GPU안에 있는 작은 프로그램을 shader라고 한다. 이 프로그램들, 즉 shader들은 그래픽스 파이프라인의 각 특정 부분에서 동작한다. shader들은 입력값들을 출력값으로 변환해주는 프로그램일뿐 그이상이 아니다. shader들은 서로 input과 output을 통해서만 통신할 뿐 그외는 허용되지 않으므로 고립되어있다.
GLSL
shader들은 C형식의 언어 GLSL로 쓰여졌다. GLSL은 그래픽스 사용에 맞춰져있으며 특히 벡터와 행렬 조작에 특화된 유용한 기능들을 가지고 있다.
shader들은 항상 버전 선언으로 시작 그다음 input, output 변수들, 그리고 uniform들과 main함수가 나온다. 각 shader의 entry point는 main함수이며 이 함수에서 output 변수에 input 변수를 처리한 출력의 결과물을 대입한다.
#version version_number
in type in_variable_name;
in type in_variable_name;
out type out_variable_name;
uniform type uniform_name;
void main()
{
// process input(s) and do some weird graphics stuff
...
// output processed stuff to output variable
out_variable_name = weird_stuff_we_processed;
}이제 vertex shader에 대해 얘기하자면, 각 input 변수는 vertex attribute라 알려져있다. 이 vertex attribute의 최대수는 하드웨어에 정해져있다. OpenGL은 항상 최소 16, 4개의 component vertex attributes를 보장한다. GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS로 현재 하드웨어의 최대허용치를 검색할 수 있다.
int nrAttributes;
glGetIntegerv(GL_MAX_VERTEX_ATTRIBS, &nrAttributes);
std::cout << "Maximum nr of vertex attributes supported: " << nrAttributes
<< std::endl;데이터 타입
GLSL의 대부분의 데이터 타입은 C 형태의 언어의 데이터 타입을 가진다.
- int, float, double, uint 그리고 bool
또한 벡터와 행렬을 사용하는 두 가지 컨테이너 타입을 가지고 있다.
vector
N은 차원을 나타낸다. e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4.
- vecN - the default vector of N floats
- bvenN - a vector of N booleans
- ivecN - a vector of N integers
- uvecN - a vector of N unsigned integers
- dvecN - a vector of N double components
기본 vecN 형식을 가장 많이 사용하며 거의 모든 작업을 하기에 충분하다.
각 component에 접근하는 방식은 ‘.’을 사용한다. e.g. vec.x, vec.y, vec.z, vec.w
- xyzw == rgba(색상) == stpq(texture coordinate, 텍스쳐 좌표계)
벡터 데이터 타입은 swizzling을 통해 component 선택을 할 수 있다.
vec2 someVec;
vec4 differentVec = someVec.xyxx;
vec3 anotherVec = differentVec.zyw;
vec4 otherVec = someVec.xxxx + anotherVec.yxzy;또한 이 문자들을 조합하여 벡터 타입을 생성시 사용 가능할 수 있다.
vec2 vect = vec2(0.5, 0.7);
vec4 result = vec4(vect, 0.0, 0.0);
vec4 otherResult = vec4(result.xyz, 1.0);Ins and Outs
GLSL은 in과 out 키워드를 이용하여 각 shader들이 주고 받을 수 있게 정의했다. 각 shader들은 이 키워드로 inputs과 outputs을 명시하고 output 변수와 다음 shader 단계의 input과 매칭되는 변수로 전달할 수 있다.
vertex shader는 input의 몇가지 형식을 받아야한다. 그렇지 않으면 좀 비효율적이다. vertex shader가 input과 다르다면 vertex data로부터 곧장 input을 받는 점이다. vertex data를 어떻게 정리할지 정의하기 위해서 location metadata와 함께 input 변수를 명시하여 CPU에 vertex attributes를 설정할 수 있다. layout(location = 0)처럼 vertex shader는 input에 관한 layout 명시를 요구하며 이는 vertex data와 연결할 수 있다.
layout(location = 0) 을 생략 가능하며 glGetAttribLocation 함수로 attribute location에 관해 OpenGL으로부터 질의하여 답을 구할 수 있다. 다만 이는 더 많은 작업이 요구된다.
