🦉Header.
- Django 소스코드를 해석하여 작성한 포스트입니다.
- 😍 틀린 부분이 있거나, 피드백은 언제든지 환영합니다.
👀Reference.
command.run_from_argv의 실행
self.fetch_command(subcommand) 에 의해
Module: django.core.management.commands.runserver의
Class: Command의 인스턴스가 생성되고
.runserver.Command인스턴스의 methodrun_from_argv를 호출한다.
해당 Class의 상속관계를 보면, 아래와 같다.
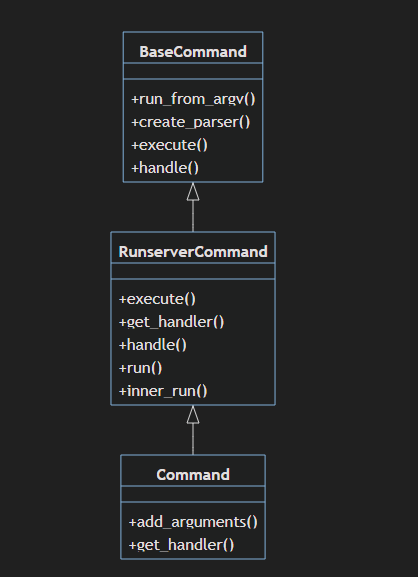
django.core.management.base의 BaseCommand
# django.core.management.base
class BaseCommand:
def run_from_argv(...):
def create_parser(...):
def execute(...):
def handle(...):모든 Command 관련 Class의 모체가되는 django.core.management 모듈의
BaseCommand의 method: run_from_argv() 가 호출이 되게 되면,
method: create_parser() 가 호출되어
인자들과 command관련 옵션들을 파싱하는 parser를 설정하고,
해당 parser를 통해 command 관련 옵션들을 파싱 및 정리하여,
method: execute()에 인자로 전달하며 호출하게 된다.
execute()는 또한 method: handle()을 호출하게 된다.
execute()와 handle()의 호출은 아래에서 좀 더 자세하게 다룰 것이다.
django.core.management.commands.runserver의 Command
from django.core.management.base import BaseCommand, CommandError
class Command(BaseCommand):
...
def execute():
def get_handler():
def handle(self, *args, **options):
"""
실제 동작을 담당한다.
부모 Class: BaseCommand 의 handle을 오버라이딩한 것.
self.run()을 호출한다.
"""
def run(self, **options):
"""
self.inner_run()을 호출한다.
"""
def inner_run():
"""
실제 서버 instance를 만들어 구동하는 부분에 해당한다.
"""BaseCommand를 상속받은 위 Class: Command 에서는
요청을 처리하기 위한 handler를 받기위한 method:get_handler() 를 정의하고,
부모 Class의 execute(), handle() 을 오버라이딩한다.
run() 과, inner_run() 은 handl()을 호출했을 때, 구체적 동작을 명시하기 위해 정의된 method이다.
오늘 글의 주인공. 중심 기능들을 담고 있는 Class 이며
용어의 혼동을 막기 위해, 위 Class를 RunserverCommand라고 칭하고자 한다.
django.contrib.staticfiles.commands.runserver의 Command
from django.core.management.commands.runserver import Command as RunserverCommand
class Command(RunserverCommand):
def add_arguments():
def get_handler():위의 Class: Command는
인자들의 처리와 handler를 가져오는 부분에 대한 overriding 으로만 이루어져있으므로,
오늘의 글에서는 RunserverCommand를 중심으로 설명하고자 한다.
RunserverCommand의 execute()에 의한 실제 구동.
# django.core.management.base
class BaseCommand:
...
def execute(self, *args, **options):
...
output = self.handle(*args, **options)
...
return output
def handle(self, *args, **options):
"""
actual logic of the command.
subclasses must implement this method.
"""
raise NotImplementedError("subclasses must provide a handle() method")RunserverCommand의 부모 Class인 BaseCommand의 method: execute()를 살펴보면,
위에서 설명한 바대로 method: handle() 을 호출한 결과를 반환한다.
BaseCommand의 method:
handle()은 자신을 상속받은 자식 Class에서필수적으로 구체적인 동작을 명시하여 오버라이딩하여야 한다.
즉, RunserverCommand에서는 handler()에서 구체적 동작을 명시해야한다.
다음, RunserverCommand를 보자.
