가시다님의 CI/CD 스터디 내용을 정리한 포스트 입니다.
1. GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions는 GitHub에서 제공하는 CI/CD(Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) 자동화 도구입니다. 이를 통해 코드를 빌드하고, 테스트하고, 배포하는 과정을 자동화할 수 있습니다.
-
주요 특징
- 워크플로우 기반
• YAML 파일로 워크플로우를 정의합니다(.github/workflows/ 폴더에 저장)
• 워크플로우는 이벤트(예: push, pull_request, schedule)에 반응하여 실행됩니다 - 다양한 이벤트 지원
• 코드 푸시, PR 생성/병합, 특정 시간(schedule), 이슈 생성 등 다양한 GitHub 이벤트에 반응 - 사용자 정의 가능
• 자체 액션(Action)을 작성하거나, GitHub Marketplace에서 미리 만들어진 액션을 가져와 사용 가능 - 병렬 작업 및 매트릭스 빌드
• 여러 환경(OS, 언어 버전 등)에서 테스트를 병렬로 수행 - 클라우드 및 자체 호스팅
• GitHub 제공 호스트 러너(클라우드) 또는 자체 호스팅 러너 사용 가능
- 워크플로우 기반
-
장점
• GitHub에 통합: 별도의 CI/CD 도구 없이 GitHub 환경 내에서 바로 사용
• 확장성: 오픈소스 액션과 커뮤니티 지원
• 무료 플랜 제공: 오픈소스 프로젝트나 개인 용도에서 제한적으로 무료로 사용 가능
2. 직접 개발 후 실행
서버 - Github : 직접 개발 후 서버 실행 → 코드 수정 후 재실행
2.1 AWS EC2에서 실행
AWS에 EC2 인스턴스 1대를 생성 후 아래 파이썬 코드를 생성 합니다.
#
python3 -V
#
cat > server.py <<EOF
from http.server import ThreadingHTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
from datetime import datetime
class RequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header('Content-type', 'text/plain')
