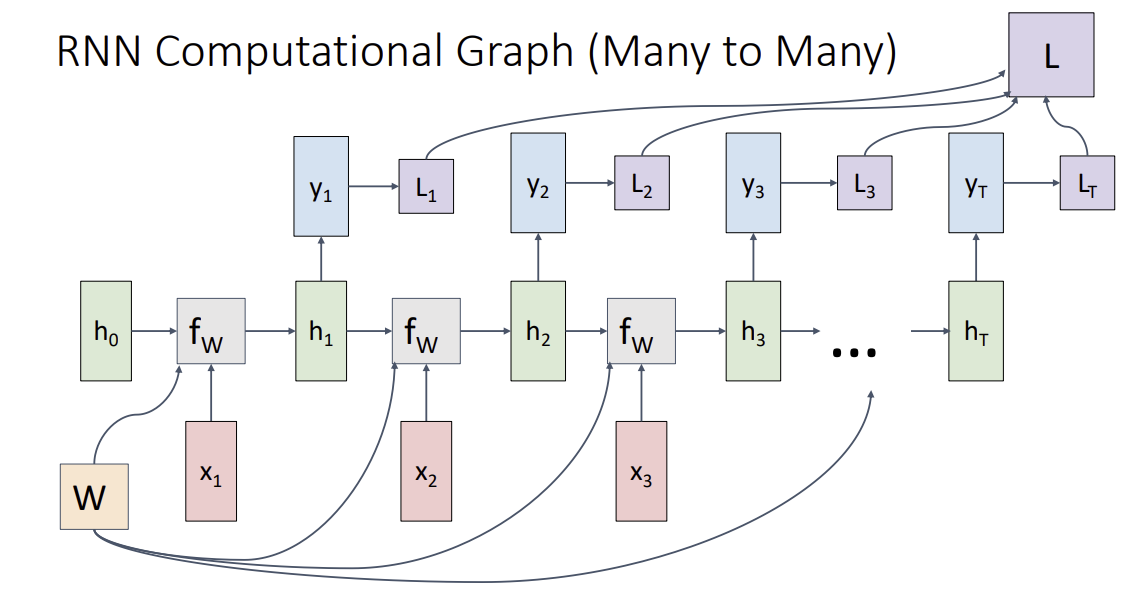
: 매 time step 마다 같은 function과 parameters가 사용된다.
Sequence to Sequence (seq2seq)
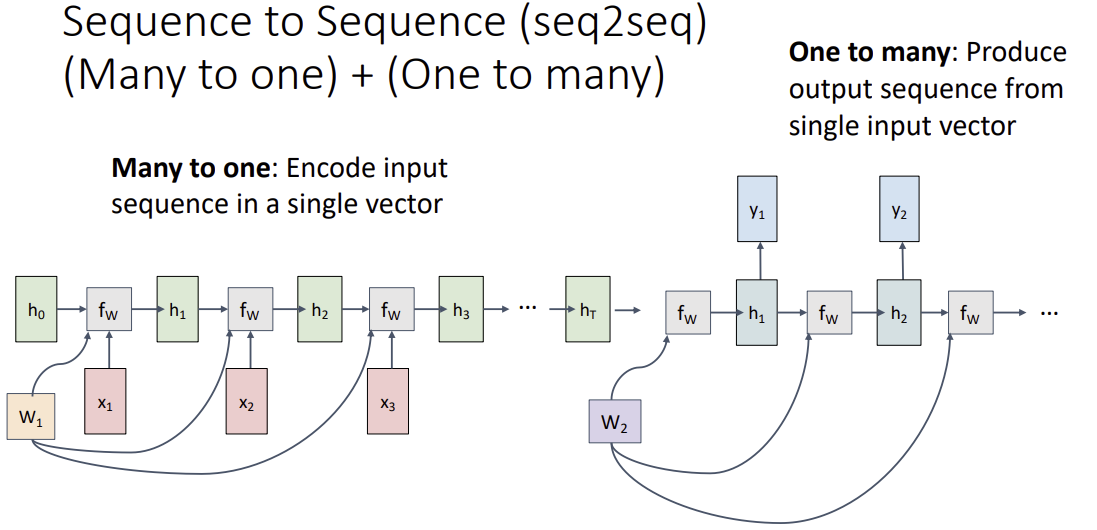
-> output token의 길이가 input token과 길이가 다를 수 있어서 다음과 같은 방법을 사용한다.
encoder(many to one)와 decoder(one to many)로 사용된다.
