알고있었던 것
JPA에서 영속성 컨텍스트라고 하여 1차 캐시, 쓰기 지연, 변경 감지 등의 장점을 가지고 있다.
쓰기 지연, 변경 감지는 트랜잭션을 커밋하면 엔티티 매니저에서 영속성 컨텍스트를 플러시하며 DB에 동기화하게 된다.
Transaction 밖에서도 계속 변경 감지를 하는 것 처럼 select + update query가 발생해 찾아보던 중 OSIV에 대해 알게되었다.
OSIV
Open Session In View : 영속성 컨텍스트 뷰를 열어둔다.
영속성 컨텍스트가 살아있으면 Entity는 영속 상태로 유지된다.
- 이전에 요청당 트랜잭션 방식의 OSIV였으나 Presentation layer에서 Entity를 변경할 수 있다는 문제로 인해 최근에는 거의 사용하지 않는다.
- Spring framework가 제공하는 OSIV는
비지니스 계층에서만 트랜잭션을 유지하는 방식이다.
비지니스 계층 트랜잭션 동작 원리
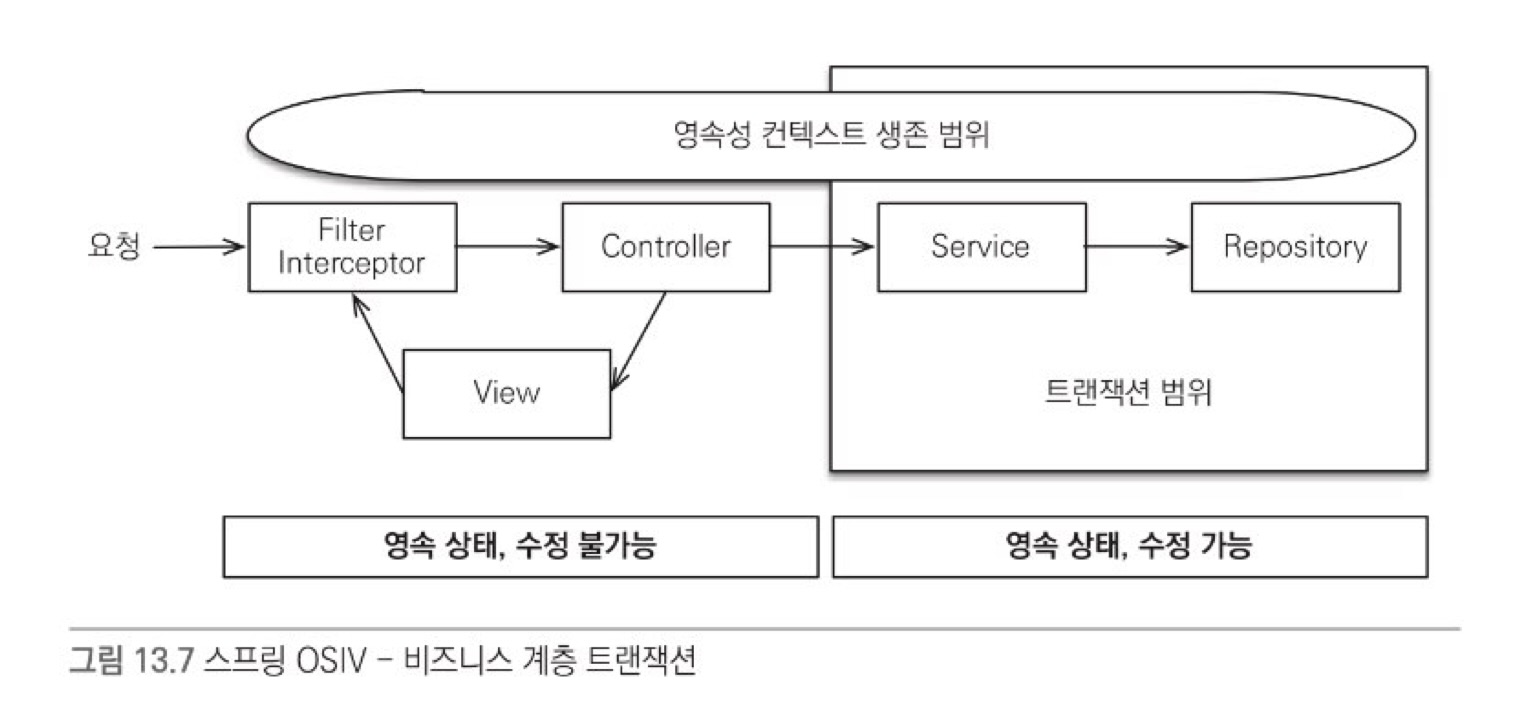
- 클라이언트의 요청이 들어오면 Filter, Interceptor에서 영속성 컨텍스트를 생성한다.