self.end_headers()
now = datetime.now()
response_string = now.strftime("The time is %-I:%M:%S %p, CloudNeta Study.\n")
self.wfile.write(bytes(response_string, "utf-8"))
def startServer():
try:
server = ThreadingHTTPServer(('', 80), RequestHandler)
print("Listening on " + ":".join(map(str, server.server_address)))
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
server.shutdown()
if __name__== "__main__":
startServer()
EOF
#
sudo python3 server.py
## 아래 확인 후
CTRL+C 로 실행 취소
# (신규터미널) 서버1 SSH 접속
curl localhost
sudo ss -tnlp
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* users:(("python3",pid=3065,fd=3))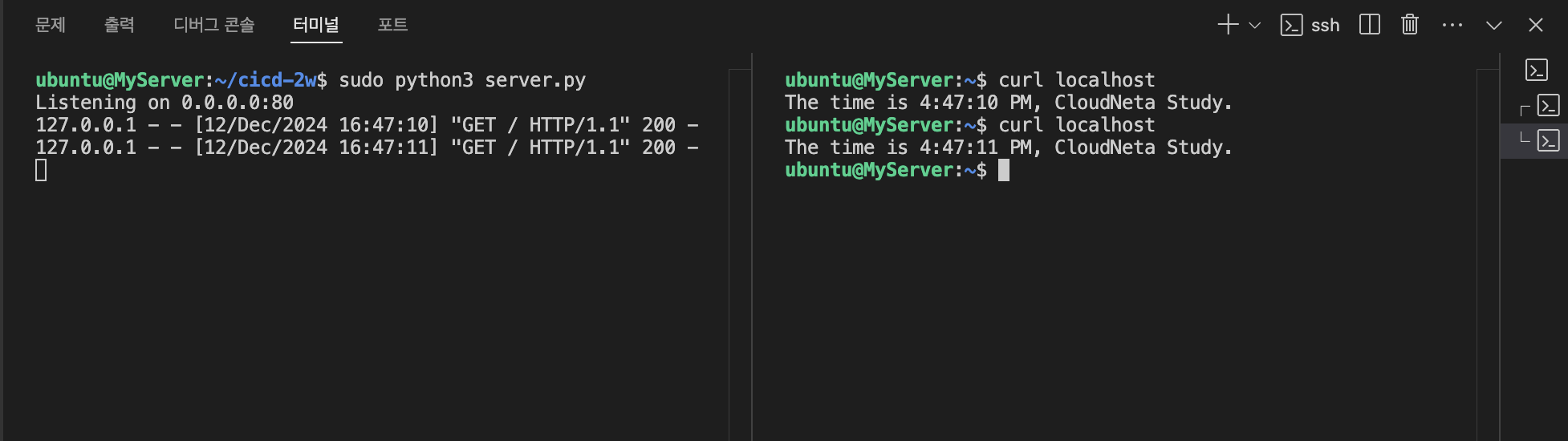
2.2 Git 작업
-
Github에서 토큰 발급: scopes(repo, workflow 지정)
참고: github에서-토큰-발급하기 -
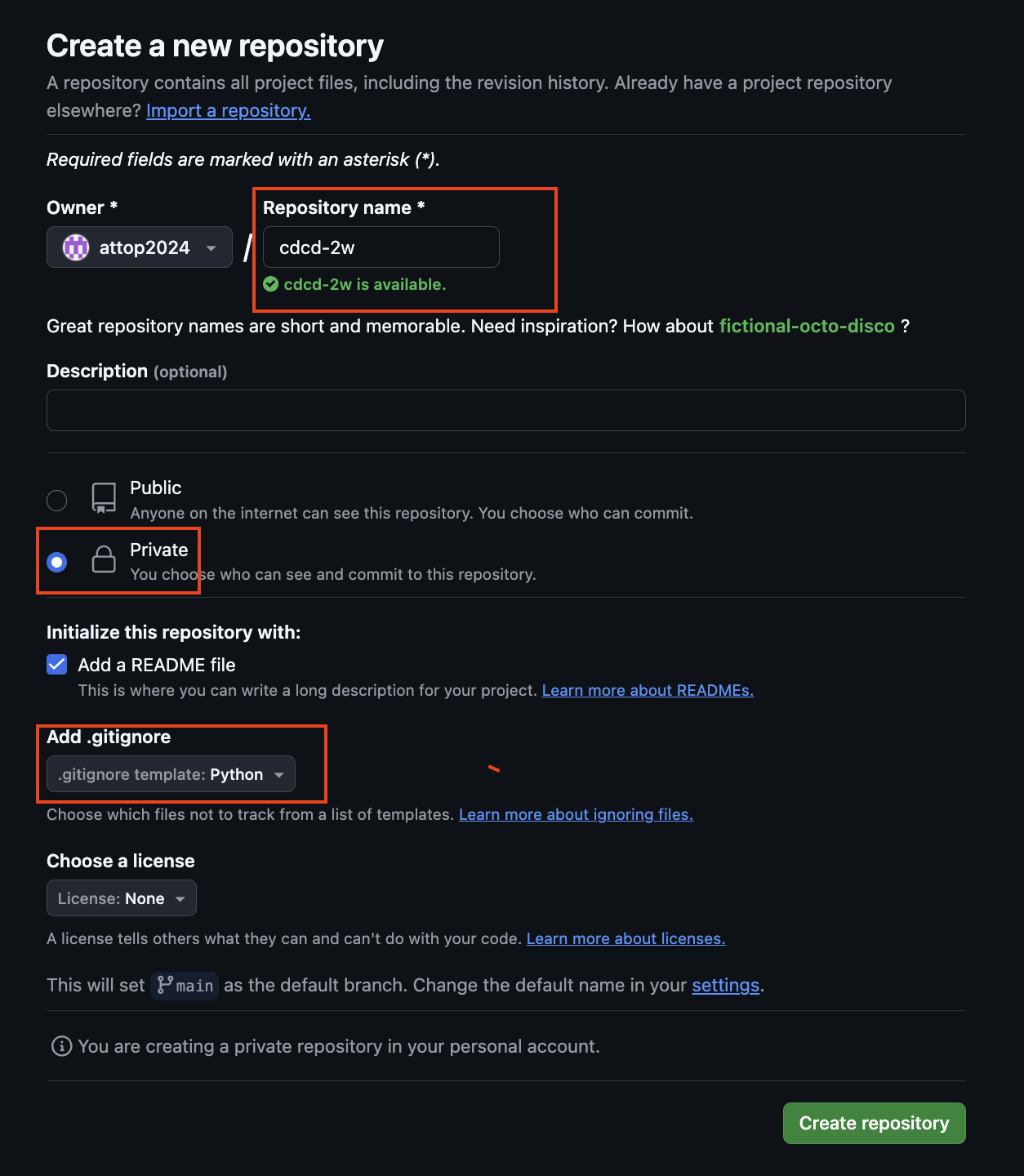
Private Repo 신규 생성
-
서버에서 Git 작업 수행
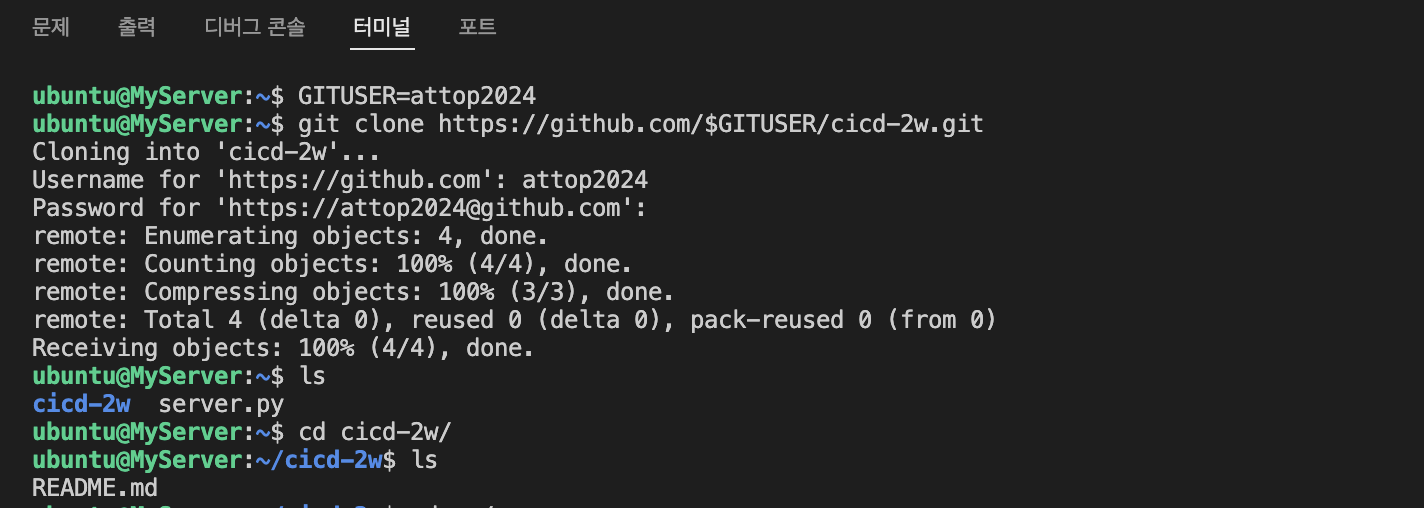
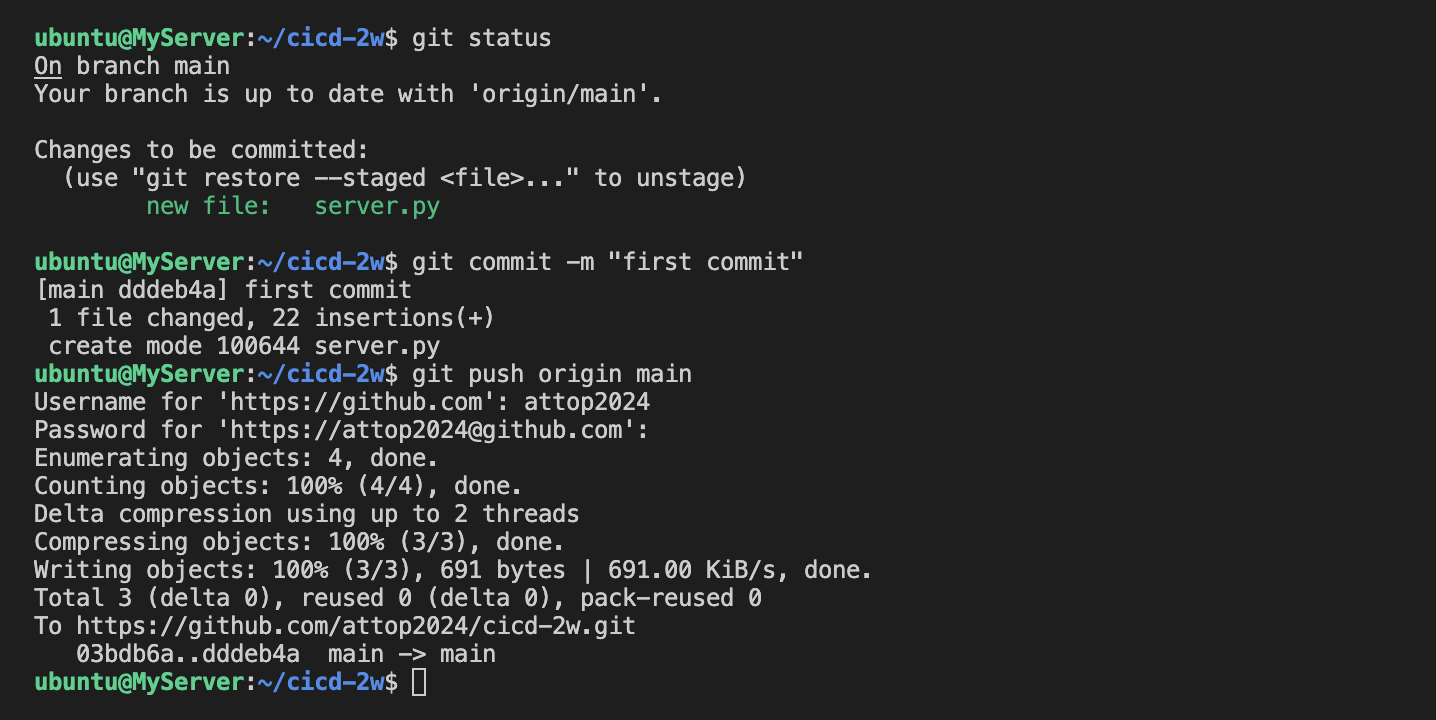
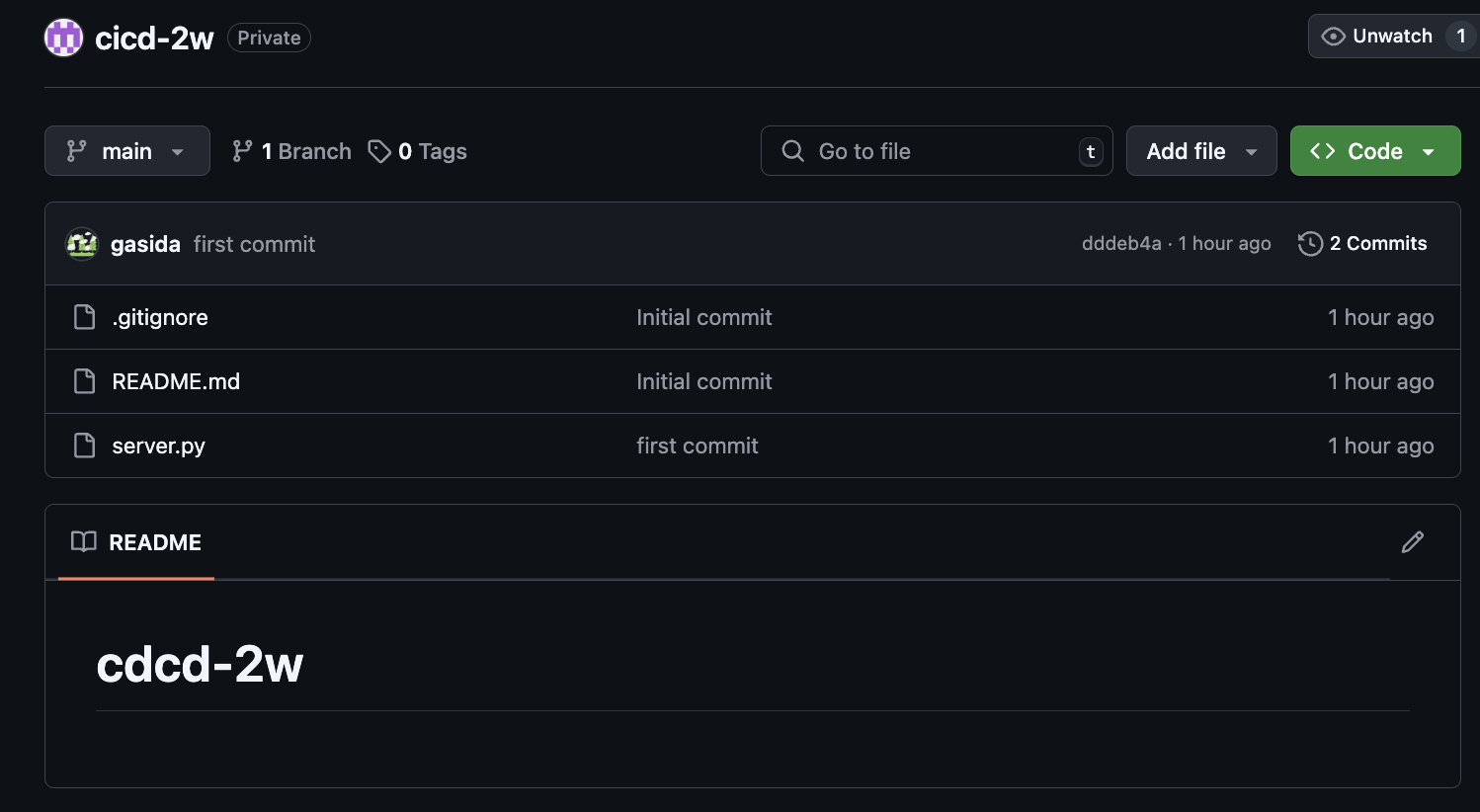
-
서버 실행
#
nohup sudo python3 server.py > server.log 2>&1 &
cat server.log
curl localhost
cat server.log
#
grep log .gitignore
*.log
#
git add .
