1. What is a Heap Data Structure in java
- A heap is a tree-based data structure and can be classified as a complete binary tree
- The relation between the root node and the child node is called as "Heap Property"
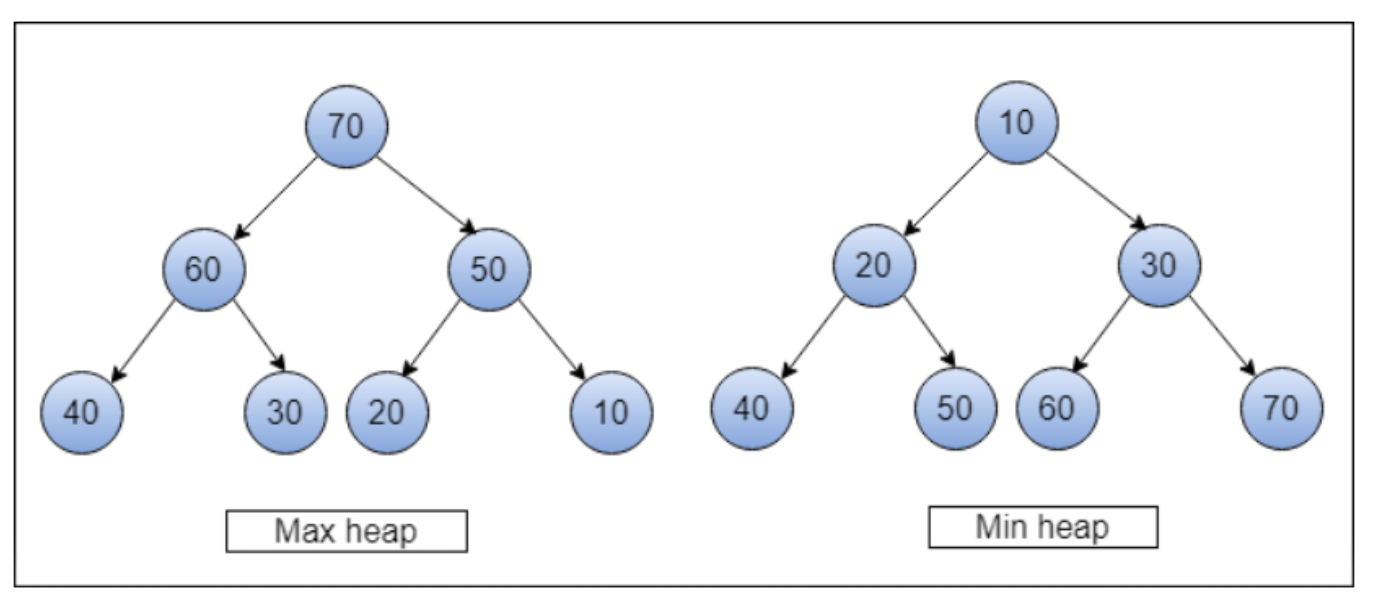
1) Max-Heap
- In a Max-Heap, the root node key is the greatest of all keys in the heap
- the root node is greater than its children
2) Min-Heap
- In a Max-Heap, the root node key is the smallest of all keys in the heap
2. Applications of Heaps
- Heaps are mostly used to implement Priority Queues
- Especially min-heap can be used to determine the shortest paths between the vertices in Graph
3. Binary Heap
- Binary Heap is a complete binary tree
- all the levels except the last level are completely filled. At the last leve, the keys are as far as left as possible
So in general for any i node in the binary heap array representation. arry[i] can represent the indices of other nodes

The binary heap in Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryHeap maxHeap = new BinaryHeap(10);
maxHeap.insert(1);
maxHeap.insert(2);
maxHeap.insert(3);
maxHeap.insert(4);
maxHeap.insert(5);
maxHeap.insert(6);
maxHeap.insert(7);
maxHeap.printHeap();
maxHeap.delete(1);
maxHeap.printHeap();
}
}
class BinaryHeap {
private static final int d = 2;
private int [] heap;
private int heapSize;
public BinaryHeap(int capacity) {
heapSize = 0;
heap = new int[capacity + 1];
Arrays.fill(heap, -1);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return heapSize == heap.length;
}
private int parent(int i) {
return (i - 1) / d;
}
private int kthChild(int i, int k) {
return d*i + k;
}
public void insert(int x) {
if(isFull())
throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is full, No space to insert new element");
heap[heapSize++] = x;
heapifyUp(heapSize-1);
}
public int delete(int x) {
if(isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty, No element to delete");
int key = heap[x];
heap[x] = heap[heapSize -1];
heapSize--;
heapifyDown(x);
return key;
}
private void heapifyUp(int i) {
int temp = heap[i];
while (i>0 && temp > heap[parent(i)]) {
heap[i] = heap[parent(i)];
i = parent(i);
}
heap[i] = temp;
}
private void heapifyDown(int i) {
int child;
int temp = heap[i];
while (kthChild(i, 1) < heapSize) {
child = maxChild(i);
if(temp < heap[child]) {
heap[i] = heap[child];
} else break;
i = child;
}
heap[i] = temp;
}
private int maxChild(int i){
int leftChild = kthChild(i, 1);
int rightChild = kthChild(i, 2);
return heap[leftChild] > heap[rightChild] ? leftChild : rightChild;
}
public void printHeap()
{
for (int i = 0; i < heapSize; i++)
System.out.print(heap[i] +" ");
}
public int findMax(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("Heap is empty.");
return heap[0];
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BinaryHeap{" +
"heap=" + Arrays.toString(heap) +
", heapSize=" + heapSize +
'}';
}
}Min heap in Java
