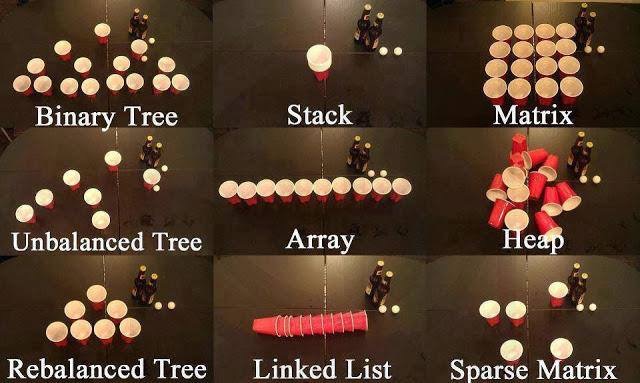
Tree
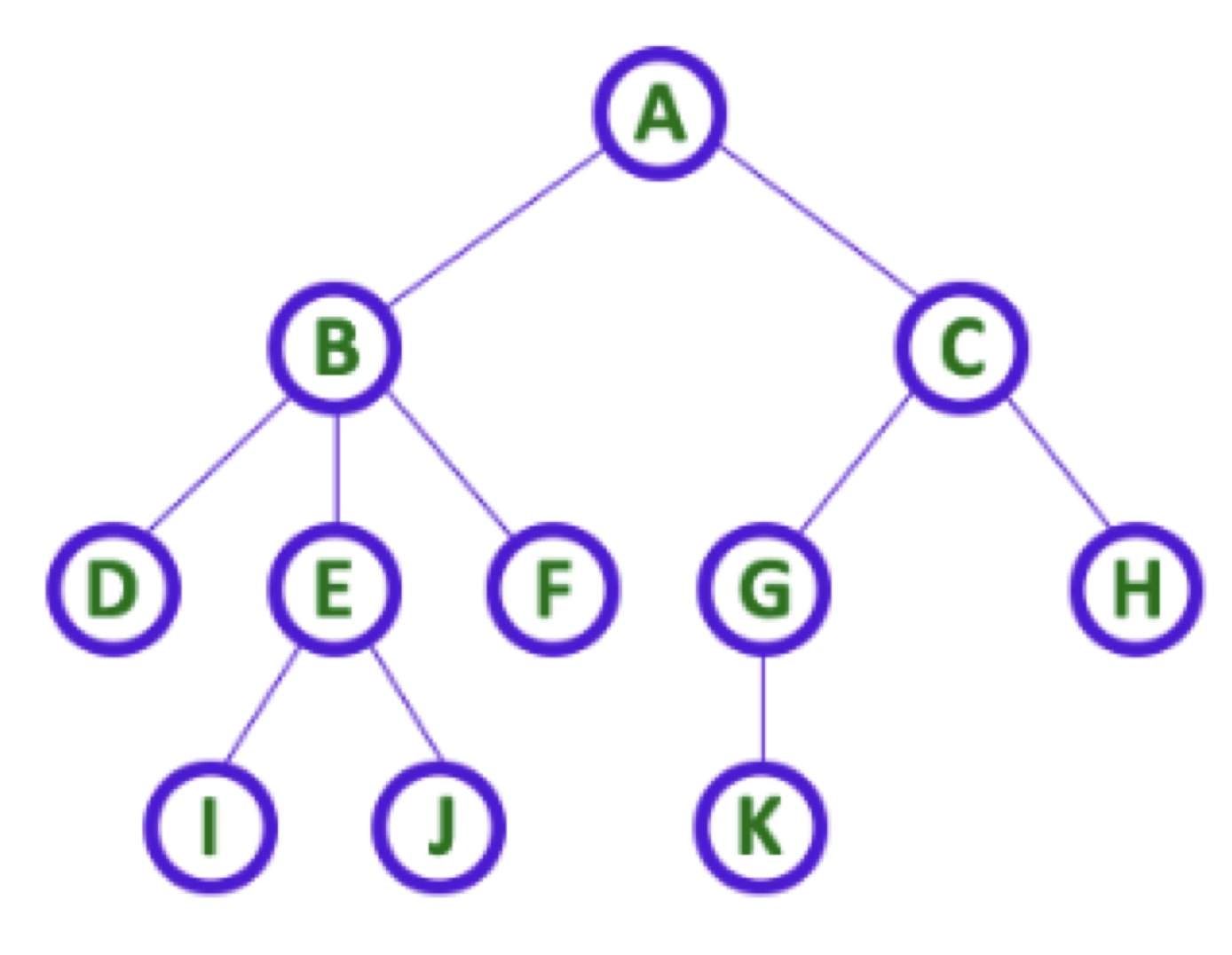
- 트리는 자료구조의 한 종류이며, 트리의 각 요소를 노드라고 부른다.
- 각 노드는 데이터를 저장하며 다음 노드를 연결한다.