git commit -m "add log file"
git status2.3 코드 수정 후 재실행
#
sed -i "s/CloudNeta/CICD/g" server.py
# 프로세스 종료
sudo ss -tnlp
sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80
sudo ss -tnlp
# 재실행
nohup sudo python3 server.py > server.log 2>&1 &
curl localhost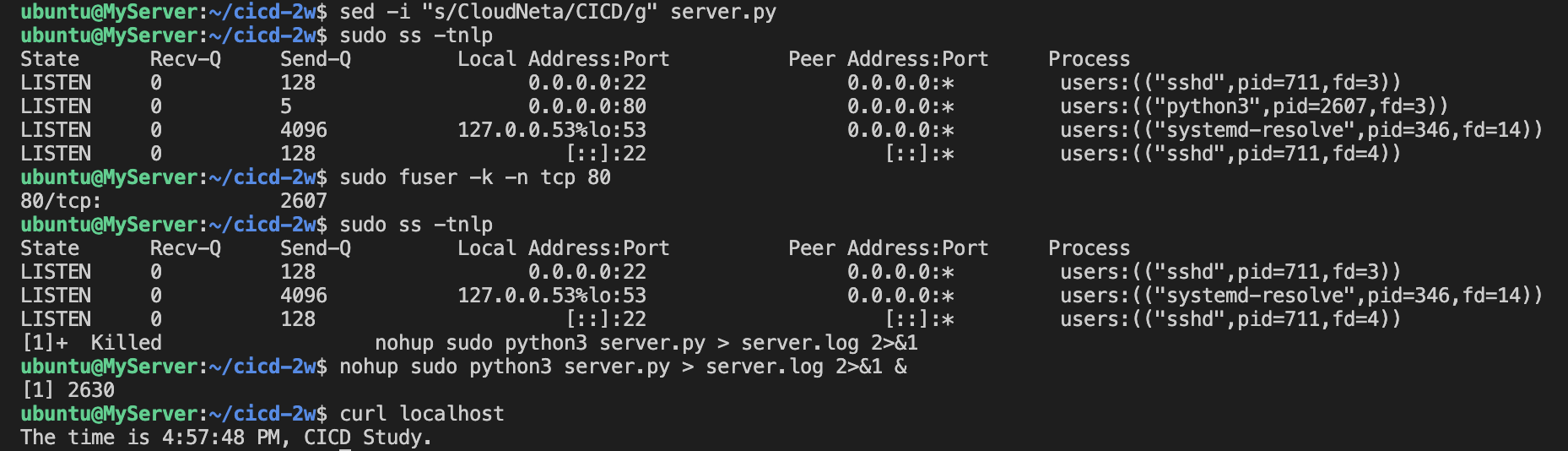
2.4 코드 Push
#
git config --global user.name gasida
git config --global user.email gasida.seo@gmail.com
git config --global credential.helper store
#
git add . && git commit -m "version update" && git push origin main
Username for 'https://github.com': <>
Password for 'https://gasida@github.com': <>
#
git push origin main
당연하지만, 코드의 변경 사항이 있을 때 마다 위와 같은 과정을 반복하는것은 휴먼 에러도 발생 할 가능성이 높아지며 작업 효율도 낮아지므로 자동화 도입을 고려해야 할 것이다!
3. GitHub Actions #1
서버 - Github/Actions - myPC : GitHub Actions 으로 CI/CD 자동화 작업 실행
3.1 GIt : SSH_PRIVATE_KEY , EC2_PIP
3.2 코드 작업
- 자신의 PC에서 아래 작업
#
git clone https://github.com/gasida/cicd-2w.git
cd cicd-2w
#
mkdir -p .github/workflows/
touch .github/workflows/deploy.yaml
sed -i -e "s/CICD/CICD 2w/g" server.py- .github/workflows/deploy.yaml
name: CICD1
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Configure the SSH Private Key Secret
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.ssh/
echo "${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}" > ~/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- name: Set Strict Host Key Checking
run: echo "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" > ~/.ssh/config
- name: Git Pull
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST << EOF
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w || exit 1
git pull origin main || exit 1
EOF
- name: Run service
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80 || true
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST "nohup sudo -E python3 /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.py > /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log 2>&1 &"3.3 Git push
git add . && git commit -m "add workflow" && git push origin main# [서버1]
cd cicd-2w/
grep -i cicd server.py
sudo ps -ef |grep server.py
tail /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log3.4 코드 수정 후 동작 확인
sed -i -e "s/CICD 2w/CICD1 End/g" server.pyname: CICD1 End
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deployfinal:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Configure the SSH Private Key Secret
