offset
- geometry 계산이 다 끝나서 fixed 넘버 체계로 바뀌어 있을때의 체계 (계산한 결과)
offset Parent
- NULL
- root , HTML, BODY
- POSITON:FIXED
- OUT OF DOM TREE
- RECURSIVE SEARCH : offset parent를 찾는 방법
- PARENT.POSITION:FIXED = NULL
- PARENT.POSITION:!STATIC = OK (static이 아니라면 거기서 정지한다.)
- position absolute의 offset parent가 될 수 있는 애는 오직 absolute와 relative 밖에 없다.
position:absolute
HTML 태그를 절대 위치에 배치할 수 있다.
절대 위치는 left, top, bottom, right 프로퍼티 값으로 정하며 이 값들은 부모 태그 안에서의 상대좌표이다.
ex
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:200px;height:200px;background:yellow;margin:100px">
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;position:absolute;background:red"></div>
<div style="width:100px;height:100px;position:absolute;background:blue;left:0"></div>
</div>
</html> 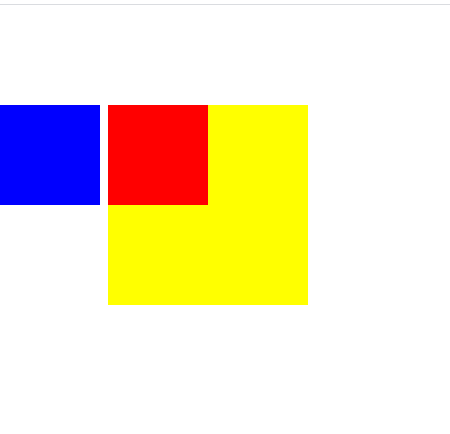
- 서로 붙어있게 하기 위해서는
body{
margin: 0 auto;
}위의 코드를 추가하면

이와같이 나타나는데 이는
1. width , height가 200px인 yellow 박스가 margin을 100px 띄어져있는 상황
2. red는 해당 absolute로 따로left, right, top ,bottom과 같은 프로퍼티가 존재하지 않으므로 static과 같이 현재 위치를 유지하고 있으나
3. blue의 경우 absolute로 따로left, right, top ,bottom과 같은 프로퍼티가 존재하여left가 적용되어 부모태그의 영향을 받아<div ~~yellow></div>부분은 따로 정해지지않은 static이므로 그 부모의body가 offsetParent가 된다.
- 즉,
<div style='yellow'></div>가 아닌 그 부모인 body를 기준으로 left : 0 을 주었다.
그러나top은 안줬으므로 노란박스의top을 유지하고 있다.
offset관련 요소
offsetLeft
offsetTop
offsetWidth
offsetHeight
- 위의 내용은 고정적으로 영향을 준다.
offsetScrollTop
offsetScrollLeft
offsetScrollWidth
offsetScrollHeight
- 위의 내용은 스크롤 시 해당 스크롤 위치의 값들이 변경된다. (해당 글자의 실제 위치를 찾을 수 있다.)
스스로 만든 position:absolute 및 scrollTop , offsetTop
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
body{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width:400px;height:600px;position:absolute;border:solid 1px black">
<div id="div" style="position:absolute;width:300px;height:300px;left:20px;top:30px;overflow:scroll">The HTMLElement.offsetLeft read-only property returns the number of pixels that the upper left corner of the current element is offset to the left within the HTMLElement.offsetParent node.
For block-level elements, offsetTop, offsetLeft, offsetWidth, and offsetHeight describe the border box of an element relative to the offsetParent.
However, for inline-level elements (such as span) that can wrap from one line to the next, offsetTop and offsetLeft describe the positions of the first border box (use Element.getClientRects() to get its width and height), while offsetWidth and offsetHeight describe the dimensions of the bounding border box (use Element.getBoundingClientRect() to get its position). Therefore, a box with the left, top, width and height of offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetWidth and offsetHeight will not be a bounding box for a span with wrapped text.
</div>
</div>
<script>
document.querySelector('#div').addEventListener('scroll',function(){
console.log(document.querySelector('#div').offsetTop,document.querySelector('#div').scrollTop)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
해당 scroll 영역을 스크롤 시
값이 유지되는offsetTop과
해당 글자의 위치만큼의 값으로 변하는scrollTop이 나타난다.
offset에서의 absolute 및 static간의 차이
1. 부모태그가 absolute이면서 margin-left가 없을 때
코드왼쪽에 딱 붙어있으면서 자식태그에
left:20px있는 상황이다.
부모태그에 영향을 받아 왼쪽으로 20px떨어져있다.
(보기에는 body에 영향을 받은 결과와 같아보인다
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
body{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="position:absolute;width:400px;height:600px;border:solid 1px black">
<div id="div" style="position:absolute;width:300px;height:300px;left:20px;top:30px;overflow:scroll">The HTMLElement.offsetLeft read-only property returns the number of pixels that the upper left corner of the current element is offset to the left within the HTMLElement.offsetParent node.
For block-level elements, offsetTop, offsetLeft, offsetWidth, and offsetHeight describe the border box of an element relative to the offsetParent.
