[Platinum II] 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열 6 - 17411
성능 요약
메모리: 495940 KB, 시간: 3084 ms
분류
이분 탐색, 자료 구조, 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열: O(n log n), 세그먼트 트리
제출 일자
2025년 1월 17일 03:38:31
문제 설명
수열 A가 주어졌을 때, 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열과 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
예를 들어, 수열 A = {10, 20, 10, 30, 20, 50} 인 경우에 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열은 A = {10, 20, 10, 30, 20, 50} 이고, 길이는 4이고, 1개이다. A = {10, 20, 30, 10, 20, 30}인 경우에는 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열의 길이는 3이고, 4개가 있다.
입력
첫째 줄에 수열 A의 크기 N (1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000,000)이 주어진다.
둘째 줄에는 수열 A를 이루고 있는 Ai가 주어진다. (-1,000,000,000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1,000,000,000)
출력
첫째 줄에 수열 A의 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열의 길이와 개수를 출력한다. 개수는 매우 커질 수 있기 때문에 109+7로 나눈 나머지를 출력한다.
문제 풀이

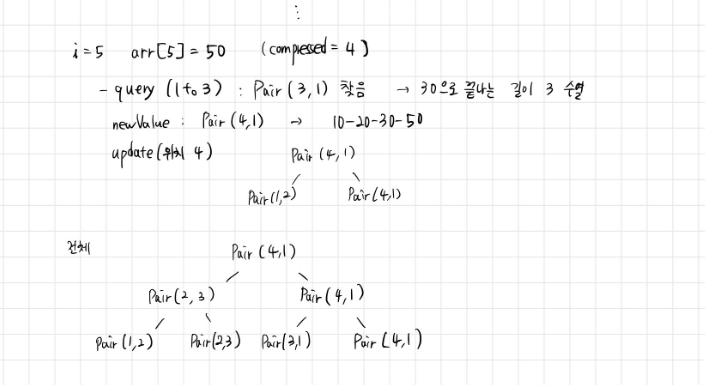
접근 방식
일반적인 LIS는 이분 탐색을 사용하여 O(N log N)에 해결할 수 있다. 하지만 이 문제는 개수도 세야 하므로, 세그먼트트리를 사용해야한다.
세가지 전략으로 접근해보겠다.
1. 좌표 압축
2. 세그먼트 트리
3. 개수 세기를 위한 DP적 접근
1. 좌표 압축
TreeSet<Integer> uniqueSet = new TreeSet<>();
for(int n : arr) uniqueSet.add(n);
ArrayList<Integer> unique = new ArrayList<>(uniqueSet);-
Why?
- 입력값의 범위가 -10^9부터 10^9까지로 매우 큼.
- 세그먼트 트리를 만들기 위해서는 이 범위를 압축해야 함.
-
How?
- TreeSet으로 중복을 제거하고 정렬.
- 각 숫자를 1부터 시작하는 인덱스로 매핑.
세그먼트트리
static class Pair {
int length; // LIS의 길이
long count; // 해당 길이를 가진 LIS의 개수
public Pair(int length, long count) {
this.length = length;
this.count = count;
}
}- length: 현재까지의 최대 LIS 길이
- count: 해당 길이를 가진 LIS의 개수
static Pair merge(Pair a, Pair b) {
if(a.length > b.length) return a;
else if(a.length < b.length) return b;
return new Pair(a.length, (a.count + b.count) % MOD);
}- 세그먼트 트리의 각 노드는 Pair 객체를 저장.
- merge 함수는 두 구간의 정보를 합칠 때 사용 :
- 길이가 다르면 더 긴 쪽을 선택
- 길이가 같으면 개수를 더함 (MOD 연산)
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
Pair curr = query(1, compressed[i]-1, 1, uniqueSize, 1);
Pair newValue = new Pair(curr.length + 1, Math.max(curr.count, 1));
update(compressed[i], newValue, 1, uniqueSize, 1);
}arr 수열의 각 숫자를 순회하면서 :
- 현재 숫자보다 작은 모든 숫자들 중에서 최대 LIS 정보를 가져온다.
- 현재 숫자를 포함하는 새로운 LIS를 만든다. ( 그 개수 그대로 하나 붙이는것임은 자명하다)
- 세그먼트 트리를 업데이트.