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.ssh/
echo "${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}" > ~/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- name: Set Strict Host Key Checking
run: echo "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" > ~/.ssh/config
- name: Git Pull
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST << EOF
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w || exit 1
git pull origin main || exit 1
EOF
- name: Run service
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80 || true
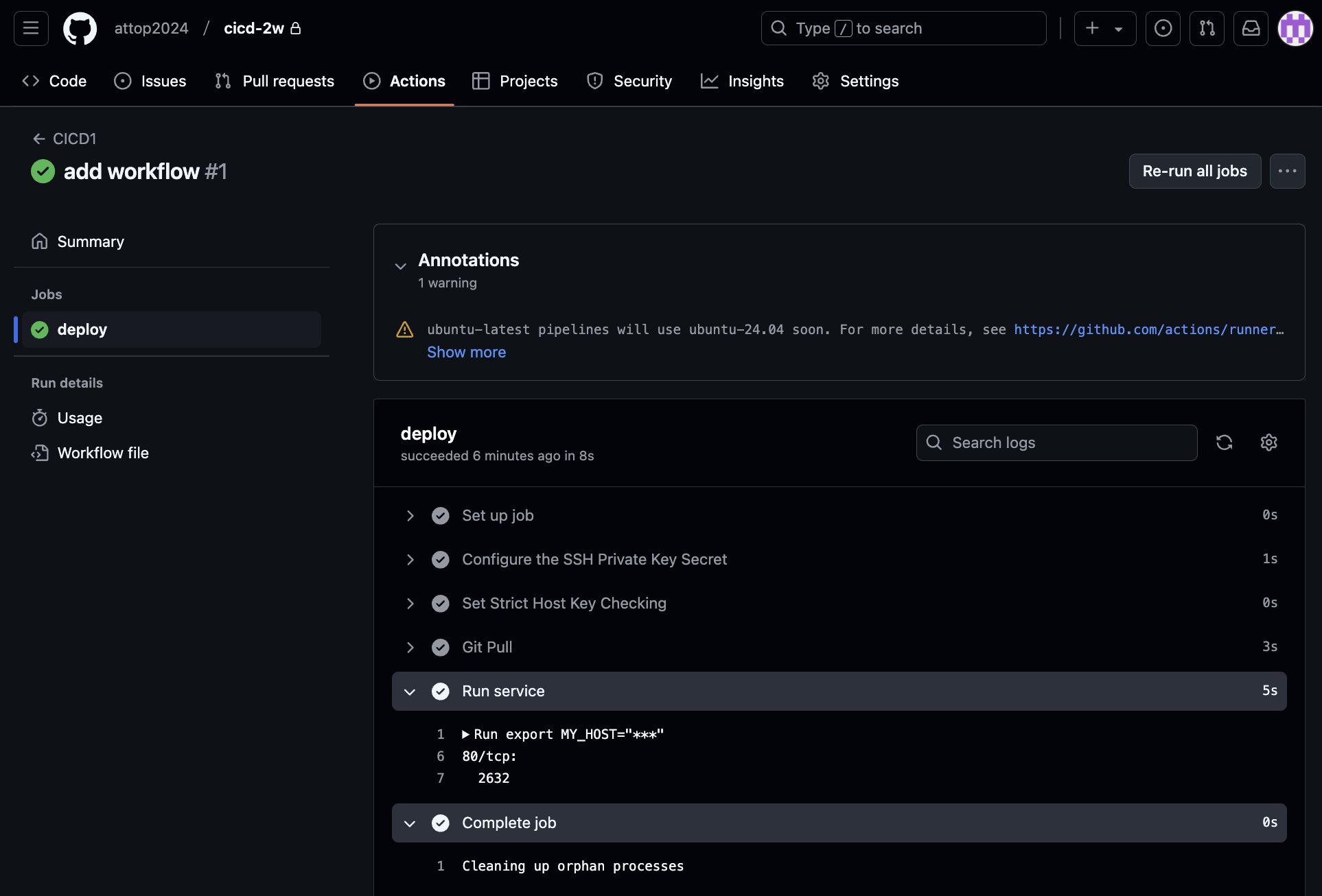
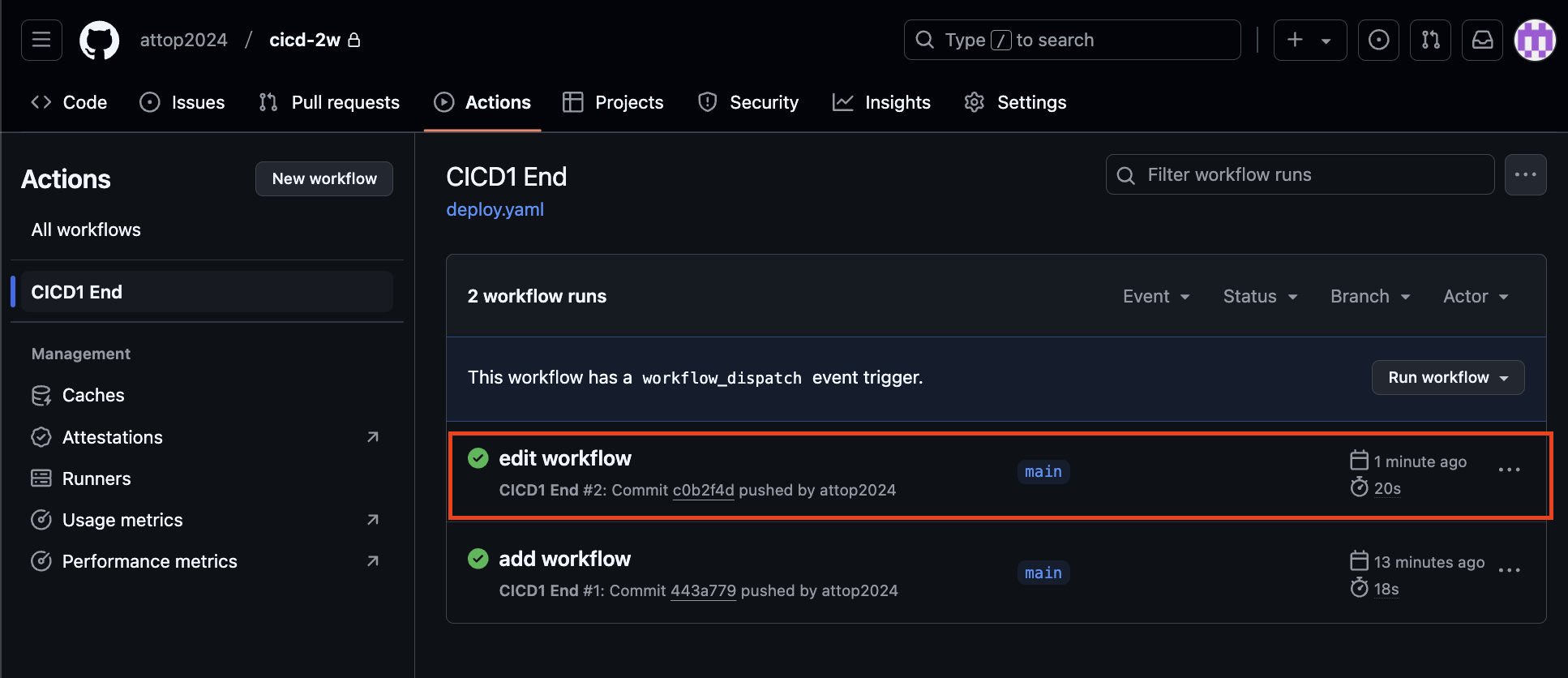
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST "nohup sudo -E python3 /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.py > /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log 2>&1 &"pc에서 push후에 github actions에서 job이 수행된 것이 확인됨.
github actions이 수행되어 aws ec2에서 코드가 수행되었습니다.
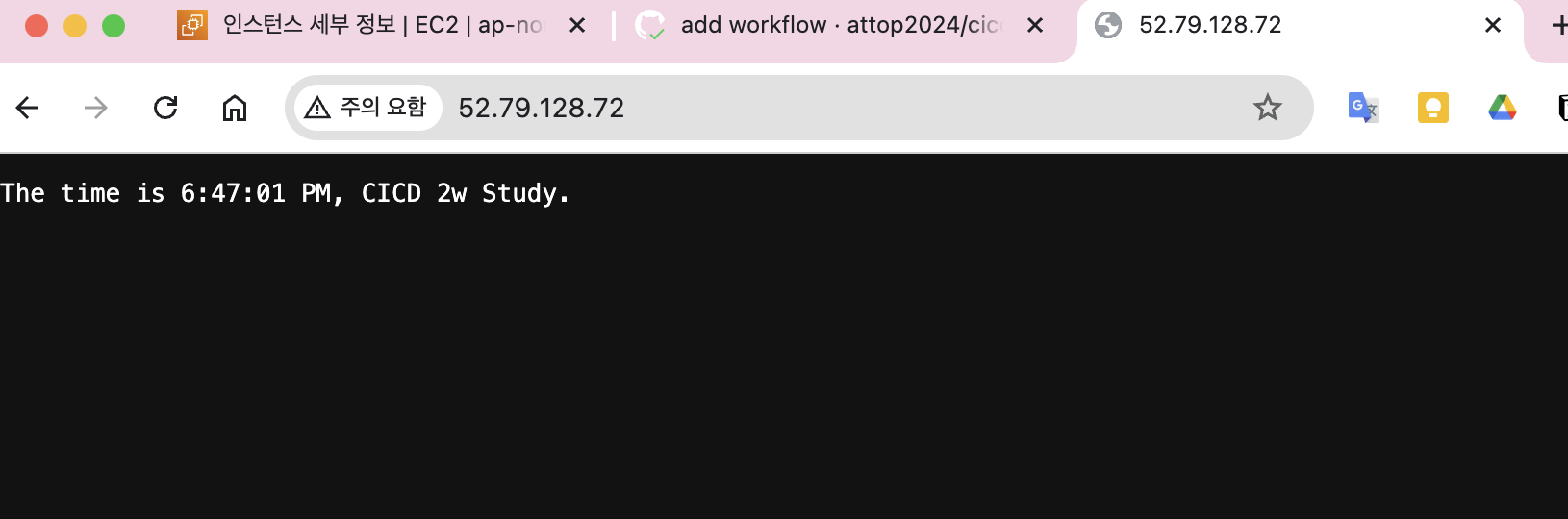
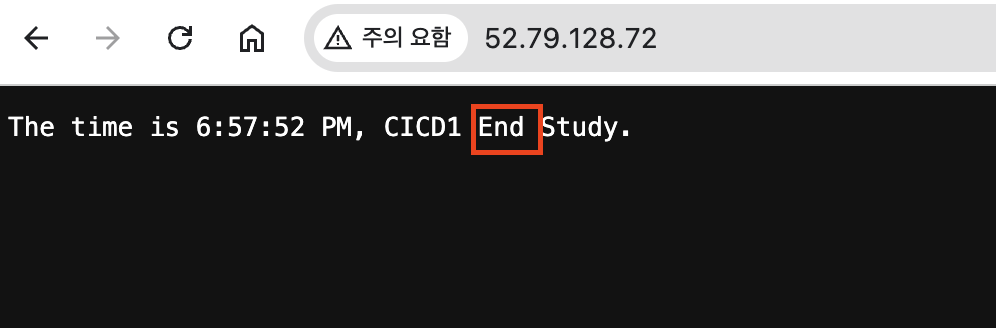
- 웹 접속 변경 확인
sed -i -e "s/CICD 2w/CICD1 End/g" server.pyname: CICD1 End
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deployfinal:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Configure the SSH Private Key Secret
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.ssh/
echo "${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}" > ~/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- name: Set Strict Host Key Checking
run: echo "StrictHostKeyChecking=no" > ~/.ssh/config
- name: Git Pull
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST << EOF
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w || exit 1
git pull origin main || exit 1
EOF
- name: Run service
run: |
export MY_HOST="${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}"
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80 || true
ssh ubuntu@$MY_HOST "nohup sudo -E python3 /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.py > /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log 2>&1 &"#
git add . && git commit -m "edit workflow" && git push origin main
# [서버1]
grep -i cicd server.py
sudo ps -ef |grep server.py
tail /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log코드 및 워크플로우 수정 후 pc에서 push후에 github actions에서 job이 수행된 것이 확인됨
aws ec2에서도 수정한 내용이 반영되었습니다.