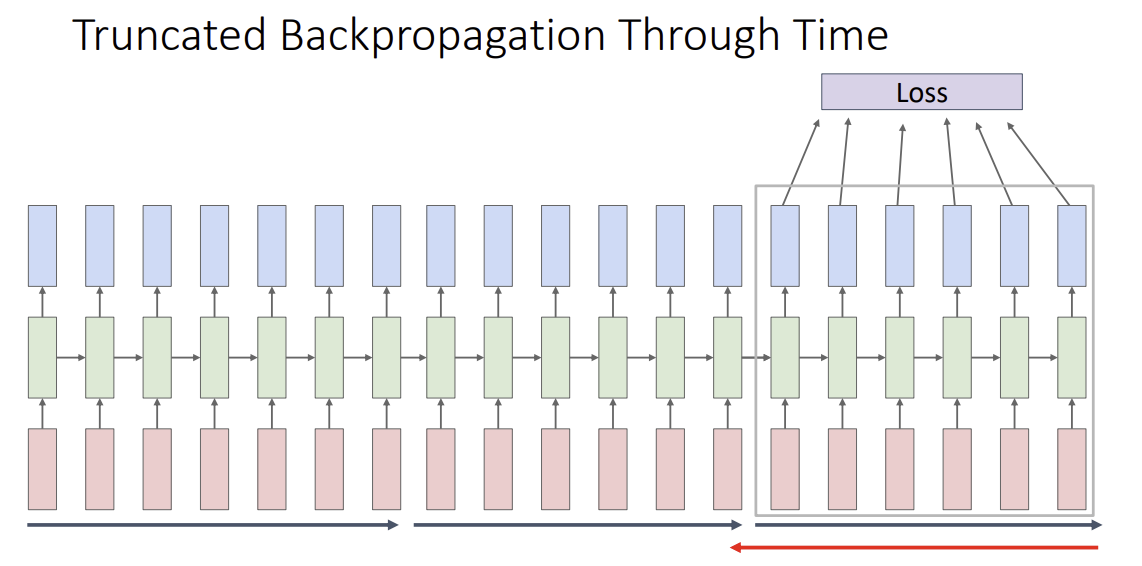
Truncated Backpropagation Thourgh Time
loss 계산을 위해서 entire sequence forward 진행, gradient 계산을 위해서 entire sequence backward 진행 하면 너무 많은 memory가 사용된다.
이를 해결하기 위해 forward, backward chunck으로 진행
carry hiddens states forward in time forever, but only backpropagate for some smaller number of steps. (쪼개서 계산한다)
example: image captioning
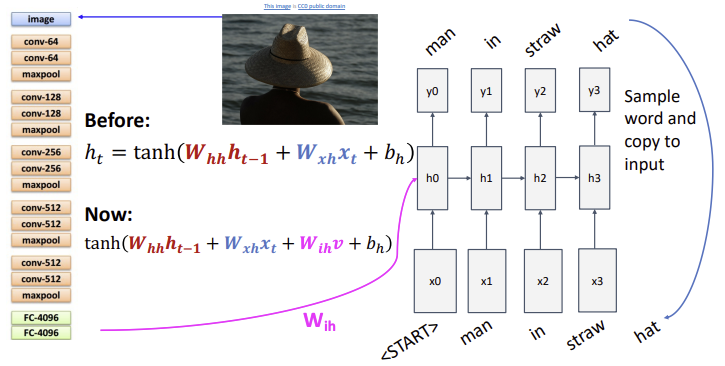
: previous
: current
: feature from CNN
Vanilla RNN Gradient Flow
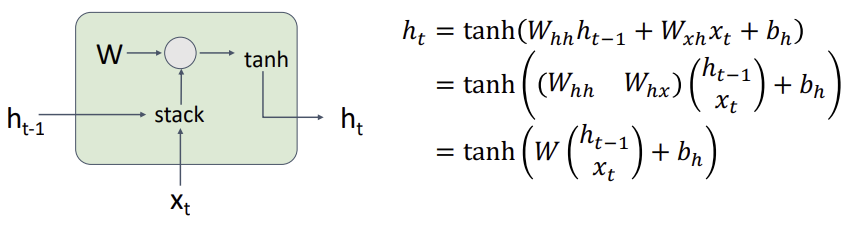
problem
1. tanh nonlinearity bad
2. backpropagation in matrix multiply cause multiply by the transpose of weight matrix -> 많은 rnn block을 거치면 계속 같은 값들이 곱해짐 -> exploding gradient or vanishing gradient -> bad