또 fragment shader는 vec4 색상 output 변수가 필요하다. 이는 fragment shader가 최종 색상 값을 출력해야기 때문이다. 만약 없다면 그 fragment에 관한 색상 버퍼 출력은 undefined(여기서 검정색이나 하얀색이 그려진다)
하나의 shader로부터 out 키워드로 정의된 변수의 데이터를 다른 shader에서 in 키워드로 정의된 데이터가 보내지는데 두 변수명은 같아야한다.
// vertex shader
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos; // position has attribute position 0
out vec4 vertexColor; // specify a color output to the fragment shader
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos, 1.0); // we give a vec3 to vec4’s constructor
vertexColor = vec4(0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // output variable to dark-red
}// fragment shader
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec4 vertexColor; // input variable from vs (same name and type)
void main()
{
FragColor = vertexColor;
}코드에서 vertex shader에서 out 키워드로 선언된 vertexColor는 fragment shader에서 in 키워드로 선언된 vertexColor와 연결된다.
result
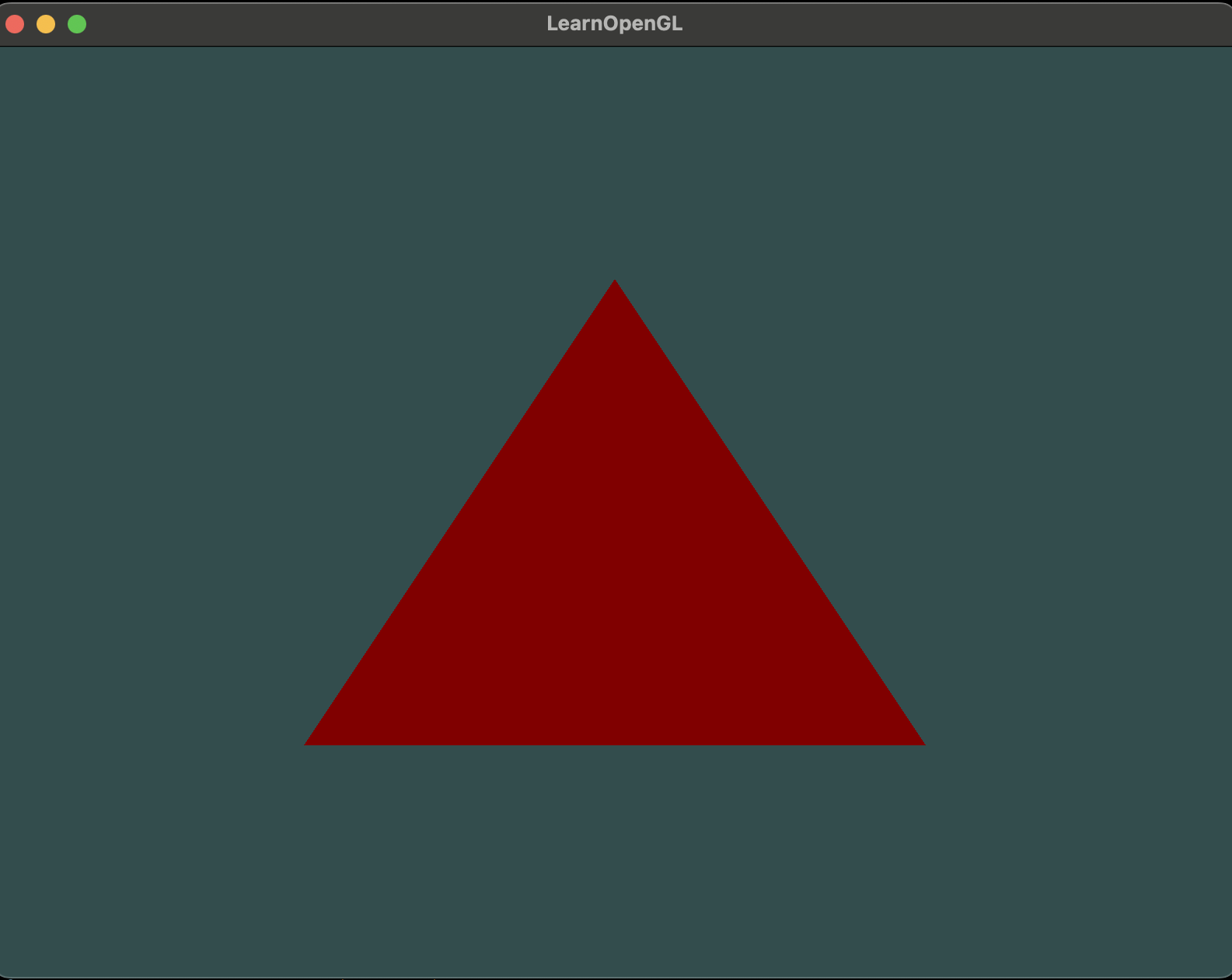
Uniforms
CPU에 있는 application으로부터 GPU에 있는 shader로 데이터를 전달하는 또 다른 방식. uniform은 vertex attributes와 비교하여 약간의 차이가 있다. 첫번째로 uniforms은 global 변수이다. uniform 변수는 shader 프로그램 전 단계에서 각 shader가 접근 가능하다. 두번째로 uniform 값을 설정하면 그 값이 재설정되거나 업데이트될 때까지 유지된다.