4. GitHub Actions #2
서버 - Github/Actions - myPC : GitHub Actions 에서 ‘코드 - 빌드 - 테스트’ 후 대상 서버에 전달 후 실행
- 목표
- GitHub Actions에서 코드 가져오기
- GitHub Actions에서 .gitignore 제외된 민감 파일 내용을 을 안전하게 가져와서 사용하기
- scp로 대상 서버 ec2 에 py 파일 전송
- 대상 서버 ec2에 기존 서비스 중지하고 다시 실행
- GitHub Actions 파이썬 버전 확인
name: CICD2
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deployfinal:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Test
run: |
python -V || true
python3 -V || true
which python || true
which python3 || true
envgit add . && git commit -m "echo env" && git push origin main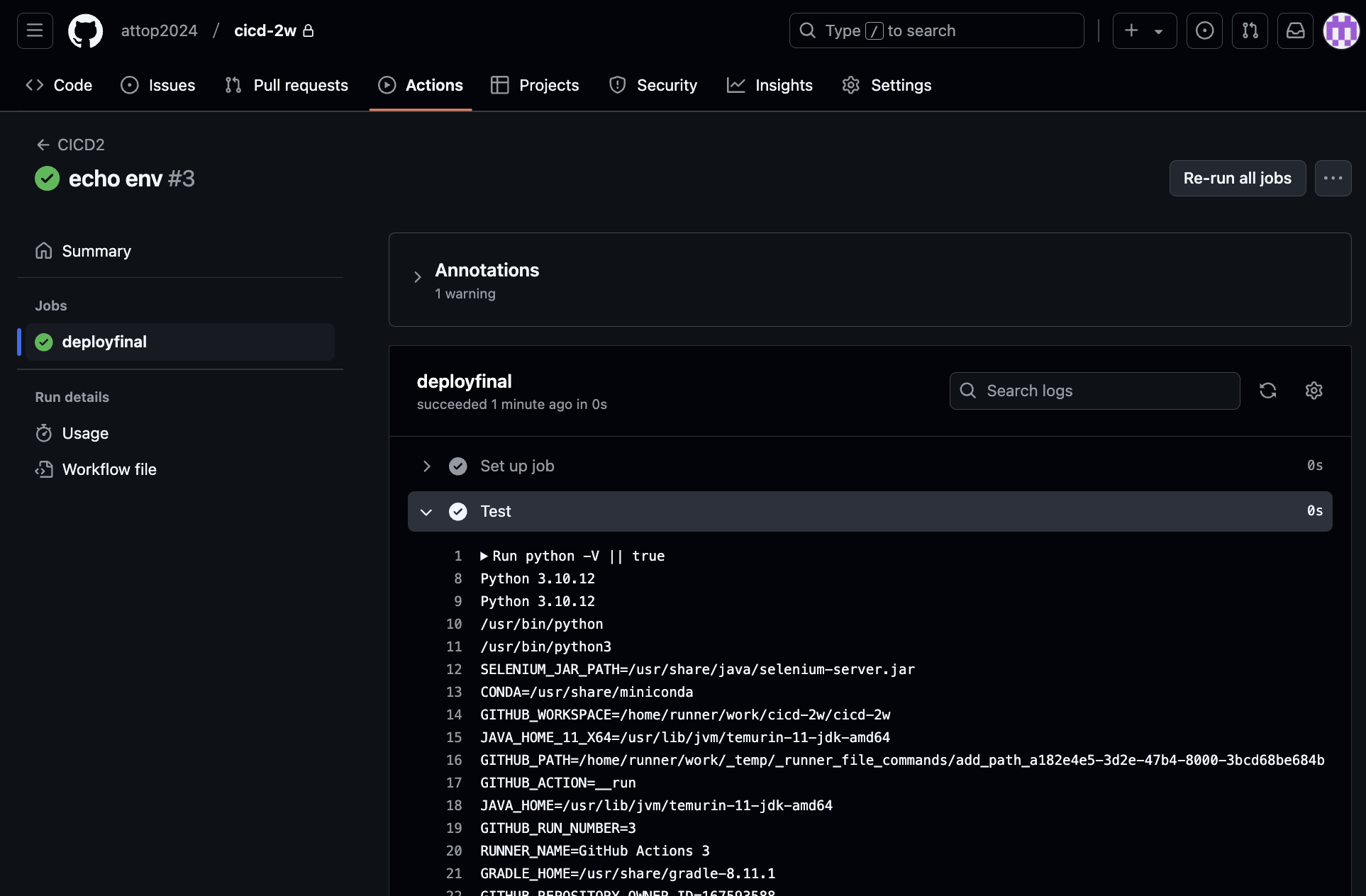
-
GitHub Actions에서 .gitignore 제외된 민감 파일 내용을 을 안전하게 가져와서 사용하기
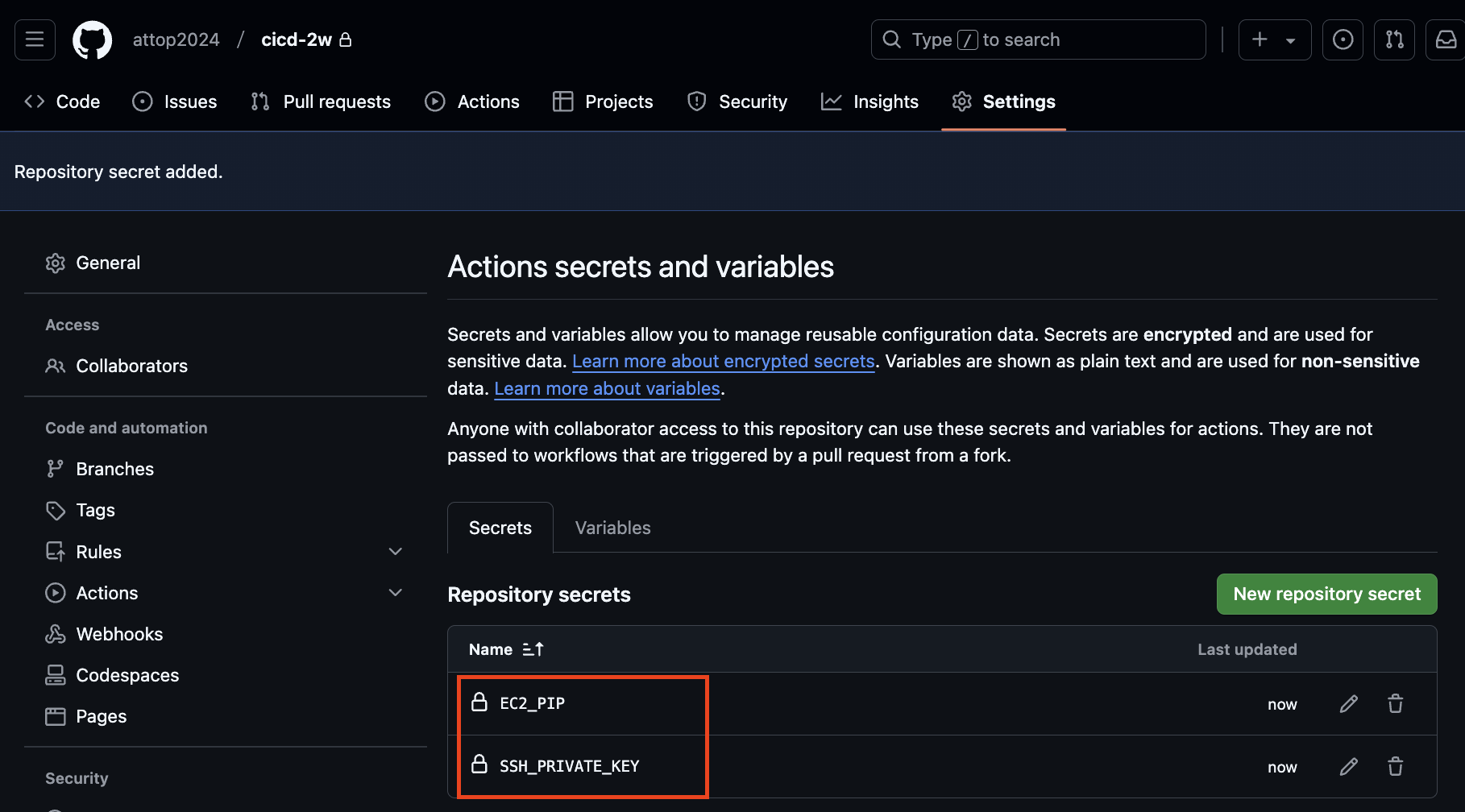
gitignore 제외된 민감 파일은 push되지 않는다. 그래서 Github에 secret으로 등록한다.