- transaction은 시작하지 않는다.
- 서비스 계층에서 @Transactional로 트랜잭션을 시작할 때 1번에서 미리 생성해둔 영속성 컨텍스트를 찾아와서 트랜잭션을 시작한다.
- 서비스 계층이 끝나면 트랜잭션을 커밋하고 영속성 컨텍스트를 flush
- Transaction은 끝내지만 영속성 컨텍스트는 종료하지 않는다.
- 컨트롤러와 뷰까지 영속성 컨텍스트가 유지되므로 조회한 엔티티는 영속 상태를 유지한다.
- 필터, 인터셉터로 요청이 돌아오면 영속성 컨텍스트를 종료한다.
- flush 호출 없이 바로 종료한다.
여기서 영속성 컨텍스트를 통한 모든 편경은 트랜잭션 안에서만 이루어져야 하는데,
프레젠테이션 계층에서는 transaction이 없으므로 Entity를 수정할 수 없고 조회만 가능하다.
내가 겪었던 상황
class MyService{
public void update(List<Integer> ids){
List<Content> contents = externalApi.get(ids);
contentRepository.saveAll(contents); // (1)
List<Picture> pictures = pictureRepository.findAllByIds(ids); // (2)
String url = pictures.get(0).getUrl();
// etc.. (3)
}
}
위의 코드에서 contents를 saveAll (1) 이후에 전혀 건드리지 않았으나 계속 dirty checking을 하고있었다.
update method을 @Transactional 처리하지 않았는데 왜 그 이후의 코드를 수행할 때 마다 dirty checking을 하게되는지 이해하지 못했다.
OSIV로 인해 영속성 컨텍스트가 살아있다면, (1) 이후에 (2), (3) 위치에서 repository를 사용하면서 트랜젝션이 계속 발생하게 되고, 비록 다른 트랜젝션으로 분리되어 있으나 하나의 영속성 컨텍스트를 공유하고 있다.
(1) 이후 다른 트랜잭션을 커밋하면서 변경 감지가 동작하게 된 것이다.
별도 값을 수정은 하지 않았지만 Entity column이 Object type이라 Object.equals로 비교를 하면서 영속성 컨텍스트와 다르다고 판단해 변경되었다고 판단했다.
이부분도 미쳐 생각하지 못한 부분이긴 했지만 이번 글의 주제는 아니다.
(@EqualsAndHashCode 에 대한 글 참고 : https://jojoldu.tistory.com/536)
책에서도 엔티티를 수정한 직후에 트랜잭션을 시작하는 서비스 계층을 호출하면 문제가 발생하기 때문에 엔티티를 변경하는 경우 비지니스 로직을 먼저 전부 다 호출하라고 하고있다.
참고로 OSIV는 default true로 되어있다.
스프링 OSIV의 단점
- 같은 영속성 컨텍스를 여러 트랜잭션이 공유할 수 있다는 점을 주의해야한다.
- 프레젠테이션 계층에서 엔티티를 수정하고 나서 비지니스 로직을 수행하면 엔티티가 수정될 수 있다.
- 프레젠테이션 계층에서 지연 로딩에 의한 쿼리가 수행될 수 있어 성능 튜닝 시에 확인해야할 부분이 넓다.
