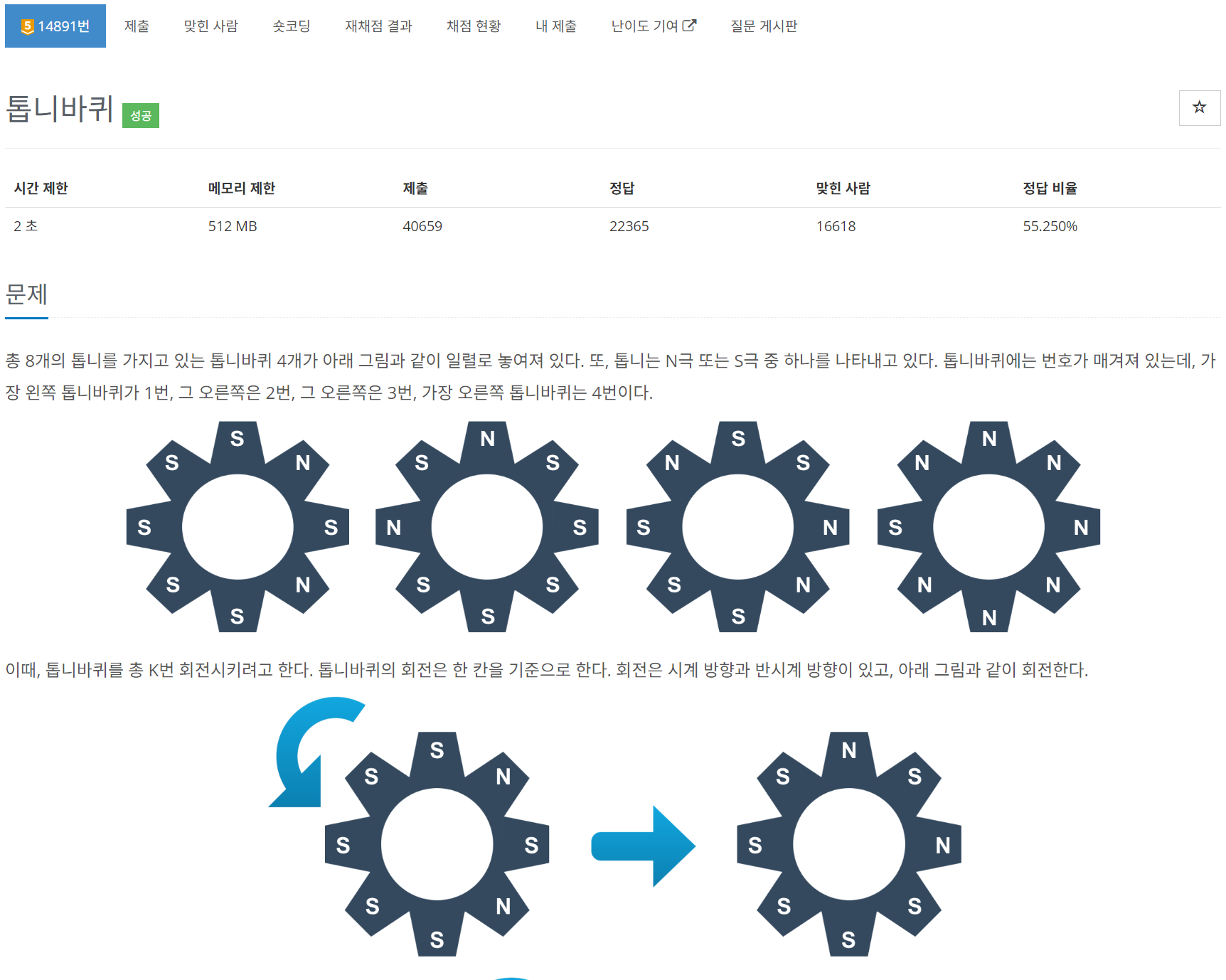
구현 문제는 많이 풀어보지 않아서 처음부터 애를 많이 먹었다. 앞으로는 구현 , 수학 , DP 문제만을 중점적으로 풀어볼 생각이다. 구현은 특별히 설명할 것이 없는 것 같다. 주어진 문제를 그때 마다 상황에 맞게 구현해야 하기 때문에 그래프, 백트래킹과 같이 풀이법이 어느정도 정형화돼있는 문제보다 많이 어렵게 느껴진다.
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
vector<deque<int>> gear(5);
int rotation_check[5];
bool check[5];
//기어 이름, 회전방향
void setrotation(int g, int c) {
rotation_check[g] = c;
check[g] = true;
//회전 설정 기준 왼쪽 톱니바퀴 설정
if (g - 1 > 0 && check[g - 1] == false) {
if (c == 0) {
setrotation(g - 1, 0);
}
//극이 똑같다면
else if (gear[g - 1][2] == gear[g][6]) {
setrotation(g - 1, 0);
}
else if (gear[g - 1][2] != gear[g][6]) {
setrotation(g - 1, -c);
}
}
if (g + 1 <= 4 && check[g + 1] == false) {
if (c == 0) {
setrotation(g + 1, 0);
}
//극이 똑같다면
else if (gear[g + 1][6] == gear[g][2]) {
setrotation(g + 1, 0);
}
else if (gear[g + 1][6] != gear[g][2]) {
setrotation(g + 1, -c);
}
}
}
void rotation() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
//시계방향
if (rotation_check[i] == 1) {
int a = gear[i].back();
gear[i].pop_back();
gear[i].push_front(a);
}
else if (rotation_check[i] == -1) {
int a = gear[i].front();
gear[i].pop_front();
gear[i].push_back(a);
}
}
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
string t;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
cin >> t;
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
gear[i].push_back(t[j] - '0');
}
}
int k, g, c;
cin >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//1 시계방향
//-1 반시계방향
cin >> g >> c;
memset(check, false, sizeof(check));
setrotation(g, c);
rotation();
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
if (gear[i][0] == 1) {
result += (int)pow(2, i - 1);
}
}
cout << result;
return 0;
}