- Secret 생성 : MYKEYS ⇒ 아래 SSH for GitHub Actions 에서 env 전달 방식 활용
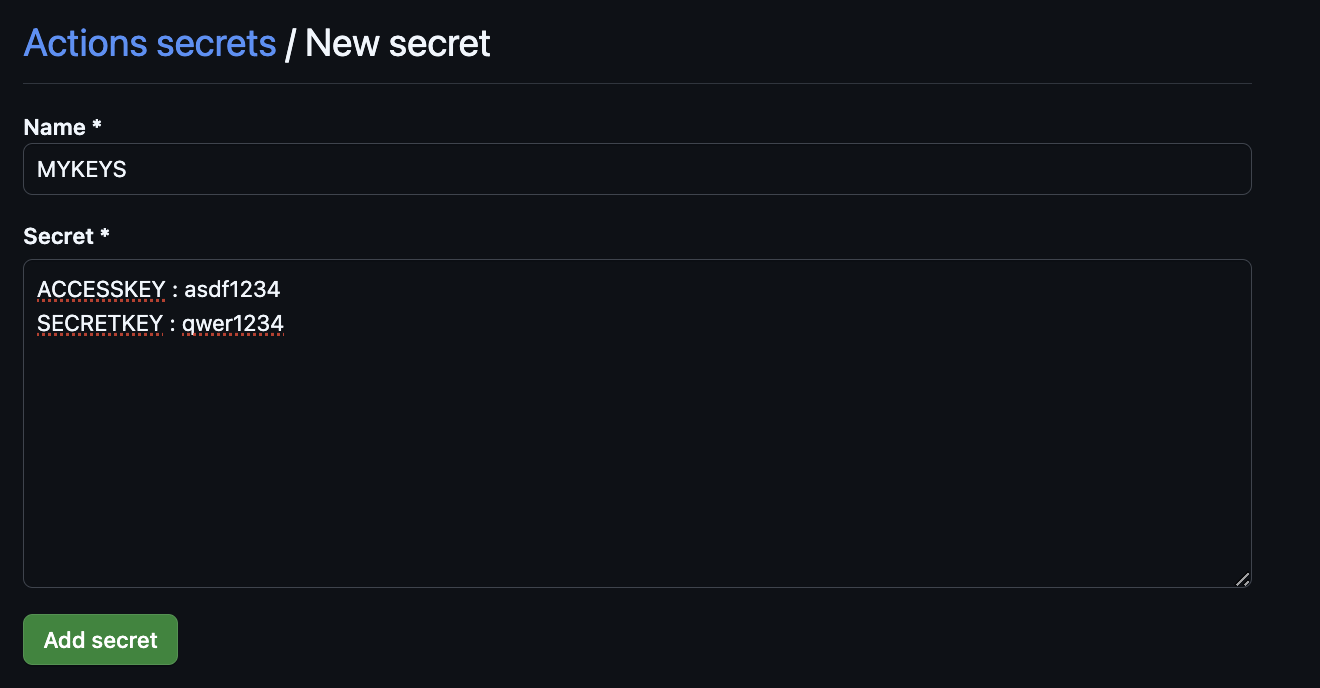
- Secret 생성 : MYKEYS ⇒ 아래 SSH for GitHub Actions 에서 env 전달 방식 활용
-
GitHub Actions Marketplaces : Enhance your workflow with extensions - to simplify tasks and automate processes
ssh, scp, aws 검색(마켓플레이스_링크)
-
워크플로 설정 후 테스트
- 코드 작업
name: CICD2
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
ssh-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Github Repository Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: executing remote ssh commands
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v1.2.0
env:
AWS_KEYS: ${{ secrets.MYKEYS }}
with:
host: ${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}
username: ubuntu
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
envs: AWS_KEYS
script_stop: true
script: |
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w
echo "$AWS_KEYS" > .envgit add . && git commit -m "ssh action test" && git push origin main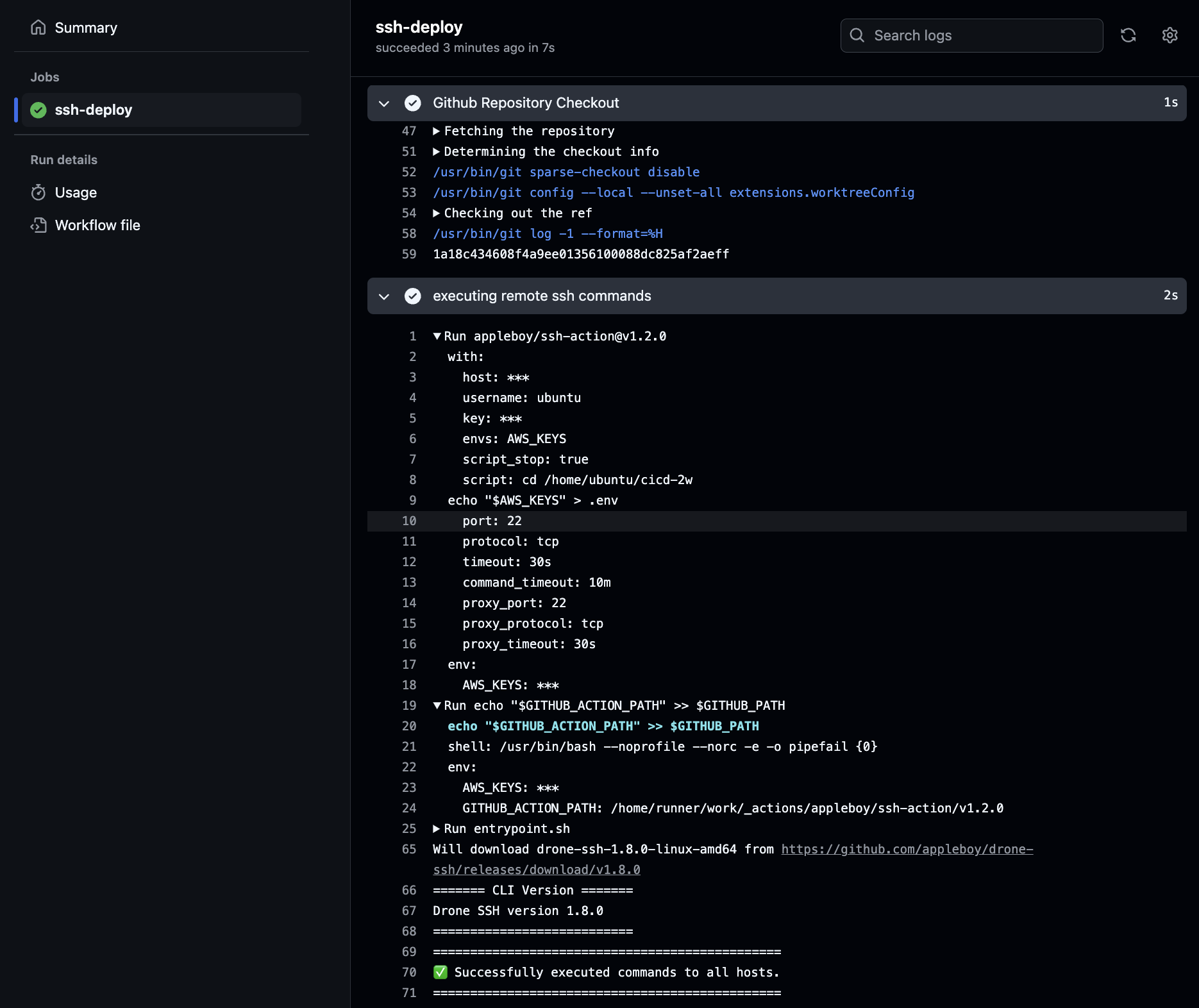
- EC2 서버 확인
# 서버 1
ls -al ~/cicd-2w/
cat ~/cicd-2w/.env
github repo 에서는 없으며, Github Secret 를 직접 업데이트 후 트리거 합니다.