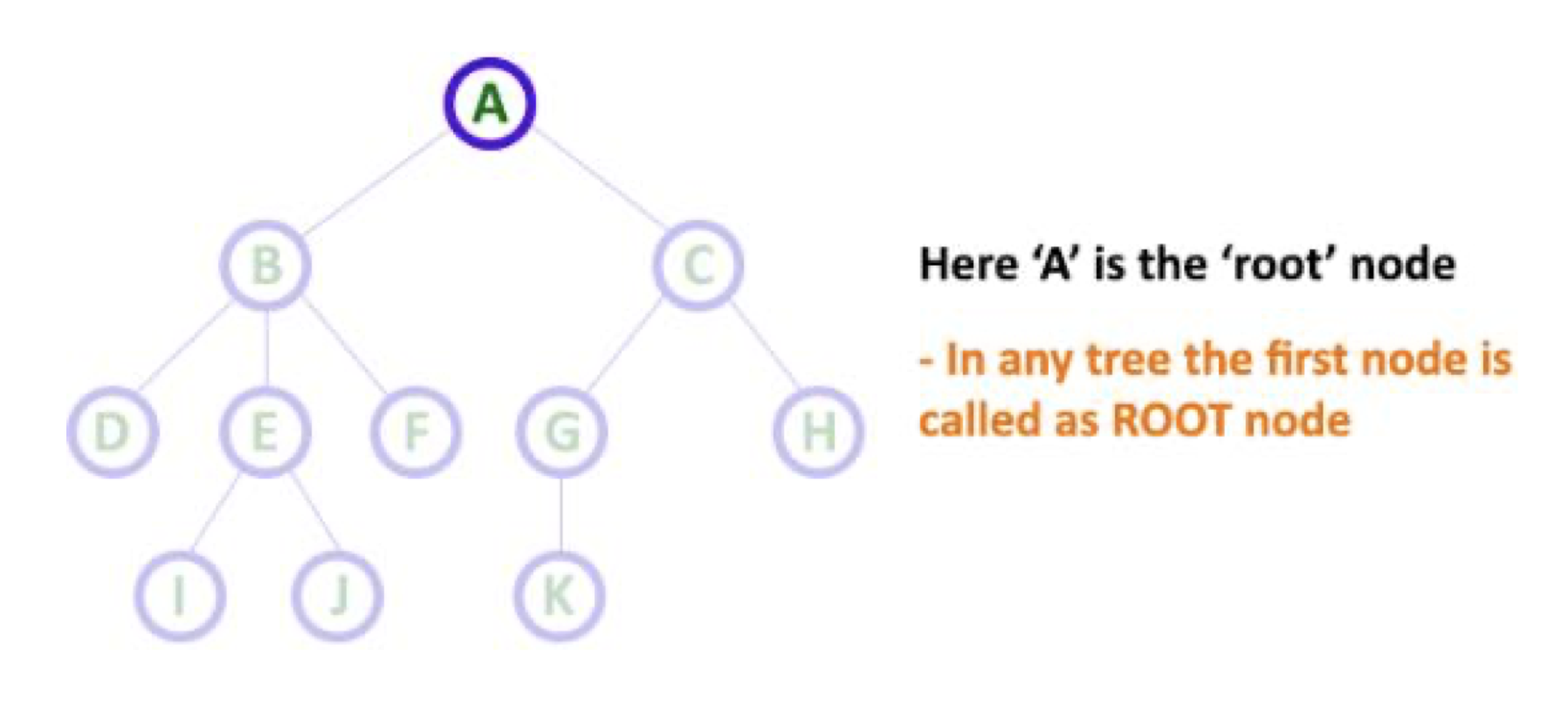
root: 트리의 맨 위에 있는 노드를 루트 노드라고 부른다.
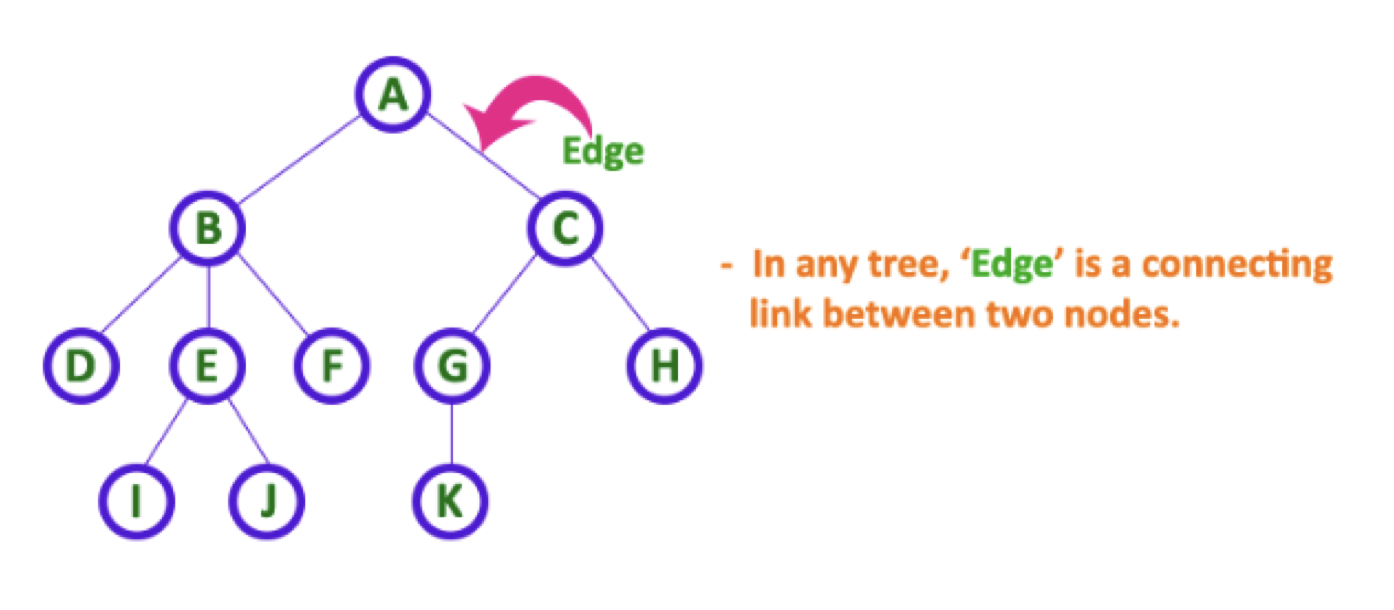
edge: 트리에서 노드와 노드 사이는 엣지로 연결되어 있다.