However, for inline-level elements (such as span) that can wrap from one line to the next, offsetTop and offsetLeft describe the positions of the first border box (use Element.getClientRects() to get its width and height), while offsetWidth and offsetHeight describe the dimensions of the bounding border box (use Element.getBoundingClientRect() to get its position). Therefore, a box with the left, top, width and height of offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetWidth and offsetHeight will not be a bounding box for a span with wrapped text.
</div>
</div>
<script>
console.log(document.querySelector('#div').offsetLeft)
</script>
</body>
</html>2. 부모태그가 absolute이면서 margin-left : 10px일때
부모태그 및 자식태그 전부가 10px 옆으로 이동한다.
왜냐하면 자식태그 absolute는 부모태그로 찾아가면서 absolute인 부모태그를 기준으로left:20px이 적용되는데 부모태그가body태그가 아닌div태그 이므로 같이 옮겨진다.
- 자식태그 위치 : body기준 20px left와 margin-left에 의해 10px 더 옮김
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
body{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="position:absolute;margin-left:10px;width:400px;height:600px;border:solid 1px black">
<div id="div" style="position:absolute;width:300px;height:300px;left:20px;top:30px;overflow:scroll">The HTMLElement.offsetLeft read-only property returns the number of pixels that the upper left corner of the current element is offset to the left within the HTMLElement.offsetParent node.
For block-level elements, offsetTop, offsetLeft, offsetWidth, and offsetHeight describe the border box of an element relative to the offsetParent.
However, for inline-level elements (such as span) that can wrap from one line to the next, offsetTop and offsetLeft describe the positions of the first border box (use Element.getClientRects() to get its width and height), while offsetWidth and offsetHeight describe the dimensions of the bounding border box (use Element.getBoundingClientRect() to get its position). Therefore, a box with the left, top, width and height of offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetWidth and offsetHeight will not be a bounding box for a span with wrapped text.
</div>
</div>
<script>
console.log(document.querySelector('#div').offsetLeft)
</script>
</body>
</html>3. 부모태그가 static이면서 margin-left : 10px일때
2번 경우와 비교해보면 자식태그 스크롤부분이 왼쪽으로 옮긴 것을 알 수 있는데 그 이유는 부모태그가 static이므로 그 다음 부모인 body태그가
offset parent가 되므로 그것을 기준으로left:20px을 적용하였으니 2번에서 margin-left로 오른쪽으로 옮겨진div부모 태그에 상관없이body태그에 영향을 받아서만20px옮겨진 것이다.
- 자식태그 위치 : body기준 20px left
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<style>
body{
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="position:static;margin-left:10px;width:400px;height:600px;border:solid 1px black">
<div id="div" style="position:absolute;width:300px;height:300px;left:20px;top:30px;overflow:scroll">The HTMLElement.offsetLeft read-only property returns the number of pixels that the upper left corner of the current element is offset to the left within the HTMLElement.offsetParent node.
For block-level elements, offsetTop, offsetLeft, offsetWidth, and offsetHeight describe the border box of an element relative to the offsetParent.
However, for inline-level elements (such as span) that can wrap from one line to the next, offsetTop and offsetLeft describe the positions of the first border box (use Element.getClientRects() to get its width and height), while offsetWidth and offsetHeight describe the dimensions of the bounding border box (use Element.getBoundingClientRect() to get its position). Therefore, a box with the left, top, width and height of offsetLeft, offsetTop, offsetWidth and offsetHeight will not be a bounding box for a span with wrapped text.
</div>
</div>
<script>
console.log(document.querySelector('#div').offsetLeft)
</script>
</body>
</html>Absolute 자식태그와 연관성
1) Relative 부모태그일때
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
</head>
<style>
.parent{
border:1px solid black;
display: inline-block;
width:200px;
height:200px;
position:relative;
}
.child{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background-color: red;
position:absolute;
left:30px;
top:30px;
}
</style>
<body>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'>
<div class='child'></div>
</div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'> <div class='child'></div></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'> <div class='child'></div></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
<div class='parent'></div>
</body>
</html>
부모태그가 relative이므로 부모태그를 기준으로 처리를 진행하므로 해당 IFC 영역에서 존재한다. ( 브라우저를 줄이거나 늘려도 결국 해당 틀 안에서 존재한다.)
2) Absolute 부모태그일때
.parent{
border:1px solid black;
display: inline-block;
width:200px;
height:200px;
position:absolute;
}- 수정

부모태그 또한 Absolute이므로 다시 body태그로 찾아가므로 전부 body태그가 offsetParent이므로 한곳에 모아진 형태이다.
relative 부모태그 absolute 자식태그 형태가 많이 쓰인다.
정리
-
position:absolute의 기본값
(left,top,bottom,right와 같은 값 존재X)은 postion:static과 같은 위치를 갖는다. -
만약 position:absolute가 기본값이 아닐 경우 부모태그로 static이 아닌 것을 계속 찾아간다.
그러다가 body태그나 root태그 같은 것을 만나면 거기에 따라 계산하여 그린다. -
left=0 top=0의 작동 경우
1) static => 무시
2) relative => normal flow로 그려졌을때로부터의 거리
3) absolute => offset parent로부터의 거리