- scp : GitHub Action that copy files and artifacts via SSH
- server.py 수정 해두기
response_string = now.strftime("The time is %-I:%M:%S %p, SCP Test\n")- 수정
name: CICD2
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
scp-ssh-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Github Repository Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: executing remote ssh commands
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v1.2.0
env:
AWS_KEYS: ${{ secrets.MYKEYS }}
with:
host: ${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}
username: ubuntu
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
envs: AWS_KEYS
script_stop: true
script: |
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w
echo "$AWS_KEYS" > .env
sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80 || true
- name: copy file via ssh
uses: appleboy/scp-action@v0.1.7
with:
host: ${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}
username: ubuntu
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
source: server.py
target: /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w git add . && git commit -m "using scp ssh action" && git push origin main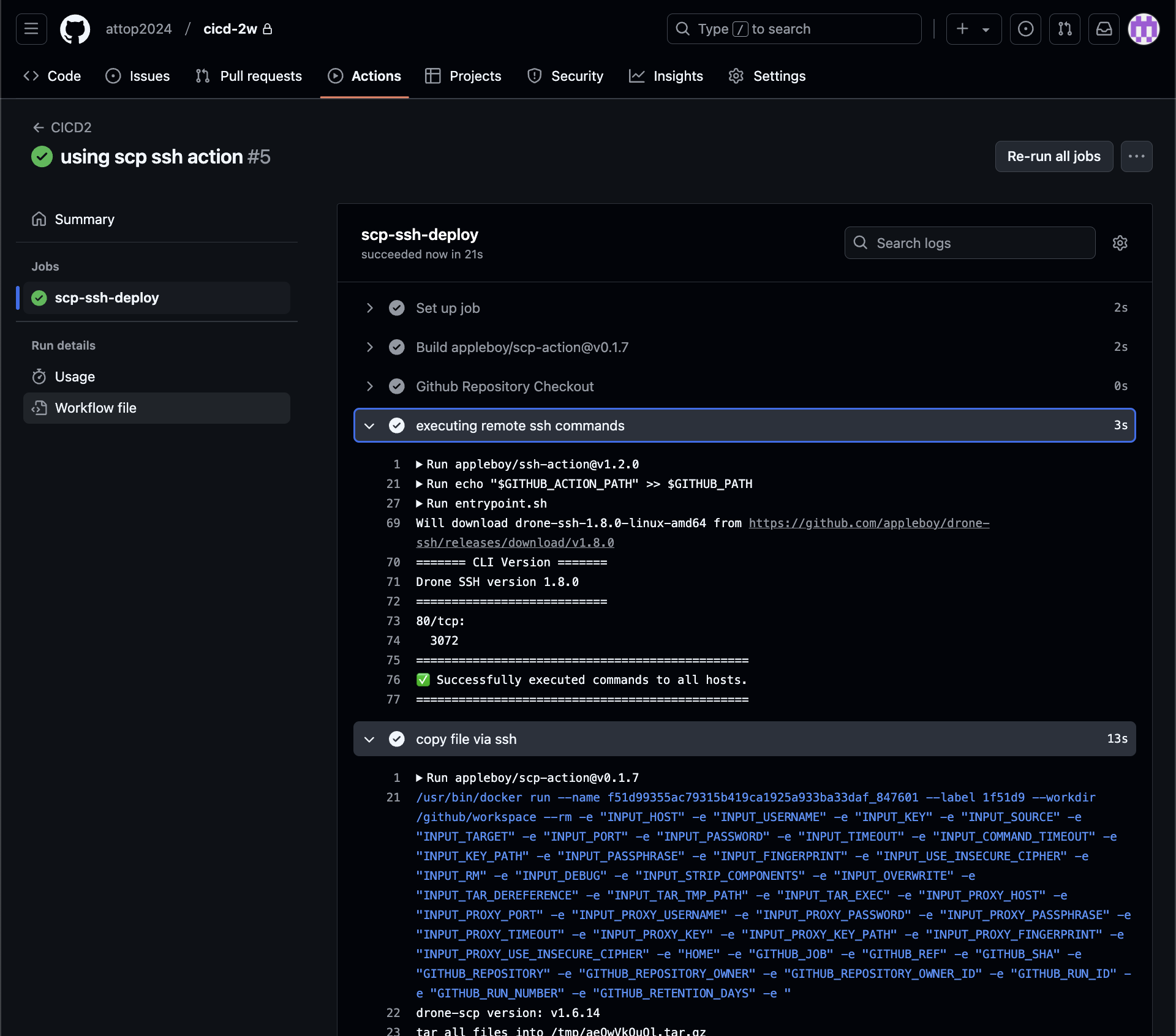
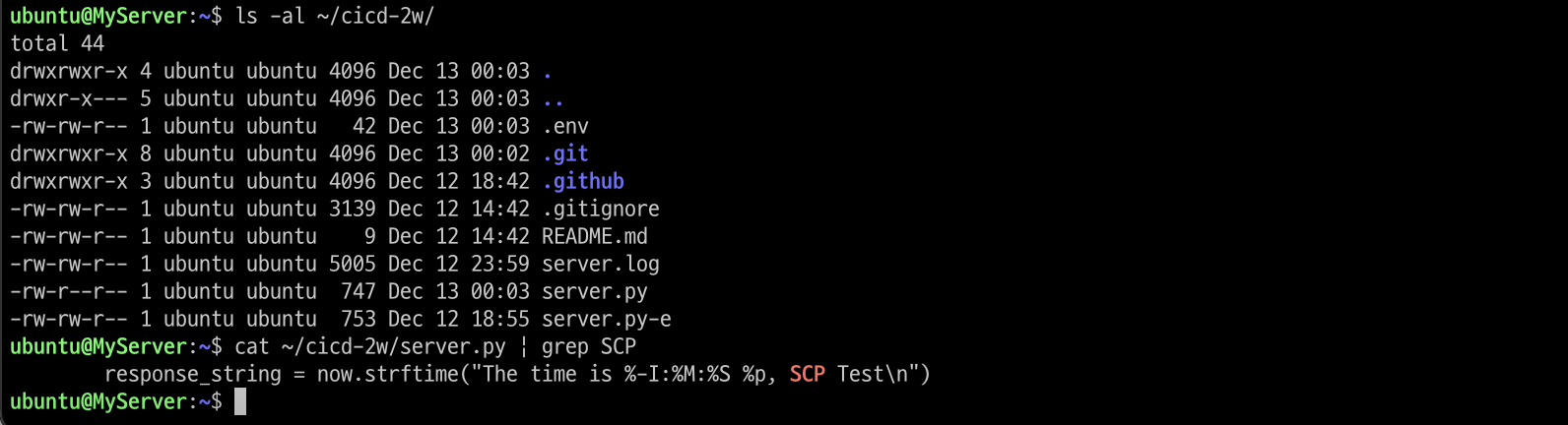
- 확인
# EC2 서버
ls -al ~/cicd-2w/
cat ~/cicd-2w/server.py | grep SCP대상 EC2 서버에 scp로 정상 복사되어 있습니다.
- 최종
github action 에서 코드 가져오고 변경된 py 파일을 전송 후 기존 서비스 중지 후 재기동- server.py 수정 해두기
response_string = now.strftime("The time is %-I:%M:%S %p, CICD2 End\n")- 수정
name: CICD2
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Github Repository Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: copy file via ssh
uses: appleboy/scp-action@v0.1.7
with:
host: ${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}
username: ubuntu
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
source: server.py
target: /home/ubuntu
- name: executing remote ssh commands
uses: appleboy/ssh-action@v1.2.0
env:
AWS_KEYS: ${{ secrets.MYKEYS }}
with:
host: ${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}
username: ubuntu
key: ${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}
envs: AWS_KEYS
script_stop: true
script: |
cd /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w
echo "$AWS_KEYS" > .env
