정리
- Custom Vector를 만들었다.
- 간단한 도서관 시스템을 만들었다.
vector
벡터는 간단히 말하면 배열의 간단한 확장 버전이다.
배열은 크기를 정하면 정해진 크기까지만 쓸 수 있지만 벡터는 마치 제한이 없는 것처럼 계속 추가하면서 쓸 수 있다.
물론 그런 건 없고 그렇게 보이기만 할 뿐이다.
벡터는 내부에 배열을 생성해 push_back으로 원소들을 하나씩 채운다.
생성된 배열이 꽉 찼는데 새로운 원소를 넣으려고 하면 아래의 그림처럼 일정량 더 큰 배열을 생성해 기존에 있던 원소를 복사하고, 뒤에 새로운 원소를 추가한다.
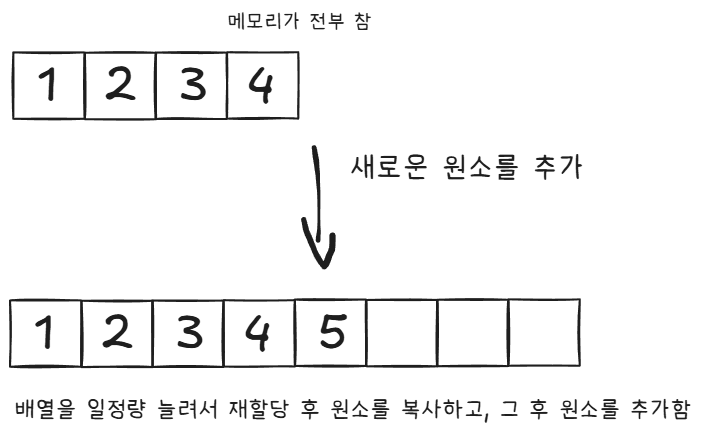
구현은 아래와 같이 했다.
template<typename T>
class SimpleVector
{
protected:
T* data;
int currentSize;
int currentCapacity;
public:
SimpleVector() : SimpleVector(10) {}
SimpleVector(int size)
{
currentSize = 0;
currentCapacity = size;
data = new T[currentCapacity];
}
//복사 생성자
SimpleVector(const SimpleVector& obj)
{
currentSize = obj.currentSize;
currentCapacity = obj.currentCapacity;
obj.resize(obj.currentCapacity);
}
~SimpleVector()
{
delete[] data;
}
T& operator[](int index)
{
if (index < 0 || index >= currentSize)
throw std::out_of_range("접근하려는 인자가 배열의 범위를 벗어났습니다.");
return data[index];
}
public:
void push_back(const T& value)
{
if (currentSize == currentCapacity)
{
currentCapacity += 5;
resize(currentCapacity);
}
data[currentSize++] = value;
}
void pop_back()
{
if (currentSize > 0)
currentSize--;
}
void sortData()
{
sort(data, data + currentSize);
}
inline int size() { return currentSize; }
inline int capacity() { return currentCapacity; }
private:
void resize(int newCapacity)
{
if (newCapacity <= currentSize)
return;
T* temp = new T[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++)
temp[i] = data[i];
delete[] data;
data = temp;
}
};Library System
간단한 도서관 시스템을 제작했다.
BookManager의 addBook으로 책을 등록하고, 현재 책의 목록을 볼 수 있다.
BorrowManager는 책의 대여를 담당하고, 현재 대여된 책의 목록을 볼 수 있다.