computing gradeint of involves many factors of W
장기 의존성 문제(Long-term dependency problem)
순환 신경망(Recurrent Neural Network, RNN)과 같은 모델이 긴 시퀀스를 처리할 때,
초기 시점의 정보가 후반부로 갈수록 점차 잊혀지는 문제를 의미
이는 주로 두 가지 원인에 의해 발생
1. 기울기 소실(Vanishing Gradient) 문제
2. 기울기 폭발(Exploding Gradient) 문제largest singular value > 1 :
exploding gradients -> gradient clipping : scale gardient if its norm is too big
largest singular value < 1 :
vanishing gradients -> change RNN architecture (LSTM)
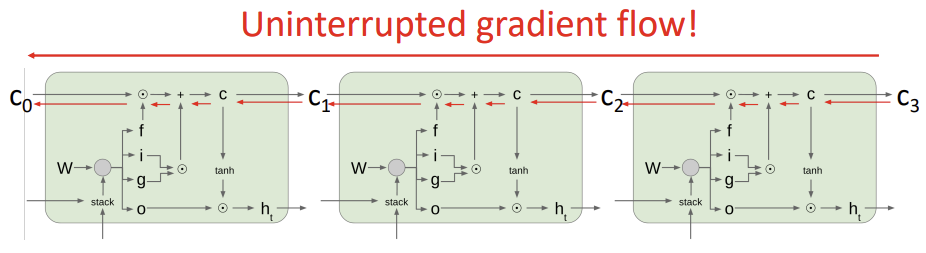
Long Short Term Memory LSTM
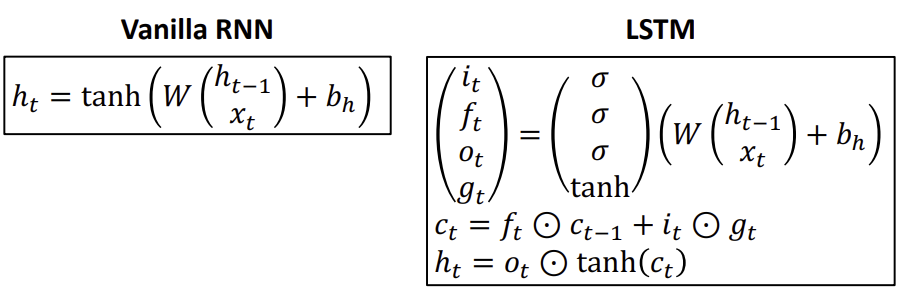
rnn과 다르게 two vectors가 나온다.
cell state : vector that carries information through the network. LSTM이 정보를 오랫동안 보존할 수 있게 도와준다.