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
uniform vec4 ourColor; // we set this variable in the OpenGL code.
void main()
{
FragColor = ourColor;
}이제 OpenGL 코드에서 어떻게 하는지 보면
float timeValue = glfwGetTime();
float greenValue = (sin(timeValue) / 2.0f) + 0.5f;
int vertexColorLocation = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "ourColor");
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glUniform4f(vertexColorLocation, 0.0f, greenValue, 0.0f, 1.0f);먼저 glfwGetTime()를 통해서 running time을 찾고 색상 범위는 sin함수를 통해 -1.0 ~ 1.0 사이로 만들고 2.0f로 나누고 0.5f를 더하면 0.0 ~ 1.0사이로 변화를 주고 그 값을 greenValue에 저장한다. glGenUniformLocation 함수를 사용하여 ourColor uniform의 위치를 질의하며 그 위치를 vertexColorLocation에 저장한다. glGenUniformLocation 함수가 -1을 리턴하면 두번째 인자명의 uniform 변수를 찾지 못한 것. 마지막으로 glUniform4f 함수를 통하여 uniform 값을 설정. uniform location을 찾는 것은 shader program을 먼저 사용하는 것을 요구하는게 아니라 uniform을 변경하는 것이 프로그램을 먼저 사용하는 것(glUseProgram 호출)을 요구하는 것. 왜냐하면 이는 현재 활성화된 shader program에서 uniform을 설정하기때문.
OpenGL은 그 내부(core)는 C library이기에 함수 오버로딩 지원을 하지않으므로 OpenGL은 새로운 함수들은 각 타입에 맞게 정의되어있고 그 타입에 맞게 호출되어야한다. glUniform 이 최적의 예시이다. 이 함수는 어떤 타입으로 uniform을 설정할 것인지 함수명에 접미사를 붙여야한다.
- f - float
- i - int
- ui - unsigned int
- 3f - 3 floats; Nf - N floats
- fv - float vector/array
위 코드를 render loop안 glUseProgram와 glBindVertexArray(VAO)사이에 넣으면 삼각형 색이 반복적으로 시간에 따라 초록색에서 점점 검정색으로 되었다가 다시 초록색으로 바뀌는 것을 볼 수 있다.
More attributes
다시 VAO와 VBO를 사용하여 색상값을 설정해보자. 아래와 같이 삼각형의 각 꼭지점을 표현하는 vertices 뒤에 RGB 색상값을 추가.
float vertices[] = {
// positions // colors
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // bottom left
0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // top
};이제 vertex shader에 더 많은 데이터를 전달하기때문에 vertex shader를 수정해야한다. 아래의 코드로 수정한다.
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos; // position has attribute position 0
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aColor; // color has attribute position 1
out vec3 ourColor; // output a color to the fragment shader
void main()
{
gl_Position = vec4(aPos, 1.0);
ourColor = aColor; // set ourColor to input color from the vertex data
}layout specifier와 함께 aColor attribute의 location을 설정
아래는 fragment shader로 uniform으로 지정한 변수를 in으로 하여 vertex shader로부터 전달 받는다.
