신경망을 이용해 단어의 분산표현을 얻을 수 있다. 단어의 분산표현이란 쉽게말해, 단어를 어떤 숫자로 이루어진 벡터로 표현하는 것을 의미.
단어의 분산표현을 얻는데는 두가지 방법이 있다.
- 통계 기반 기법
- 추론 기반 기법
여기서 추론 기반 기법이 신경망을 이용해 얻어내는 기법이며 이를 word2vec이라고 함.
word2vec에서 사용하는 모델 : CBOW
CBOW는 주변단어를 통해 중심단어를 예측해주는 모델.
간단한 CBOW 모델 구현
-
우선 text 데이터를 입력받는다. ex) 'You say goodbye and I say hello.'
-
이 text데이터를 단어별로 split해서 각 단어들에 id를 부여해준다.
| word/id | you | say | goodbye | and | i | hello | . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
- 예시 문장을 다시 id로 표현 ex) 'You say goodbye and I say hello' -> 0 1 2 3 4 1 6
2~3의 과정을 코드로 표현하면 다음과 같음
def preprocess(text):
text = text.lower()
text = text.replace('.', ' .')
words = text.split(' ')
word_to_id = {}
id_to_word = {}
for word in words:
if word not in word_to_id:
new_id = len(word_to_id)
word_to_id[word] = new_id
id_to_word[new_id] = word
corpus = np.array([word_to_id[w] for w in words])
return corpus, word_to_id, id_to_word- 이 문장으로 context, target을 만든다. 이때 context란 맥락을 의미. 중심 단어가 있다고 할때 그 주변 단어를 의미한다.
예를들어 goodbye의 경우 주변에 say, and가 있으므로 context는 say, and target은 goodbye가 된다.
따라서 context, target의 데이터셋이 다음과같이 만들어진다.
| context | target |
|---|---|
| 0,2 | 1 |
| 1,3 | 2 |
| 2,4 | 3 |
| 3,1 | 4 |
| 4,6 | 1 |
def create_contexts_target(corpus, window_size=1):
'''맥락과 타깃 생성
:param corpus: 말뭉치(단어 ID 목록)
:param window_size: 윈도우 크기(윈도우 크기가 1이면 타깃 단어 좌우 한 단어씩이 맥락에 포함)
:return:
'''
target = corpus[window_size:-window_size]
contexts = []
for idx in range(window_size, len(corpus)-window_size):
cs = []
for t in range(-window_size, window_size + 1):
if t == 0:
continue
cs.append(corpus[idx + t])
contexts.append(cs)
return np.array(contexts), np.array(target)- 이 데이터를 학습시키는 모델이 CBOW모델이다. CBOW모델의 그림은 다음과 같다.
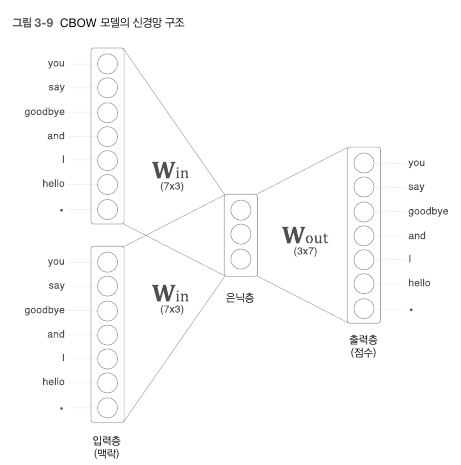
class CBOW:
def __init__(self,vocab_size,hidden_size):
V,H = vocab_size,hidden_size
W_in = 0.01 * np.random.randn(V,H).astype('f')
W_out = 0.01 * np.random.randn(H,V).astype('f')
self.in_layer0 = MatMul(W_in)
self.in_layer1 = MatMul(W_in)
self.out_layer = MatMul(W_out)
self.loss_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
layers = [self.in_layer0,self.in_layer1,self.out_layer]
self.params, self.grads = [],[]
for layer in layers:
self.params += layer.params
self.grads += layer.grads
self.word_vecs = W_in
def forward(self,contexts,target):
h0 = self.in_layer0.forward(contexts[:,0])
h1 = self.in_layer1.forward(contexts[:,1])
h = 0.5*(h0+h1)
score = self.out_layer.forward(h)
loss = self.loss_layer.forward(score,target)
return loss
def backward(self,dout = 1):
ds = self.loss_layer.backward(dout)
da = self.out_layer.backward(ds)
da *= 0.5
self.in_layer1.backward(da)
self.in_layer0.backward(da)
return None7 x 3 가중치의 각 행이 해당 단어의 분산표현이라고 볼 수 있다.