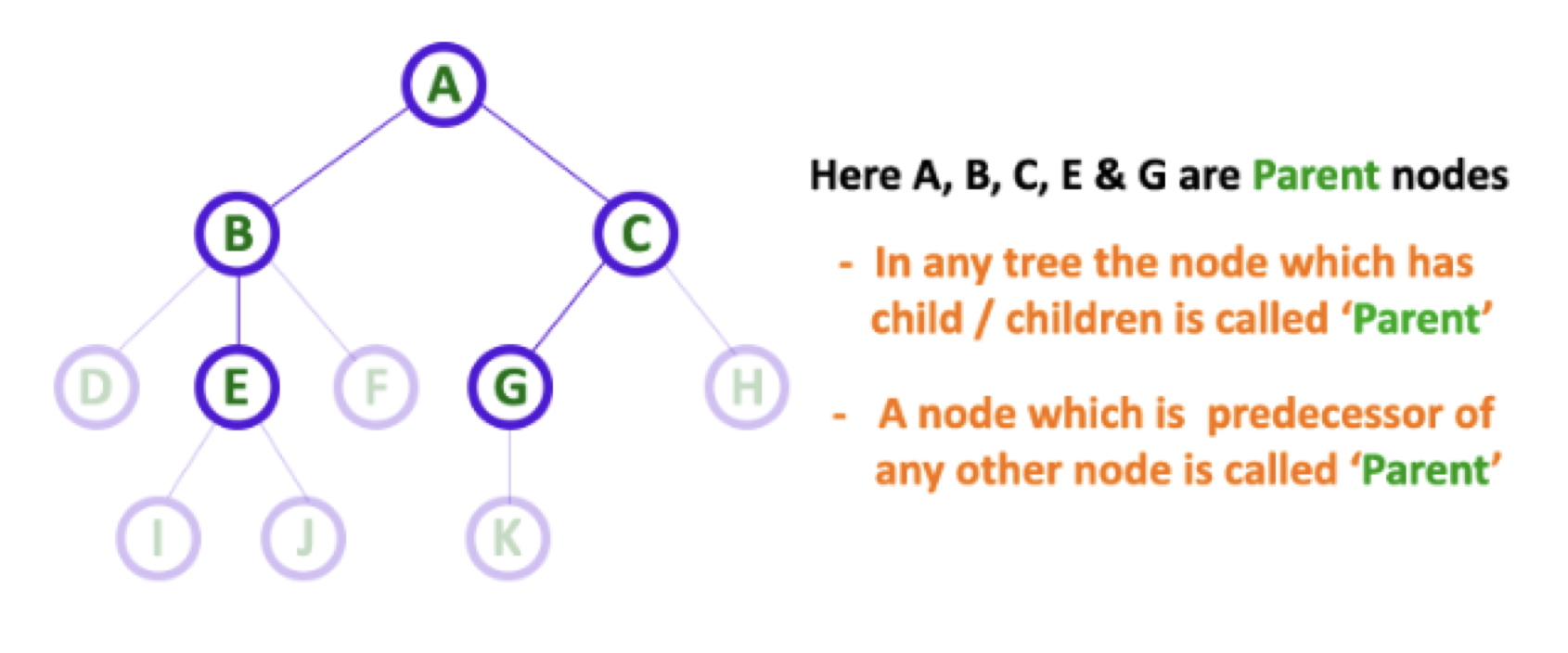
parent: 자신보다 하위 노드를 가지고 있는 노드의 경우parent라고 한다.
- 위 사진에서는
ABCEG가 부모 노드이다.
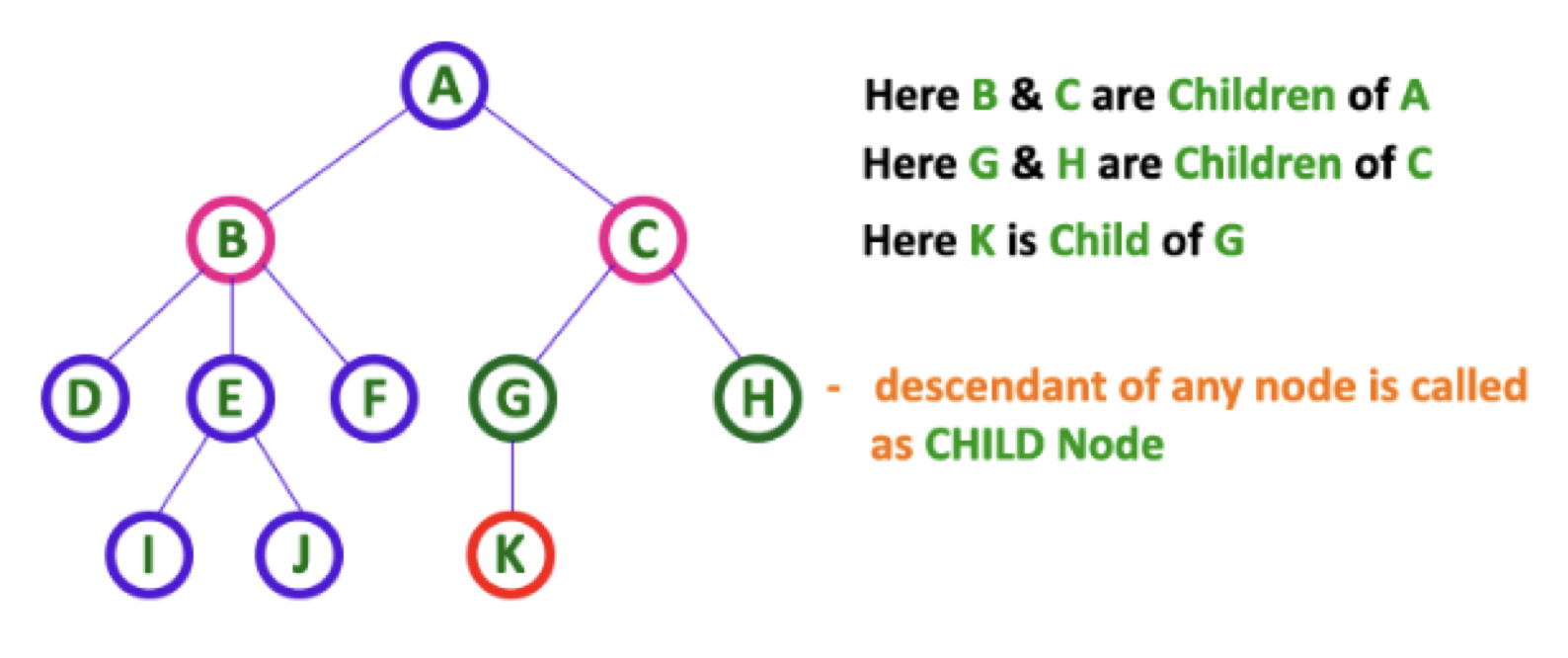
child:
BC는A의 자식 노드이다.DEF는B의 자식 노드이다.IJ는E의 자식 노드이다.GH는C의 자식 노드이다.K는G의 자식 노드이다.