단계별 과정
- Step 1: 첫 번째 숫자 (10)
현재 숫자: 10 (압축값: 1)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 0))
- 결과: length = 0, count = 0 (아무것도 없음)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 1 (0 + 1)
- count = 1 (새로운 수열 시작)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 1에 (length=1, count=1) 저장
현재까지 찾은 LIS들:
- {10} (길이 1, 개수 1)- Step 2: 두 번째 숫자 (20)
현재 숫자: 20 (압축값: 2)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 1))
- 결과: length = 1, count = 1 (10으로 끝나는 수열)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 2 (1 + 1)
- count = 1 (이전 수열에서 이어짐)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 2에 (length=2, count=1) 저장
현재까지 찾은 LIS들:
- {10} (길이 1, 개수 1)
- {10, 20} (길이 2, 개수 1)- Step 3: 세 번째 숫자 (10)
현재 숫자: 10 (압축값: 1)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 0))
- 결과: length = 0, count = 0 (더 작은 수 없음)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 1 (0 + 1)
- count = 1 (새로운 수열 시작)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 1의 상태 유지 (merge 결과 변화 없음)
현재까지 찾은 LIS들:
- {10} (길이 1, 개수 1)
- {10, 20} (길이 2, 개수 1)
- {10} (새로운 시작점)- Step 4: 네 번째 숫자 (30)
현재 숫자: 30 (압축값: 3)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 2))
- 결과: length = 2, count = 1 ({10, 20}으로 끝나는 수열)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 3 (2 + 1)
- count = 1 (이전 수열에서 이어짐)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 3에 (length=3, count=1) 저장
현재까지 찾은 LIS들:
- {10} (길이 1)
- {10, 20} (길이 2)
- {10, 20, 30} (길이 3, 개수 1)- Step 5: 다섯 번째 숫자 (20)
현재 숫자: 20 (압축값: 2)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 1))
- 결과: length = 1, count = 1 (10으로 끝나는 수열)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 2 (1 + 1)
- count = 1 (이전 수열에서 이어짐)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 2의 상태 갱신 (merge로 count 합산)
현재까지 찾은 LIS들:
- {10} (길이 1)
- {10, 20} (길이 2)
- {10, 20, 30} (길이 3)
- {10, 20} (새로운 경로)- Step 6: 마지막 숫자 (50)
1. 이전 작은 숫자들 조회 (query(1, 3))
- 결과: length = 3, count = 1 ({10, 20, 30}으로 끝나는 수열)
2. 새로운 상태
- length = 4 (3 + 1)
- count = 1 (이전 수열에서 이어짐)
3. 세그먼트 트리 업데이트
- 위치 4에 (length=4, count=1) 저장
최종 LIS들:
- {10, 20, 30, 50} (길이 4, 개수 1)- 세그먼트 트리 최종
각 위치는 해당 값을 마지막으로 하는 LIS의 정보를 저장:
위치 1 (값 10): length=1, count=1
위치 2 (값 20): length=2, count=1
위치 3 (값 30): length=3, count=1
위치 4 (값 50): length=4, count=1
코드
/**
* Author: nowalex322, Kim HyeonJae
*/
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static final int MOD = 1000000007;
static class Pair{
int length;
long count;
public Pair(int length, long count){
this.length = length;
this.count = count;
}
}
static Pair merge(Pair a, Pair b){
if(a.length > b.length) return a;
else if (a.length < b.length) return b;
// 같은 길이일때는 count를 더함
return new Pair(a.length, (a.count + b.count) % MOD);
}
static BufferedReader br;
static BufferedWriter bw;
static StringTokenizer st;
static int N, arr[], compressed[];
static Pair segment[];
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new Main().solution();
}
public void solution() throws Exception {
br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
// br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("src/main/java/BOJ_17411_가장긴증가하는부분수열6/input.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
// 좌표압축
TreeSet<Integer> uniqueSet = new TreeSet<>();
for(int n : arr) uniqueSet.add(n);
ArrayList<Integer> unique = new ArrayList<>(uniqueSet); // 중복제거
compressed = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
int pos = binarySearch(unique, arr[i]);
compressed[i] = pos + 1; // 1-based
}
int uniqueSize = unique.size();
segment = new Pair[4*uniqueSize];
for (int i=0; i<4*uniqueSize; i++) {
segment[i] = new Pair(0, 0);
}
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
// 지금i위치보다 앞에있는 작은수들 중 LIS 찾기
Pair curr = query(1, compressed[i]-1, 1, uniqueSize, 1);
/*
지금위치i까지 포함해서 길이 1 증가
count가 0일땐 새로운수열 시작 (1)
count가 0아닐땐 이전까지 count 다 더함
*/
Pair newValue = new Pair(curr.length + 1, Math.max(curr.count, 1));
update(compressed[i], newValue, 1, uniqueSize, 1);
}
Pair result = query(1, uniqueSize, 1, uniqueSize, 1);
bw.write(result.length + " " + result.count + "\n");
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
private int binarySearch(ArrayList<Integer> unique, int target) {
int left = 0, right = unique.size() - 1;
int res = 0;
while(left <= right){
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
if(unique.get(mid) >= target) {
res = mid;
right = mid - 1;
}
else left = mid + 1;
}
return res;
}
/*
구간 [left, right]에서 최댓값 찾기
*/
static Pair query(int left, int right, int start, int end, int node){
if(left > end || right < start) return new Pair(0, 0);
if(left <= start && end <= right) return segment[node];
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
Pair leftRes = query(left, right, start, mid, node*2);
Pair rightRes = query(left, right, mid+1, end, node*2 + 1);
return merge(leftRes, rightRes);
}
/*
pos 위치를 value로 업데이트
*/
static void update(int pos, Pair value, int start, int end, int node){
if(pos > end || pos < start) return;
if(start == end){
segment[node] = merge(segment[node], value);
return;
}
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
update(pos, value, start, mid, node * 2);
update(pos, value, mid+1, end, node * 2 + 1);
segment[node] = merge(segment[node * 2], segment[node * 2 + 1]);
}
}