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
in vec3 ourColor;
void main()
{
FragColor = vec4(ourColor, 1.0);
}위와 같이 vertex attribute를 추가하였고 VBO memory를 수정했으므로 vertex attribute pointer를 재설정해야한다. 업데이트된 VBO 메모리는 아래와 같을 것이다.
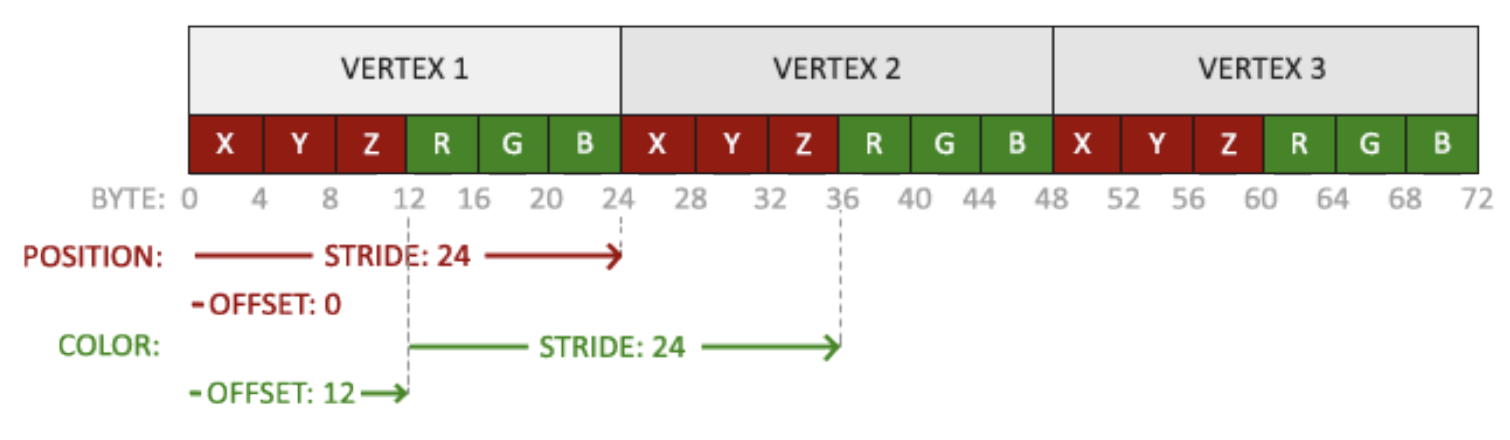
위와 같이 코드를 수정하면
// position attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float),
(void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// color attribute
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 6 * sizeof(float),
(void*)(3* sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);달라진 점은 VBO의 vertices에 따라 location이 추가됨에따라 glVertexAttribPointer 함수와 glEnableVertexAttribArray 함수 각각 하나씩 더 추가되었고, 첫번째 glVertexAttribPointer에서 수정한 부분은 5번째 인자의 stride 부분을 수정했다. 위치에 맞게 색상값을 건너뛰게 24바이트로 설정. 두번째 location 1 색상값을 설정하기 위해서 첫번째 인자는 1 그리고 위와 마찬가지로 stride 부분을 24바이트로 설정, 마지막 인자는 offset으로 색상 attribute가 위치 데이터 뒤에 시작하므로 12바이트로 설정.
result

설정해준 부분을 보면 삼각형의 세꼭지점의 지점과 그 지점의 색상값이다. 위 결과물을 보면 세꼭지점에서 중점으로 오면서 색상이 변한다. 이는 fragment shader에서 fragment interpolation으로 불리는 것의 결과다. 실제 삼각형을 렌더링할 때 rasterization 단계에서 원래 명시했던 vertices보다 더 많은 fragment들을 낳는다. rasterizer는 fragment가 삼각형 모양에 속하는 것을 토대로 각각의 fragment의 위치를 결정, 이 위치에 따라서 fragment shader의 input 변수 모두 interpolate(보간)한다.
나머지 부분들은 책에서 나오듯이 shader 클래스를 만들고 메인에서 코드 정리하면된다.
책에서 제공하는 코드도 참고하여 변경하면 된다.