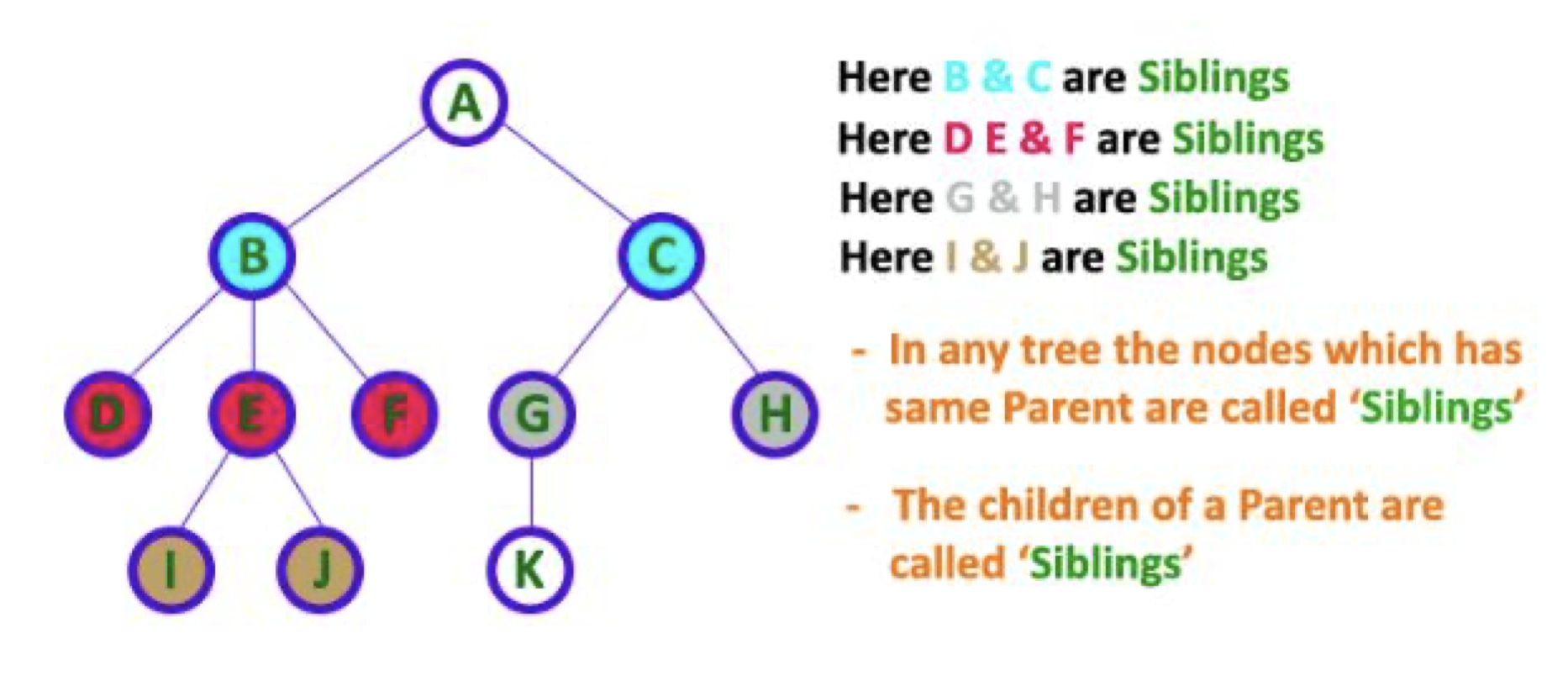
sibling: 같은 부모노드를 가지고 있는 노드들을sibling이라고 한다.- 아래 같은줄에 나오는 노드들은 서로
sibling관계이다.
BC.DEF.GH.IJ.
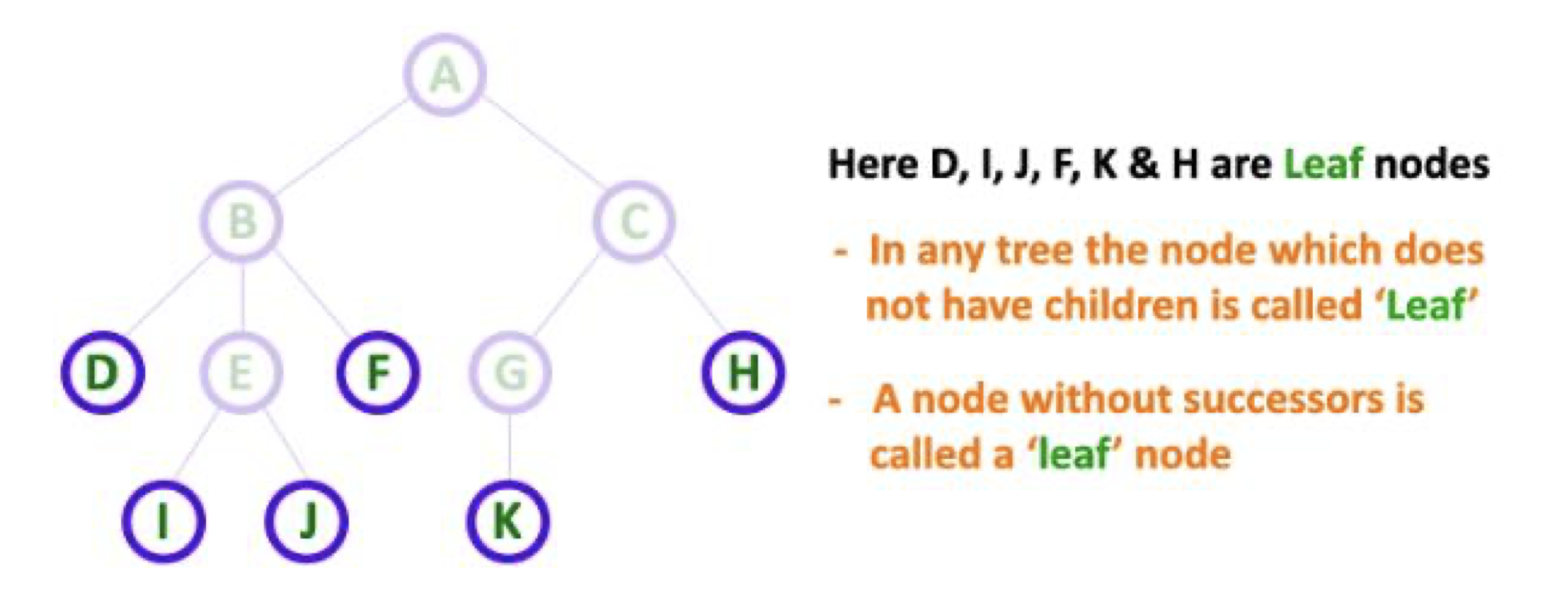
leaf: 자식 노드를 가지지 않는 노드를leaf라고 부른다.
- 후계자가 없는 노드.
DFHIJK.