- 영속성 컨텍스트가 사라지면서 DB connection을 반환하는데, 너무 오랜시간 데이터베이스 커넥션을 사용하면서 커넥션이 전체적으로 부족할 수 있다.
- 요청이 많지 않은 간단한 서비스나 커넥션을 많이 사용하지 않은 곳에서는 OSIV true
- 실시간 서비스에서는 OSIV false를 권장
OSIV 구현 열어보기
원리는 책을 찾아보고 이해했는데 실체가 궁금해서 코드 레벨에서 한번 찾아봤다.
Spring framework가 제공하는 OSIV 라이브러리
- spring framework의 spring-orm.jar는 다양한 OSIV 클래스를 제공한다.
- OSIV를 서블릿 필터에서 적용할지 스트링 인터셉터에서 적용할지에 따라 원하는 클래스에서 선택하여 사용할 수 있다.
- 하이버네이트 OSIV 서블릿 필터
- 하이버네이트 OSIV 스프링 인터셉터
- JPA OEIV 서블릿 필터
- JPA OEIV 스프링 인터셉터
코드 실제로 확인해보기
spring-configuration-metadata.json
- 앞서 OSIV default가 true라고 해서 찾아보니 meta data file에 true로 저장되어있었다.
{
"name": "spring.jpa.open-in-view",
"type": "java.lang.Boolean",
"description": "Register OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor. Binds a JPA EntityManager to the thread for the entire processing of the request.",
"sourceType": "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties",
"defaultValue": true
}JpaBaseConfiguration
spring.jpa.open-in-view가 true인 경우 아래 Configuration에서 OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor를 빈으로 생성하고 Interceptor에 등록하는 부분이 나온다.
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(JpaProperties.class)
public abstract class JpaBaseConfiguration implements BeanFactoryAware {
// ~~
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(WebMvcConfigurer.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor.class, OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingFilterBean(OpenEntityManagerInViewFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.jpa", name = "open-in-view", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
protected static class JpaWebConfiguration {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(JpaWebConfiguration.class);
private final JpaProperties jpaProperties;
protected JpaWebConfiguration(JpaProperties jpaProperties) {
this.jpaProperties = jpaProperties;
}
@Bean
public OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor openEntityManagerInViewInterceptor() { // 빈 생성
if (this.jpaProperties.getOpenInView() == null) {
logger.warn("spring.jpa.open-in-view is enabled by default. "
+ "Therefore, database queries may be performed during view "
+ "rendering. Explicitly configure spring.jpa.open-in-view to disable this warning");
}
return new OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor();
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer openEntityManagerInViewInterceptorConfigurer(OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor interceptor) {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // 인터셉터 등록
registry.addWebRequestInterceptor(interceptor);
}
};
}
}
}
OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor
- WebRequestInterceptor를 상속받아 구현하고 있다.
- preHandler에서 영속성 컨텍스를 만드는 과정만 살펴보면
- getParticipateAttributeName() 메소드를 통해 영속성 컨텍스트 참여 여부를 나타내는 키 값을 얻는다.
- 영속성 컨텍스트를 생성할 EntityManagerFactory를 얻는다.
- 현재 트랜잭션에 이미 영속성 컨텍스트가 있는지 확인
- 영속성 컨텍스트가 없을 경우 새로운 영속성 컨텍스트를 생성한다.
- 새로 생성된 영속성 컨텍스트를 EntityManagerHolder에 감싸고, 이를 현재 트랜잭션에 바인딩
- EntityManagerHolder : 트랜잭션 동안의 영속성 컨텍스트 관리하고 트랜잭션 종료 시 영속성 컨텍스트의 자원을 반환한다.
