참고자료
1. NumPy
Numerical Python의 약자로, scientific computing을 위한 기본적인 파이썬 패키지다. What is NumPy?
일반적으로 Alias(별칭) np를 사용하여 import한다. 코드의 보편성 및 가독성을 위해서 관행적으로 사용하는 용어를 함께 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.
import numpy as np # import numpy로 사용해도 무방하다.
numpy 변수의 출력값은 List와 헷갈릴 수 있기 때문에 헷갈릴 때는 type() 및 dir()로 확인하는 것이 바람직하다. array를 print를 해보면,(Comma) 없이 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
>>> a = np.zeros(3) >>> a array([0., 0., 0.]) >>> print(a) [0. 0. 0.] >>> print(type(a)) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> >>> print(type(a[0])) <class 'numpy.float64'> >>> print(dir(a)) ['T', '__abs__', '__add__', '__and__', '__array__', '__array_finalize__', '__array_function__', '__array_interface__', '__array_prepare__', '__array_priority__', '__array_struct__', '__array_ufunc__', '__array_wrap__', '__bool__', '__class__', '__complex__', '__contains__', '__copy__', '__deepcopy__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__divmod__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__float__', '__floordiv__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__iand__', '__ifloordiv__', '__ilshift__', '__imatmul__', '__imod__', '__imul__', '__index__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__int__', '__invert__', '__ior__', '__ipow__', '__irshift__', '__isub__', '__iter__', '__itruediv__', '__ixor__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lshift__', '__lt__', '__matmul__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__neg__', '__new__', '__or__', '__pos__', '__pow__', '__radd__', '__rand__', '__rdivmod__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rfloordiv__', '__rlshift__', '__rmatmul__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__ror__', '__rpow__', '__rrshift__', '__rshift__', '__rsub__', '__rtruediv__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__setstate__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__truediv__', '__xor__', 'all', 'any', 'argmax', 'argmin', 'argpartition', 'argsort', 'astype', 'base', 'byteswap', 'choose', 'clip', 'compress', 'conj', 'conjugate', 'copy', 'ctypes', 'cumprod', 'cumsum', 'data', 'diagonal', 'dot', 'dtype', 'dump', 'dumps', 'fill', 'flags', 'flat', 'flatten', 'getfield', 'imag', 'item', 'itemset', 'itemsize', 'max', 'mean', 'min', 'nbytes', 'ndim', 'newbyteorder', 'nonzero', 'partition', 'prod', 'ptp', 'put', 'ravel', 'real', 'repeat', 'reshape', 'resize', 'round', 'searchsorted', 'setfield', 'setflags', 'shape', 'size', 'sort', 'squeeze', 'std', 'strides', 'sum', 'swapaxes', 'take', 'tobytes', 'tofile', 'tolist', 'tostring', 'trace', 'transpose', 'var', 'view'] >>> b = [0, 0, 0] >>> b [0, 0, 0] >>> print(b) [0, 0, 0] >>> type(b) list
2. Array
Array(배열)은
1. 순서가 있는(Sequence)
2. 같은 종류의 데이터가 저장된(Homogeneous)
3. 값을 변경할 수 있는(Mutable)
집합이다.
NumPy에서는 ndarray를 사용하는데, N-dimensional array type을 의미한다. ndarray의 모든 값은 같은 크기의 메모리 영역에 저장된다.
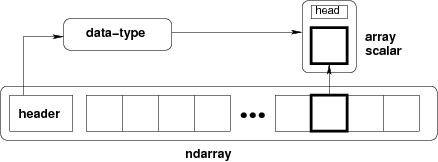
array는 대괄호의 개수로 몇 차원 배열인지 알 수 있다.
Vector
1차원 배열(1D array)을 의미한다.
>>> vector = np.array([0, 1, 2, 3]) >>> vector array([0, 1, 2, 3]) >>> print(vector) [0 1 2 3]
Matrix(행렬)
2차원 배열(2D array)을 의미한다.
>>> matrix = np.array([[0, 1], [2, 3]]) >>> matrix array([[0, 1], [2, 3]]) >>> print(matrix) [[0 1] [2 3]]
Tensor
3차원(3D array) 이상의 배열을 의미한다.
>>> tensor = np.array([[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]]) >>> tensor array([[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]]) >>> print(tensor) [[[0 1 2] [3 4 5] [6 7 8]]]
array([3, 2])는 3행(row) 2열(column)을 의미한다. 동시에 좌표평면 상에서는 (2, -3)으로 표현할 수 있다. 이때 y를 음수로 표기하는 이유는 배열이 위에서 아래로 출력되기 때문에 보는 것과 동일하게 만들기 위함이다.
3. NumPy 특징
- 같은 Data type(자료형)만을 처리할 수 있다. 특히 NumPy는 수치 연산을 위해 사용하는 도구이므로 일반적으로 숫자를 사용한다.
# 문자와 숫자가 혼합되어 있는 경우 모두 문자로 형변환하여 저장된다. >>> arr = np.array([1, '2', True]) >>> arr array(['1', '2', 'True'], dtype='<U21') >>> for i in arr: print(type(i)) <class 'numpy.str_'> <class 'numpy.str_'> <class 'numpy.str_'>
-
str(문자열)을 unsigned int(부호가 없는 정수형)으로 처리한다.
>>> np.array(["ab", "cd"]).dtype dtype('<U2') -
bytes(character)는 str(문자열)로 처리하낟.
>>> np.array([b'a', b'b']).dtype dtype('S1')
4. NumPy 데이터 형식
| dtype | type code | descrition |
|---|---|---|
| int8 | i1 | 부호 있는 8비트 정수형 |
| int16 | i2 | 부호 있는 16비트 정수형 |
| int32 | i4 | 부호 있는 32비트 정수형 |
| int64 | i8 | 부호 있는 64비트 정수형 |
| unit8 | u1 | 부호 없는 8비트 정수형 |
| unit16 | u2 | 부호 없는 16비트 정수형 |
| unit32 | u4 | 부호 없는 32비트 정수형 |
| unit64 | u8 | 부호 없는 64비트 정수형 |
| float16 | f2 | 실수형 ; 반 정밀도 부동소수점형 (부호 1비트, 지수 5비트, 가수 10비트) |
| float32 | f4 | 실수형; 단 정밀도 부동소수점형 (부호 1비트, 지수 8비트, 가수 23비트) |
| float64 | f8 | 실수형; 배 정밀도 부동소수점형 (부호 1비트, 지수 11비트, 가수 54비트) |
| float128 | f16 | 실수형; 네배 정밀도 부동소수점형 (부호 1비트, 지수 15비트, 가수 112비트) |
| complex64 | c8 | 복소수 (실수부, 허수부 각각float32) |
| complex128 | c16 | 복소수 (실수부, 허수부 각각float64) |
| complex256 | c32 | 복소수 (실수부, 허수부 각각float128) |
| bool | b | True or False |
| string | S | (byte) string |
| unicode | U | unicode |
| object | O | python object(객체) |
| date | M | datetime(날짜) |
![array([3, 2])](https://velog.velcdn.com/images%2Fkkiyou%2Fpost%2F8d4aa711-7ad6-4442-bf1c-1570ac8d7543%2F3%20by%203%20array.png)