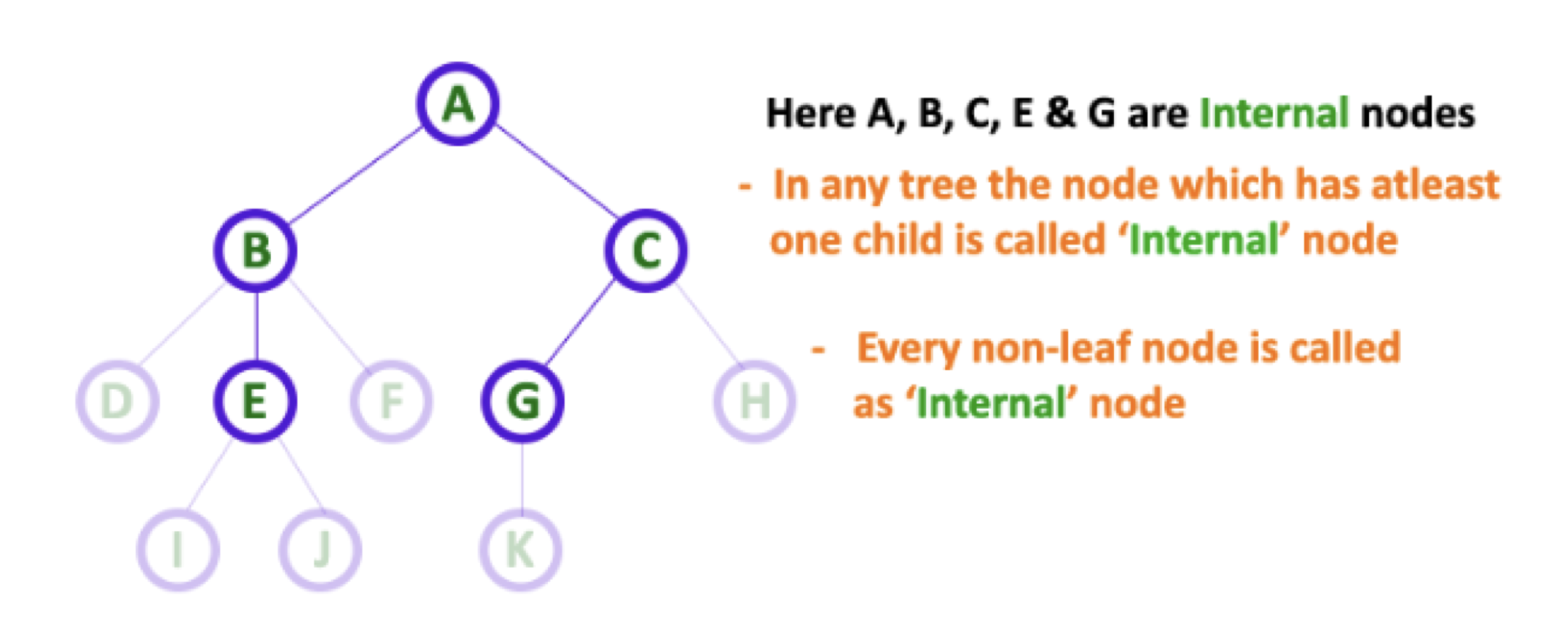
internal node: 적어도 하나 이상의 자식노드를 포함하는 노드를internal node라고 부른다.
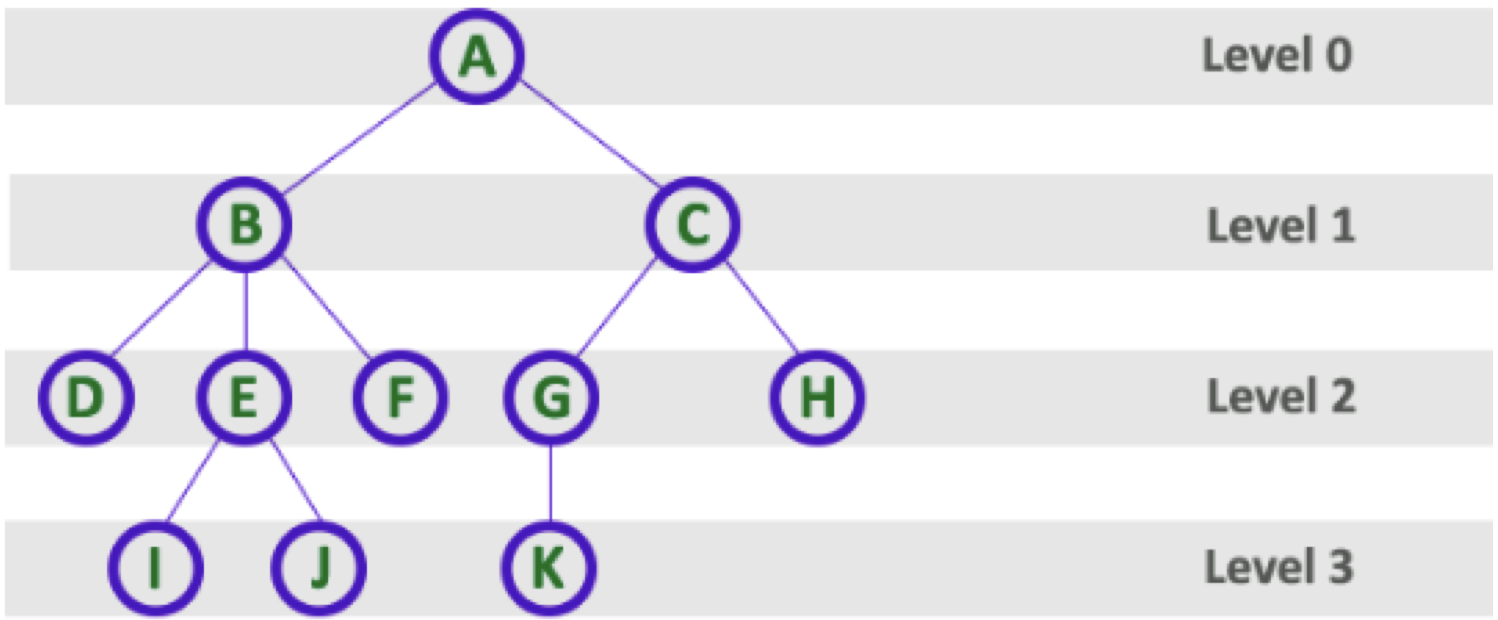
level: 루트부터 레벨0, 그 하위 단계를 레벨1, 점차 늘려나간다.