# django.core.management.commands.runserver
class Command(BaseCommand):
...
def execute(self, *args, **options):
if options["no_color"]:
# We rely on the environment because it's currently the only
# way to reach WSGIRequestHandler. This seems an acceptable
# compromise considering `runserver` runs indefinitely.
os.environ["DJANGO_COLORS"] = "nocolor"
super().execute(*args, **options)
def handle(self, *args, **options):
# validation & sanitization
"""
실제 동작을 담당한다.
부모 Class: BaseCommand 의 handle을 오버라이딩한 것.
"""
self.run(**options)
def run(self, **options)
use_reloader = options["use_reloader"]
if use_reloader:
autoreload.run_with_reloader(self.inner_run, **options)
else:
self.inner_run(None, **options)
def inner_run(self, *args, **options):
...
try:
handler = self.get_handler(*args, **options)
run(
self.addr,
int(self.port),
handler,
ipv6=self.use_ipv6,
threading=threading,
sefver_cls=self.server_cls
)handle()에서self.run(**options)self.run()에서inner_run()inner_run()의 동작은 두 단계로 나뉜다.get_handler()로 handler를 받아옴.- run 함수를 통해 실제로 서버를 구동시킴.
inner_run()의 동작 Step1) get_handler()를 통한 wsgi_handler 받아오기.
# django.core.management.commands.runserver
class Command(BaseCommand):
..
def get_handler(self, *args, **options):
""" Return the default WSGI handler for the runner."""
return get_internal_wsgi_application()
RunserverCommand의 method: get_handler()에 의해, 동작한다.
get_handler() 에서 호출하는 get_internal_wsgi_application() 은 아래와 같다.
흐름을 위해 자세한 설명은 생략하고자 한다.
# django.core.servers.basehttp
def get_internal_wsgi_application():
"""
사용자에 의해 설정된 settings.WSGI_APPLICATION
"""
from django.conf import settings
app_path = getattr(settings, "WSGI_APPLCIATION")
if app_path in None:
return get_wsgi_application()
try:
return import_string(app_path)
except ...
# django.core.wsgi
from django.core.handlers.wsgi import WSGIHandler
def get_wsgi_application():
"""
the public interface to Django's WSGI support.
Return a WSGI callable.
"""
django.setup(set_prefix=False)
return WSGIHanler()inner_run()의 동작 Step2) get_handler()를 통해 받아온 wsgi_handler를 인자로 넘겨 서버를 실제로 구동.
# django.core.management.commands.runserver
class Command(BaseCommand):
default_addr = "127.0.0.1"
default_addr_ipv6 = "::1"
default_port = "8000"
protocol = "http"
server_cls = WSGIServer
def inner_run(self, *args, **options):
...
try:
handler = self.get_handler(*args, **options)
run(
self.addr,
int(self.port),
handler,
ipv6=self.use_ipv6,
threading=threading,
server_cls=self.server_cls,
)# django.core.servers.basehttp
def run(addr, port, wsgi_handler, ipv6=False, threading=False, server_cls=WSGIServer):
server_address = (addr, port)
if threading:
httpd_cls = type("WSGIServer", (socketserver.ThreadingMixIn, server_cls), {})
else:
httpd_cls = server_cls
httpd = httpd_cls(server_address, WSGIRequestHandler, ipv6=ipv6)
if threading:
# ThreadingMixIn.daemon_threads indicates how threads will behave on an
# abrupt shutdown; like quitting the server by the user or restarting
# by the auto-reloader. True means the server will not wait for thread
# termination before it quits. This will make auto-reloader faster
# and will prevent the need to kill the server manually if a thread
# isn't terminating correctly.
httpd.daemon_threads = True
httpd.set_app(wsgi_handler)
httpd.serve_forever()wsgi_handler를 인자로 받아서, 실제로 구동하는 부분이라고 할 수 있다.
server_cls의 인자를 보면 WSGIServer 이다.
해석해보면,
httpd = httpd_cls(server_address, WSGIRequestHanlder, ipv6=ipv6)를 통해Server의 instance를 만들고,
httpd.set_app(wsgi_hanlder)를 통해 전달받은 wsgi_handler를 application으로 등록한다.
httpd.server_forever()를 통해 server를 구동한다.
여기까지 ‘runserver’ 명령어에 의해 생성된
RunserverCommand 가 handler를 받아서,
서버 인스턴스를 생성하여 구동시키는 부분까지 흐름을 파악해보았다.
다음 글에서는, 설명에 지속적으로 등장하는
wsgi_handler (?) 와
서버 구동을 위해 만들어내는 서버 Class와 인스턴스에 대하여 정리해보고자한다.