- 참고 : Interceptor 동작 순서
- preHandler
- 요청 처리
- postHandler
- View 렌더링
- afterCompletion
public class OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor extends EntityManagerFactoryAccessor implements AsyncWebRequestInterceptor {
public static final String PARTICIPATE_SUFFIX = ".PARTICIPATE";
@Override
public void preHandle(WebRequest request) throws DataAccessException {
String key = getParticipateAttributeName();
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult() && applyEntityManagerBindingInterceptor(asyncManager, key)) {
return;
}
EntityManagerFactory emf = obtainEntityManagerFactory();
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.hasResource(emf)) {
// Do not modify the EntityManager: just mark the request accordingly.
Integer count = (Integer) request.getAttribute(key, WebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
int newCount = (count != null ? count + 1 : 1);
request.setAttribute(getParticipateAttributeName(), newCount, WebRequest.SCOPE_REQUEST);
}
else {
logger.debug("Opening JPA EntityManager in OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor");
try {
EntityManager em = createEntityManager();
EntityManagerHolder emHolder = new EntityManagerHolder(em);
TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(emf, emHolder);
AsyncRequestInterceptor interceptor = new AsyncRequestInterceptor(emf, emHolder);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(key, interceptor);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptor(key, interceptor);
}
catch (PersistenceException ex) {
throw new DataAccessResourceFailureException("Could not create JPA EntityManager", ex);
}
}
}
@Override
public void postHandle(WebRequest request, @Nullable ModelMap model) {
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(WebRequest request, @Nullable Exception ex) throws DataAccessException {
if (!decrementParticipateCount(request)) {
EntityManagerHolder emHolder = (EntityManagerHolder)
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(obtainEntityManagerFactory());
logger.debug("Closing JPA EntityManager in OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor");
EntityManagerFactoryUtils.closeEntityManager(emHolder.getEntityManager());
}
}
}
실행 로그
- 위의 코드에서 debug, warn으로 나오는 부분이 처음 실행 때, 요청이 들어오고 끝났을 때 로그로 남는다.
2024-01-15 18:55:10.486 DEBUG 12132 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.f.s.DefaultListableBeanFactory : Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'openEntityManagerInViewInterceptorConfigurer'
2024-01-15 18:55:10.486 DEBUG 12132 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.f.s.DefaultListableBeanFactory : Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaBaseConfiguration$JpaWebConfiguration'
2024-01-15 18:55:10.487 DEBUG 12132 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.f.s.DefaultListableBeanFactory : Autowiring by type from bean name 'org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaBaseConfiguration$JpaWebConfiguration' via constructor to bean named 'spring.jpa-org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.JpaProperties'
2024-01-15 18:55:10.487 DEBUG 12132 --- [ restartedMain] o.s.b.f.s.DefaultListableBeanFactory : Creating shared instance of singleton bean 'openEntityManagerInViewInterceptor'
2024-01-15 18:55:10.488 WARN 12132 --- [ restartedMain] JpaBaseConfiguration$JpaWebConfiguration : spring.jpa.open-in-view is enabled by default. Therefore, database queries may be performed during view rendering. Explicitly configure spring.jpa.open-in-view to disable this warning
// 요청이 들어왔을 때
2024-01-15 18:57:08.970 DEBUG 12132 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] s.w.s.m.m.a.RequestMappingHandlerMapping : Mapped to TestController
2024-01-15 18:57:08.970 DEBUG 12132 --- [nio-8081-exec-3] o.j.s.OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor : Opening JPA EntityManager in OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor
// 비지니스 로직 수행
// ~~~
2024-01-15 18:56:29.319 DEBUG 12132 --- [nio-8081-exec-2] o.j.s.OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor : Closing JPA EntityManager in OpenEntityManagerInViewInterceptor
2024-01-15 18:56:29.320 DEBUG 12132 --- [nio-8081-exec-2] o.s.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet : Completed 200 OK참조
책 : 자바 ORM 표준 JPA 프로그래밍
https://hstory0208.tistory.com/entry/SpringJPA-OSIV-%EC%A0%84%EB%9E%B5%EC%9D%B4%EB%9E%80-%EC%96%B8%EC%A0%9C-%EC%82%AC%EC%9A%A9%ED%95%B4%EC%95%BC-%ED%95%A0%EA%B9%8C