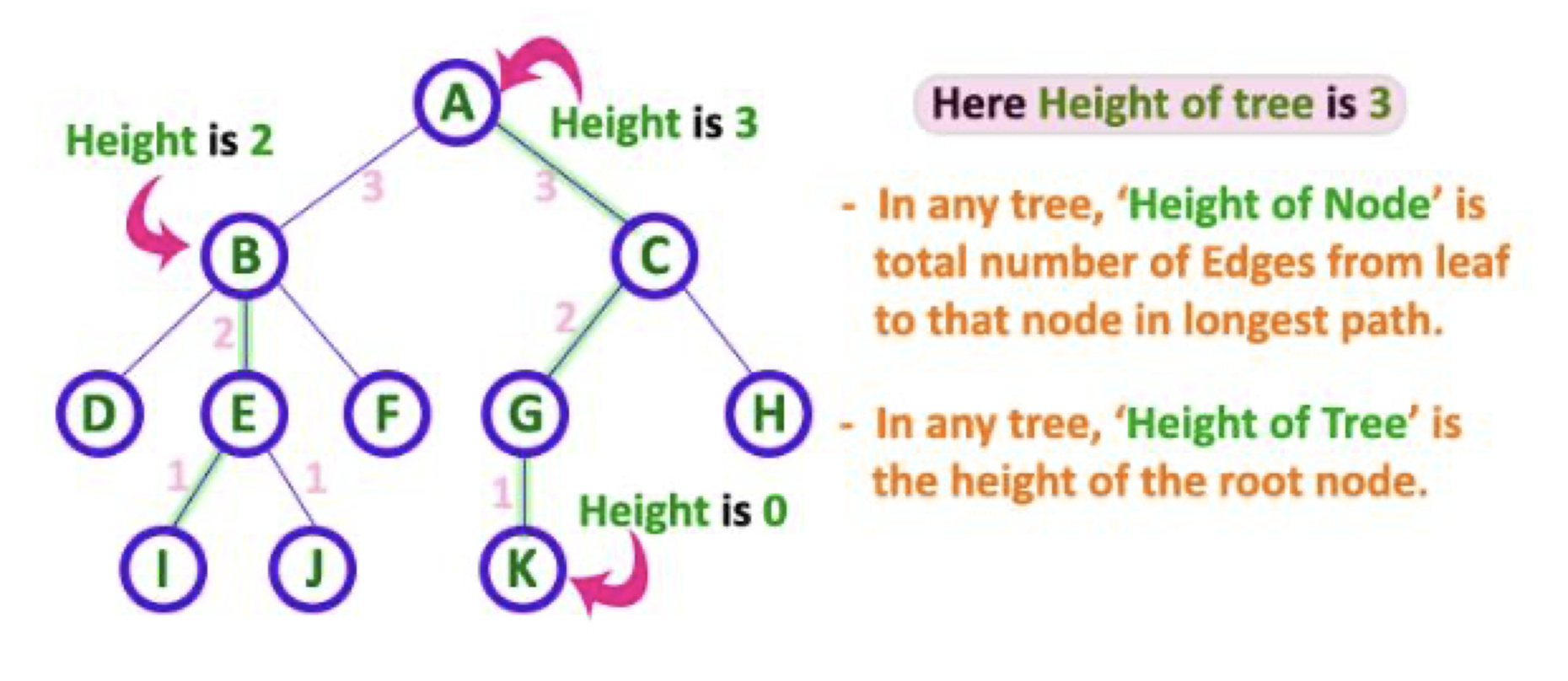
height: 레벨의 역순.
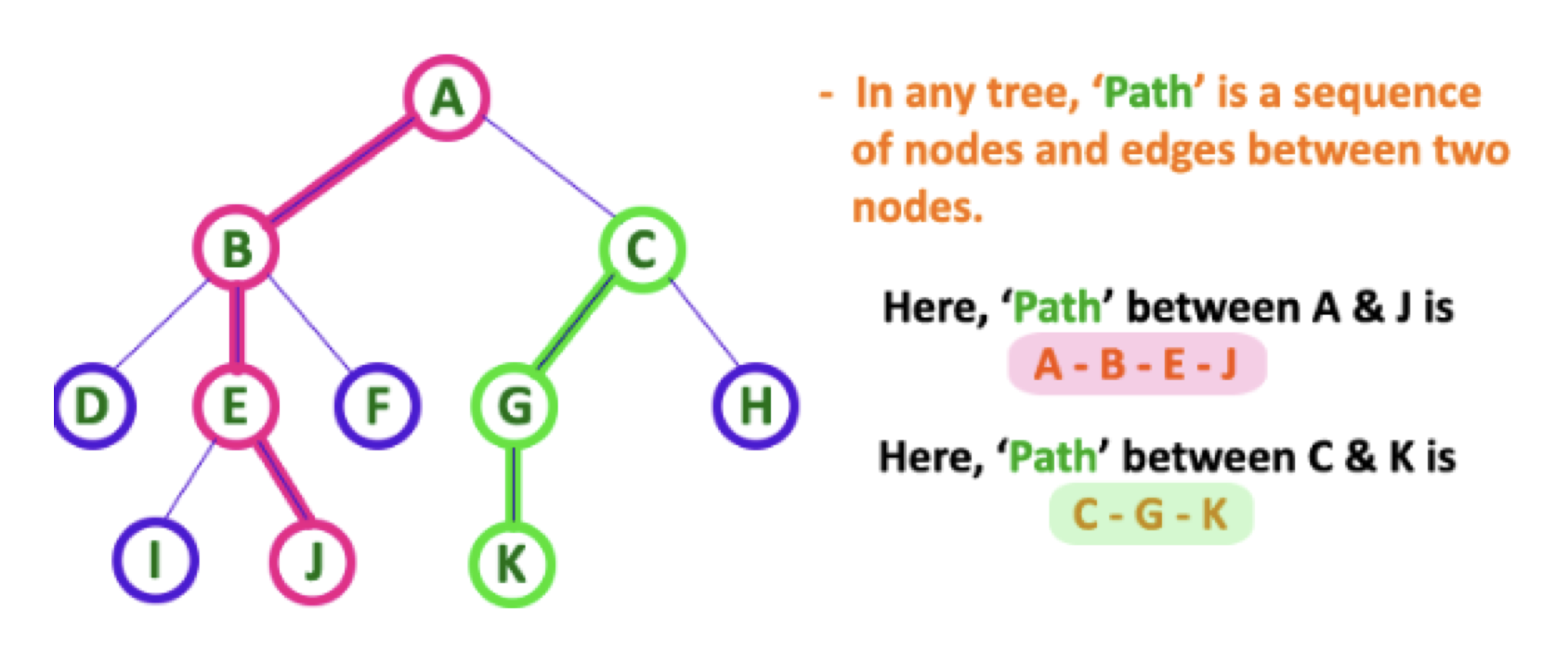
path: 노드와 노드 사이간에 나타나는 노드와 엣지의 순서.