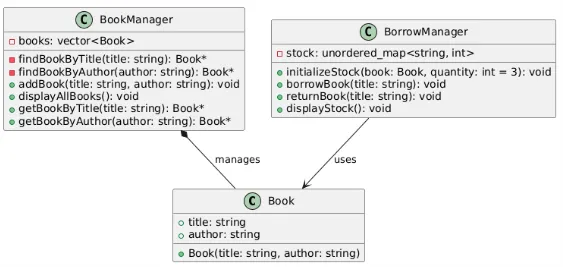
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Book
{
public:
string title;
string author;
Book(const string& title, const string& author) : title(title), author(author) {}
};
class BookManager
{
private:
vector<Book> books; // 책 목록 저장
public:
// 책 추가 메서드
void addBook(const string& title, const string& author)
{
books.push_back(Book(title, author)); // push_back 사용
cout << "책이 추가되었습니다: " << title << " by " << author << endl;
}
// 모든 책 출력 메서드
void displayAllBooks() const
{
if (books.empty())
{
cout << "현재 등록된 책이 없습니다." << endl;
return;
}
cout << "현재 도서 목록:" << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < books.size(); i++)
{ // 일반적인 for문 사용
cout << "- " << books[i].title << " by " << books[i].author << endl;
}
}
void searchByTitle(string title)
{
cout << "제목으로 찾습니다..." << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++)
if (books[i].title == title)
{
cout << "찾으시는 " << title << " 책이 있습니다." << endl;
return;
}
cout << "찾으시는 책이 없습니다." << endl;
}
void searchByAuthor(string author)
{
cout << "저자로 찾습니다..." << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++)
if (books[i].author == author)
{
cout << "찾으시는 " << books[i].title << " 책이 있습니다." << endl;
return;
}
cout << "찾으시는 책이 없습니다." << endl;
}
Book* findBookByTitle(string title)
{
for (int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++)
if (books[i].title == title)
return &books[i];
return nullptr;
}
Book* findBookByAuthor(string author)
{
for (int i = 0; i < books.size(); i++)
if (books[i].author == author)
return &books[i];
return nullptr;
}
};
class BorrowManager
{
private:
unordered_map<string, int> stock;
public:
void initializeStock(Book book, int quantity = 3)
{
stock[book.title] = quantity;
}
//대여
void borrowBook(string title)
{
if (stock[title] <= 0)
cout << "남은 책이 없어 대여할 수 없습니다." << endl;
else
{
stock[title]--;
cout << title << "이 대여 되었습니다." << endl;
}
}
//반납
void returnBook(string title)
{
if (stock[title] >= 3)
cout << "이미 책이 모두 반납되어 있습니다." << endl;
else
{
stock[title]++;
cout << title << "이 반납 되었습니다." << endl;
}
}
void displayStock()
{
if (stock.empty())
{
cout << "현재 등록된 책이 없습니다." << endl;
return;
}
cout << "현재 보유 도서 목록 : " << endl;
for (unordered_map<string, int>::iterator iter = stock.begin(); iter != stock.end(); iter++)
{
cout << "- " << iter->first << ", " << iter->second << "개" << endl;
}
}
};
int main()
{
BookManager manager;
BorrowManager borrowManager;
// 도서관 관리 프로그램의 기본 메뉴를 반복적으로 출력하여 사용자 입력을 처리합니다.
// 프로그램 종료를 선택하기 전까지 계속 동작합니다.
while (true)
{
cout << "\n도서관 관리 프로그램" << endl;
cout << "1. 책 추가" << endl; // 책 정보를 입력받아 책 목록에 추가
cout << "2. 모든 책 출력" << endl; // 현재 책 목록에 있는 모든 책 출력
cout << "3. 종료" << endl; // 프로그램 종료
cout << "4. 책 찾기" << endl;
cout << "5. 대여소 책 목록" << endl;
cout << "선택: ";
int choice; // 사용자의 메뉴 선택을 저장
cin >> choice;
if (choice == 1)
{
// 1번 선택: 책 추가
// 사용자로부터 책 제목과 저자명을 입력받아 BookManager에 추가합니다.
string title, author;
cout << "책 제목: ";
cin.ignore(); // 이전 입력의 잔여 버퍼를 제거
getline(cin, title); // 제목 입력 (공백 포함)
cout << "책 저자: ";
getline(cin, author); // 저자명 입력 (공백 포함)
manager.addBook(title, author); // 입력받은 책 정보를 추가
borrowManager.initializeStock(*manager.findBookByTitle(title)); //대여할 수 있게 책 정보 추가
}
else if (choice == 2)
{
// 2번 선택: 모든 책 출력
// 현재 BookManager에 저장된 책 목록을 출력합니다.
manager.displayAllBooks();
}
else if (choice == 3)
{
// 3번 선택: 종료
// 프로그램을 종료하고 사용자에게 메시지를 출력합니다.
cout << "프로그램을 종료합니다." << endl;
break; // while 루프 종료
}
else if (choice == 4)
{
//책 찾기
string str;
cout << "책 제목/저자 : ";
cin >> str;
manager.searchByTitle(str);
manager.searchByAuthor(str);
cout << endl;
Book* book;
book = manager.findBookByTitle(str);
if (book == nullptr)
book = manager.findBookByAuthor(str);
if (book == nullptr)
continue;
cout << "찾으신 책의 이름은 " << book->title << ", 저자는 " << book->author << " 입니다." << endl;
cout << "대여하시겠습니까?" << endl;
cout << "대여 : 0, 반납 : 1, 취소 : 아무숫자 ";
int inputNum;
cin >> inputNum;
cout << endl;
if (inputNum == 0)
borrowManager.borrowBook(book->title);
else if (inputNum == 1)
borrowManager.returnBook(book->title);
}
else if (choice == 5)
{
borrowManager.displayStock();
}
else
{
// 잘못된 입력 처리
// 메뉴에 없는 번호를 입력했을 경우 경고 메시지를 출력합니다.
cout << "잘못된 입력입니다. 다시 시도하세요." << endl;
}
}
return 0; // 프로그램 정상 종료
}