sudo fuser -k -n tcp 80 || true
rm server.py
cp /home/ubuntu/server.py ./
nohup sudo -E python3 /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.py > /home/ubuntu/cicd-2w/server.log 2>&1 &
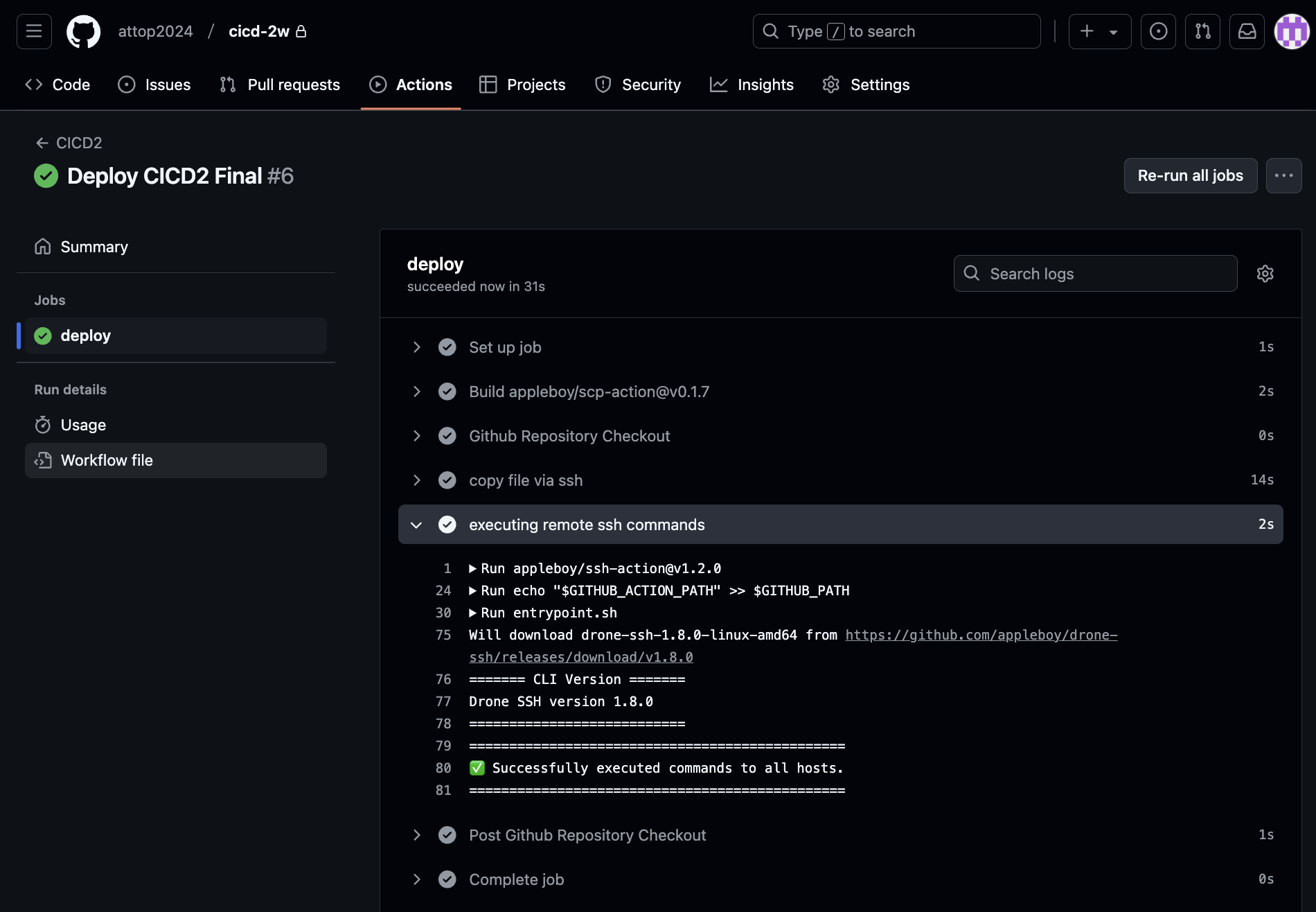
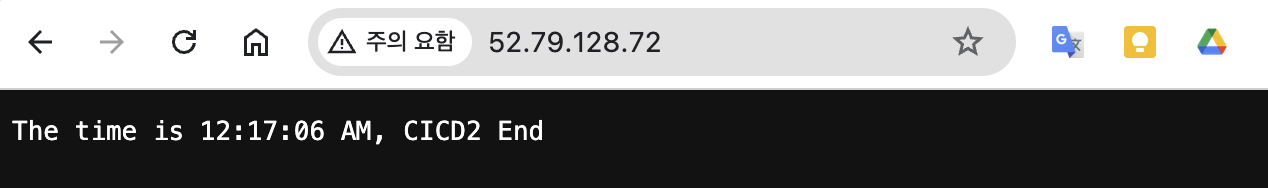
echo "test" >> /home/ubuntu/text.txtgit add . && git commit -m "Deploy CICD2 Final" && git push origin maingithub actions 정상
대상 서버 ec2에 기존 서비스 중지하고 다시 실행되었다.
- 확인
# 서버1
cat /home/ubuntu/text.txt
# 트러거 후 다시 확인
cat /home/ubuntu/text.txt
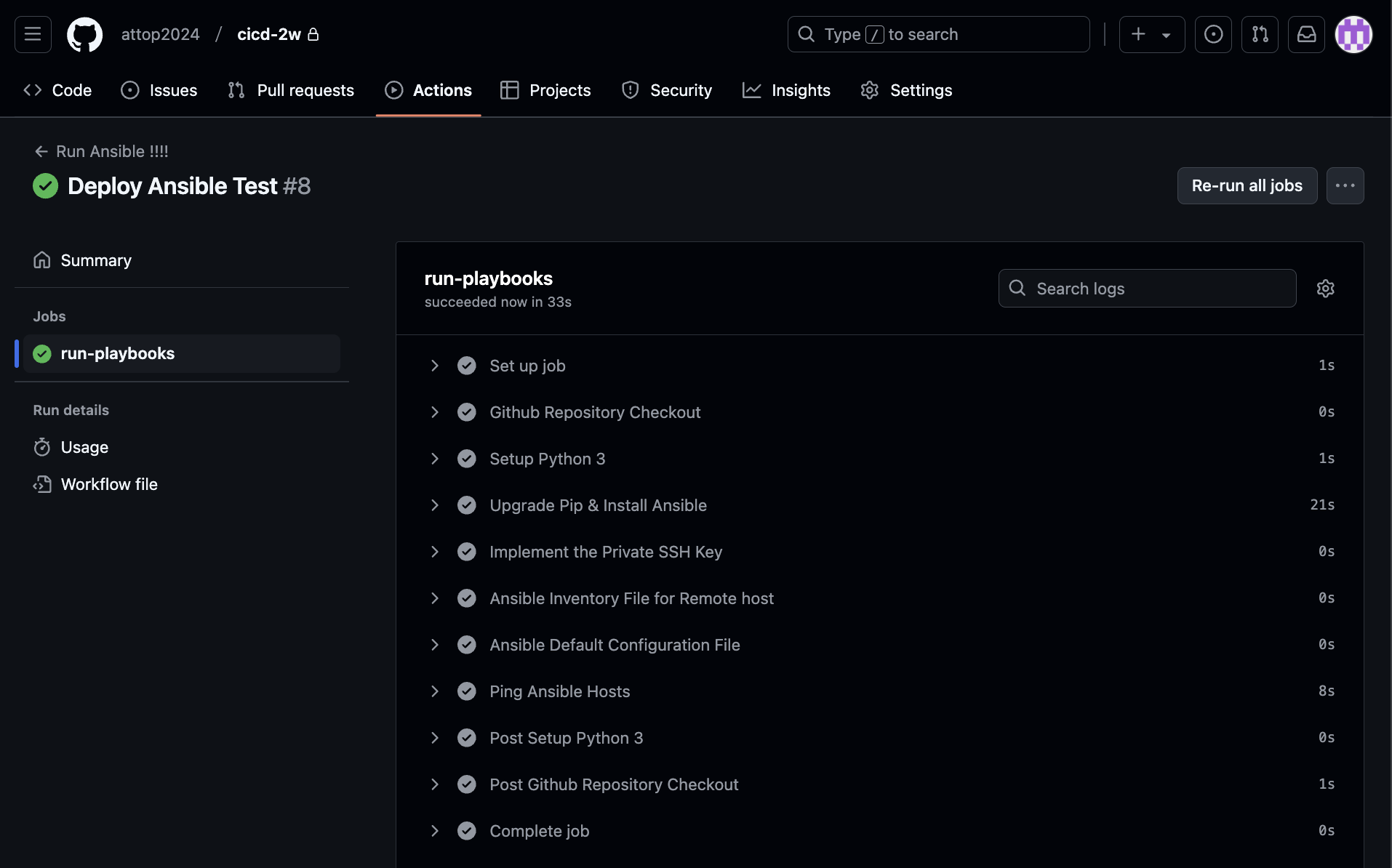
5. GitHub Actions with Ansible
스크립트 기반 서버에 명령어등을 수행하는 것보다는 멱등성등 여러 관리 이점이 있는 Ansible 같은 솔루션을 Github action을 통해서 구현해 볼 수 있습니다. 이번에는 개념만 알아보기 위해서 간단하게 Ansible 을 수행해 봅니다.
- deploy.yaml을 업데이트 합니다.
name: Run Ansible
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
run-playbooks:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Github Repository Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Setup Python 3
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.8"
- name: Upgrade Pip & Install Ansible
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
python -m pip install ansible
- name: Implement the Private SSH Key
run: |
mkdir -p ~/.ssh/
echo "${{ secrets.SSH_PRIVATE_KEY }}" > ~/.ssh/id_rsa
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- name: Ansible Inventory File for Remote host
run: |
mkdir -p ./devops/ansible/
export INVENTORY_FILE=./devops/ansible/inventory.ini
echo "[my_host_group]" > $INVENTORY_FILE
echo "${{ secrets.EC2_PIP }}" >> $INVENTORY_FILE
- name: Ansible Default Configuration File
run: |
mkdir -p ./devops/ansible/
cat <<EOF > ./devops/ansible/ansible.cfg
[defaults]
ansible_python_interpreter = '/usr/bin/python3'
ansible_ssh_private_key_file = ~/.ssh/id_rsa
remote_user = ubuntu
inventory = ./inventory.ini
host_key_checking = False
EOF
- name: Ping Ansible Hosts
working-directory: ./devops/ansible/
run: |
ansible all -m ping
# - name: Run Ansible Playbooks
# working-directory: ./devops/ansible/
# run: |
# ansible-playbook install-nginx.yaml
# - name: Deploy Python via Ansible
# working-directory: ./devops/ansible/
# run: |
# ansible-playbook deploy-python.yamlgit add . && git commit -m "Deploy Ansible Test" && git push origin main