class Min_Heap {
private int[] HeapArray;
private int size;
private int maxsize;
private static final int FRONT = 1;
public Min_Heap(int maxsize) {
this.maxsize = maxsize;
this.size = 0;
HeapArray = new int[this.maxsize + 1];
HeapArray[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
private int parent(int pos) {
return pos / 2;
}
private int leftChild(int pos) {
return ( 2 * pos );
}
private int rightChild(int pos) {
return (2 * pos ) + 1;
}
// checks if the node is a leaf node
private boolean isLeaf(int pos) {
if (pos >= (size / 2) && pos <= size) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void swap(int fpos, int spos) {
int tmp;
tmp = HeapArray[fpos];
HeapArray[fpos] = HeapArray[spos];
HeapArray[spos] = tmp;
}
private void minHeapify(int pos) {
// check if the node is non-leaf and greater than its child
if (!isLeaf(pos)) {
if (HeapArray[pos] > HeapArray[leftChild(pos)]
|| HeapArray[pos] > HeapArray[rightChild(pos)]) {
// swap with left child and then heapify the left child
if (HeapArray[leftChild(pos)] < HeapArray[rightChild(pos)]) {
swap(pos, leftChild(pos));
minHeapify(leftChild(pos));
}
// Swap with the right child and heapify the right child
else {
swap(pos, rightChild(pos));
minHeapify(rightChild(pos));
}
}
}
}
// insert a node into the heap
public void insert(int element) {
if (size >= maxsize) {
return;
}
HeapArray[++size] = element;
int current = size;
while (HeapArray[current] < HeapArray[parent(current)]) {
swap(current, parent(current));
current = parent(current);
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(HeapArray));
}
// Function to print the contents of the heap
public void display() {
System.out.println("PARENT NODE" + "\t" + "LEFT NODE" + "\t" + "RIGHT NODE");
for (int i = 1; i <= size / 2; i++) {
System.out.print(" " + HeapArray[i] + "\t\t" + HeapArray[2 * i]
+ "\t\t" + HeapArray[2 * i + 1]);
System.out.println();
}
}
// build min heap
public void minHeap() {
for (int pos = (size / 2); pos >= 1; pos--) {
minHeapify(pos);
}
}
// remove and return the heap elment
public int remove() {
int popped = HeapArray[FRONT];
HeapArray[FRONT] = HeapArray[size--];
minHeapify(FRONT);
return popped;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Min_Heap{" +
"HeapArray=" + Arrays.toString(HeapArray) +
", size=" + size +
", maxsize=" + maxsize +
'}';
}
}Priority Queue Min Heap In Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue_heap = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
pQueue_heap.add(100);
pQueue_heap.add(30);
pQueue_heap.add(20);
pQueue_heap.add(40);
// Print the head (root node of min heap) using peek method
System.out.println("Head (root node of min heap):" + pQueue_heap.peek());
// Print min heap represented using PriorityQueue
System.out.println("\n\nMin heap as a PriorityQueue:");
Iterator iter = pQueue_heap.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
// remove head (root of min heap) using poll method