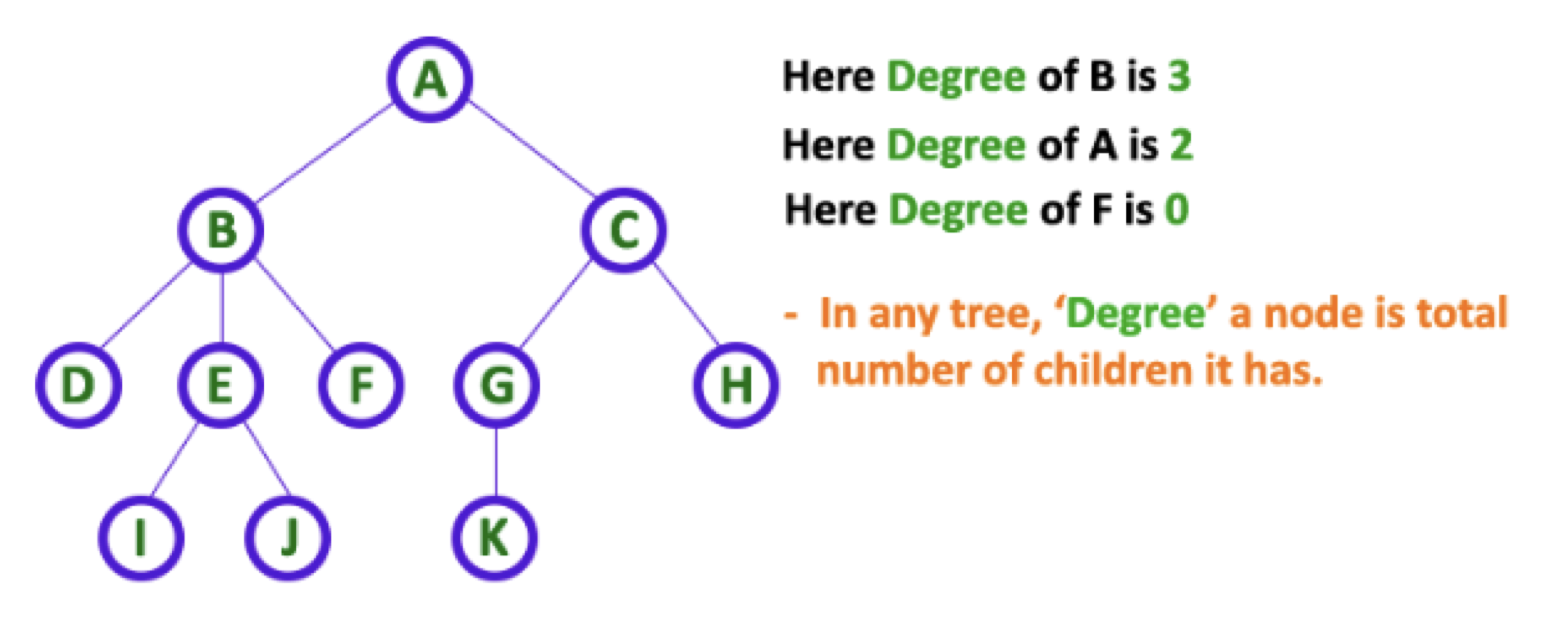
degree: 해당 노드가 포함하는 자식노드의 갯수.
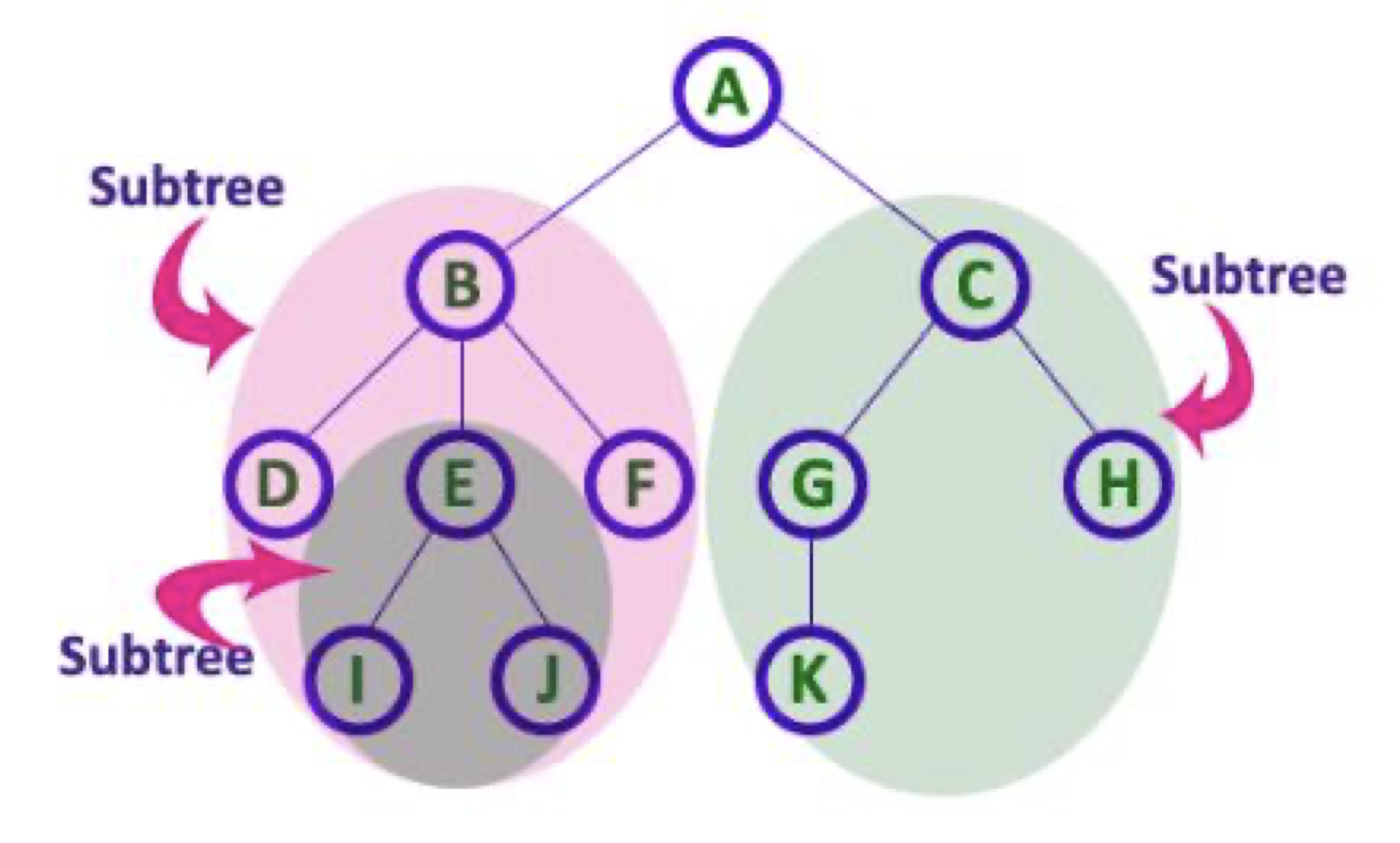
subtree: 노드의 각 자식은 재귀적으로 하위 트리를 형성한다.- 모든 자식 노드는 부모 노드에서 하위 트리를 형성한다.