hidden state
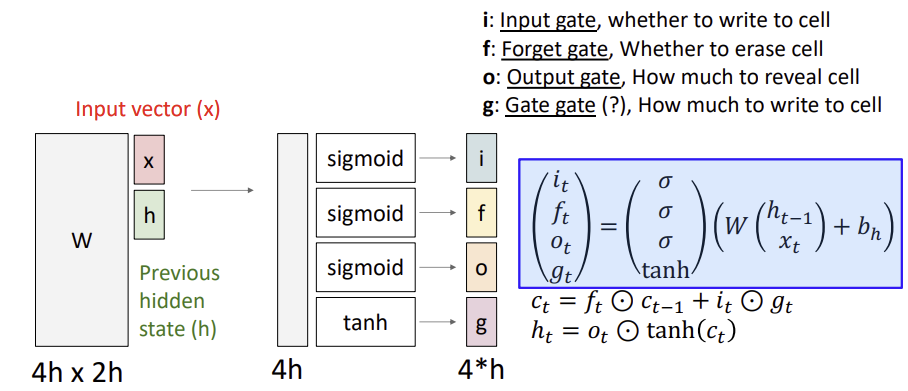
i : input gate, how much do we actually want to add or subtract at each point
f : Forget gate, whether to erase cell
o : Output gate, How much to reveal cell
g: Gate gate, how much to write to cell (at every point of the cell we can either add 1 or subtract 1)
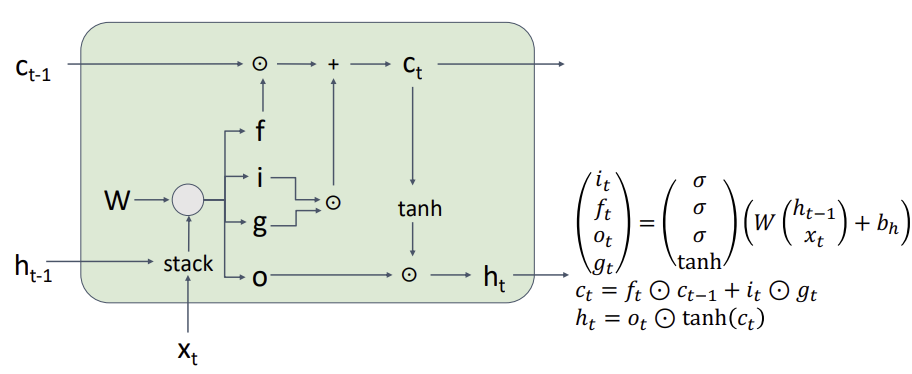
Gradient Flow
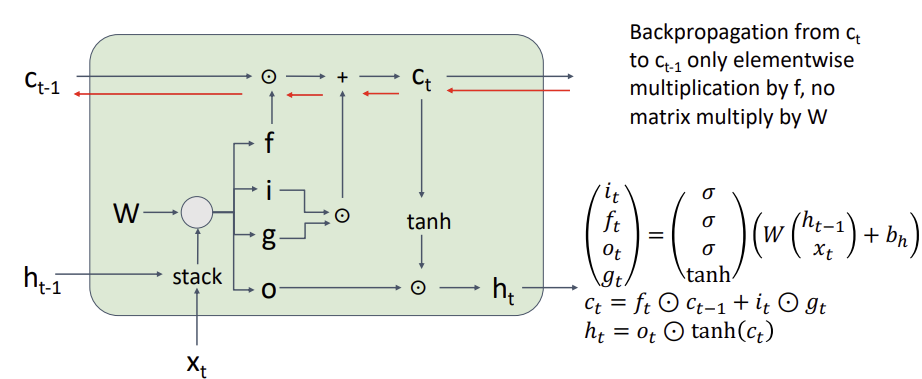
f는 sigmoid를 통과하기 때문에 0에서 1 사이의 값이다.
f gate를 통과한 값이 0에 가까우면 gradient가 vanishing 되긴하지만, non-linearity가 아니므로 vanishing되는 것은 문제가 없다.
Uniterrupted gradient flow!
LSTM에서는 역전파 과정 동안 정보가 어느 정도 보존되는 경로가 항상 존재한다. -> similar to ResNet
Summary
- RNN allow a lot of fexibility in architecture design
- Vanilla RNN 간단하지만, don't work very well
- common to use LSTM or GRU : additive interactions improve gradient flow
- backward flow of gradients in RNN can explode or vanish
4.1 exploding gradient -> gradient clipping
4.2 vanishing gradient -> LSTM