pQueue_heap.poll();
System.out.println("\n\nMin heap after removing root node:");
//print the min heap again
Iterator<Integer> iter2 = pQueue_heap.iterator();
while (iter2.hasNext())
System.out.print(iter2.next() + " ");
}
}Max heap in Java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int size = array.size();
MaxHeap h = new MaxHeap();
h.insert(array, 3);
h.insert(array, 4);
h.insert(array, 9);
h.insert(array, 5);
h.insert(array, 7);
h.deleteNode(array, 7);
System.out.println("Max-Heap array: ");
h.printArray(array, size);
}
}
class MaxHeap {
void heapify(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int i) {
int size = hT.size();
int largest = i;
int l = 2 * i + 1;
int r = 2 * i + 2;
if (l < size && hT.get(l) > hT.get(largest))
largest = l;
if (r < size && hT.get(r) > hT.get(largest))
largest = r;
if (largest != i) {
int temp = hT.get(largest);
hT.set(largest, hT.get(i));
hT.set(i, temp);
heapify(hT, largest);
}
}
void insert(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int newNum) {
int size = hT.size();
if (size == 0) {
hT.add(newNum);
} else {
hT.add(newNum);
for (int i = size / 2 -1; i >= 0; i--) {
heapify(hT, i);
}
}
}
void deleteNode(ArrayList<Integer> hT, int num) {
int size = hT.size();
int i;
for (i = 0; i<size; i++) {
if(num == hT.get(i))
break;
}
int temp = hT.get(i);
hT.set(i, hT.get(size-1));
hT.set(size-1, temp);
hT.remove(size-1);
for(int j = size / 2 - 1; j>=0; j--) {
heapify(hT, j);
}
}
void printArray(ArrayList<Integer> array, int size) {
System.out.println("array" + array.toString());
for (Integer i : array) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}Priority Queue Max Heap In Java
class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create empty priority queue
//with Collections.reverseOrder to represent max heap
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue_heap =
new PriorityQueue<Integer>(Collections.reverseOrder());
// Add items to the pQueue using add()
pQueue_heap.add(10);
pQueue_heap.add(90);
pQueue_heap.add(20);
pQueue_heap.add(40);
// Printing all elements of max heap
System.out.println("The max heap represented as PriorityQueue:");
Iterator iter = pQueue_heap.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext())
System.out.print(iter.next() + " ");
// Print the highest priority element (root of max heap)
System.out.println("\n\nHead value (root node of max heap):" +
pQueue_heap.peek());
// remove head (root node of max heap) with poll method
pQueue_heap.poll();
//print the max heap again
System.out.println("\n\nMax heap after removing root: ");
Iterator<Integer> iter2 = pQueue_heap.iterator();
while (iter2.hasNext())
System.out.print(iter2.next() + " ");
}
}결론 - Heap 자료 구조를 통해 최소, 최대값을 구하는데 특화됨, 루트의 값만 사용하므로 O(1)의 시간 복잡도로 최소값, 최대값 찾을 수 있다.
참고자료
https://shanepark.tistory.com/261
https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/heap-data-structure-in-java