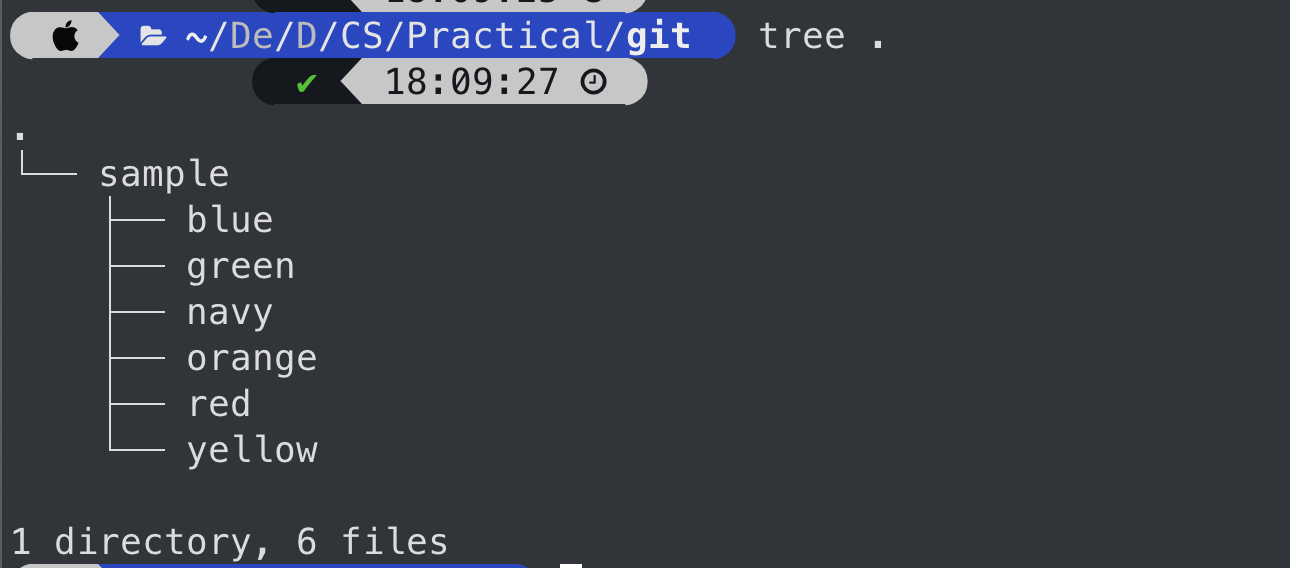
대표적인 사용 예시
- 컴퓨터 파일 매니저 시스템(디렉토리 내부 디렉토리 및 파일들)
Binary Tree
- 자식노드가 최대 두개까지 있는 트리를 이진 트리라고 부른다.
- 이때 보통 자식 노드를
left childright child라고 부른다.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
// Val is the key or the value that has to be added to the data part
Node(int val)
{
data = val;
// Left and right child for node will be initialized to null
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
int main()
{
//create root
Node* root = new Node(1);
/* following is the tree after above statement
1
/ \
NULL NULL
*/
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
/* 2 and 3 become left and right children of 1
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
NULL NULL NULL NULL
*/
root->left->left = new Node(4);
/* 4 becomes left child of 2
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 NULL NULL NULL
/ \
NULL NULL
*/
return 0;
}Implementation
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
};
Node* CreateNode(int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node();
if (!newNode) {
cout << "Memory error\n";
return NULL;
}
newNode->data = data;
newNode->left = newNode->right = NULL;
return newNode;
}
Node* InsertNode(Node* root, int data)
{
// If the tree is empty, assign new node address to root.
if (root == NULL) {
root = CreateNode(data);
return root;
}
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if (temp->left != NULL)
q.push(temp->left);
else {
temp->left = CreateNode(data);
return root;
}
if (temp->right != NULL)
q.push(temp->right);
else {
temp->right = CreateNode(data);
return root;
}
}
}
void preorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
cout << node->data << "->";
preorder(node->left);
preorder(node->right);
}
void inorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
inorder(node->left);
cout << node->data << "->";
inorder(node->right);
}
void postorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
postorder(node->left);
postorder(node->right);
cout << node->data << "->";
}
int main()
{
Node* root = CreateNode(1);
root = InsertNode(root, 2);
root = InsertNode(root, 3);
root = InsertNode(root, 4);
preorder(root);
cout<<endl;
inorder(root);
cout<<endl;
postorder(root);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}Traversal
PreOrder:root-left child-right childInOrder:left child-root-right childPostOrder:left child-right child-root
//Tree
------------------------------------------
1 //Root Node
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7 //Leaf Nodes
------------------------------------------
- PreOrder Traversal: 1-2-4-5-3-6-7
- InOrder Traversal: 4-2-5-1-6-3-7
- PostOrder Traversal: 4-5-2-6-7-3-1
void preorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
cout << node->data << "->";
preorder(node->left);
preorder(node->right);
}
void inorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
inorder(node->left);
cout << node->data << "->";
inorder(node->right);
}
void postorder(struct Node* node) {
if (node == NULL) return ;
postorder(node->left);
postorder(node->right);
cout << node->data << "->";
}