큐(Queue)
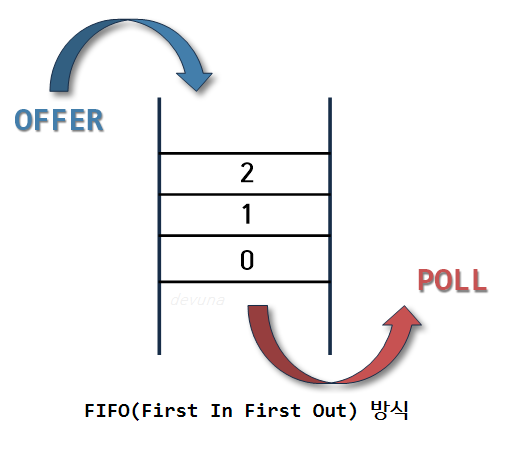
큐(Queue)는 선형 자료구조 중 하나로, 데이터를 선입선출(FIFO, First In First Out) 방식으로 관리합니다. 즉, 먼저 삽입된 데이터가 가장 먼저 제거되거나 사용됩니다. 큐는 양쪽 끝에서 작동하며, 한쪽 끝에서는 데이터를 삽입하고 다른 쪽 끝에서는 데이터를 제거합니다.
큐의 주요 연산
- enqueue: 큐의 끝(Rear)에 데이터를 삽입.
- dequeue: 큐의 앞(Front)에서 데이터를 제거하고 반환.
- peek (또는 front): 큐의 앞(Front) 데이터를 제거하지 않고 반환.
- isEmpty: 큐가 비어 있는지 확인.
- isFull: 큐가 꽉 찼는지 확인 (고정 크기 큐인 경우).
큐의 특징
-
선입선출(FIFO): 먼저 삽입된 데이터가 먼저 사용됨.
-
양쪽 끝 활용: 삽입과 삭제 작업이 각각 Rear와 Front에서 이루어짐.
-
연속적 저장: 일반적으로 배열(Array) 또는 연결 리스트(Linked List)로 구현.
큐의 구현
1. 배열 기반 큐
class Queue {
private int[] queue;
private int front;
private int rear;
private int size;
private int capacity;
public Queue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.queue = new int[capacity];
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.size = 0;
}
// 데이터 삽입
public void enqueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("큐가 가득 찼습니다.");
}
rear = (rear + 1) % capacity; // 순환 큐 구현
queue[rear] = value;
size++;
}
// 데이터 제거 및 반환
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
}
int value = queue[front];
front = (front + 1) % capacity; // 순환 큐 구현
size--;
return value;
}
// 큐의 맨 앞 요소 반환
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
}
return queue[front];
}
// 큐가 비어 있는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 큐가 가득 찼는지 확인
public boolean isFull() {
return size == capacity;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new Queue(5);
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(20);
queue.enqueue(30);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue()); // 출력: 10
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 출력: 20
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); // 출력: false
}
}2. 연결 리스트 기반 큐
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedListQueue {
private Node front;
private Node rear;
public LinkedListQueue() {
this.front = null;
this.rear = null;
}
// 데이터 삽입
public void enqueue(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (rear != null) {
rear.next = newNode;
}
rear = newNode;
if (front == null) {
front = rear;
}
}
// 데이터 제거 및 반환
public int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
}
int value = front.data;
front = front.next;
if (front == null) {
rear = null;
}
return value;
}
// 큐의 맨 앞 요소 반환
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("큐가 비어 있습니다.");
}
return front.data;
}
// 큐가 비어 있는지 확인
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListQueue queue = new LinkedListQueue();
queue.enqueue(10);
queue.enqueue(20);
queue.enqueue(30);
System.out.println(queue.dequeue()); // 출력: 10
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 출력: 20
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); // 출력: false
}
}큐의 활용
- CPU 스케줄링: 프로세스 관리 및 실행 순서 결정.
- 프린터 작업 관리: 인쇄 대기열 관리.
- 데이터 버퍼링: 네트워크나 파일 처리에서 데이터 처리 대기열로 활용.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): 그래프 탐색 알고리즘에서 큐를 사용.
큐의 장점과 단점
장점:
- FIFO 방식으로 데이터 순서를 관리하기 용이.
- 데이터 스트림이나 대기열 처리에 적합.
단점:
- 고정 크기 배열 기반 구현에서는 크기가 초과되면 확장 불가.
- 순환 큐로 구현하지 않으면 배열이 효율적이지 않음.
큐는 순서를 유지하면서 데이터를 처리해야 하는 다양한 상황에서 사용되며, 그 효율성과 간단한 구현으로 많은 응용 분야에서 중요한 역할을 합니다.
추가 학습 자료
