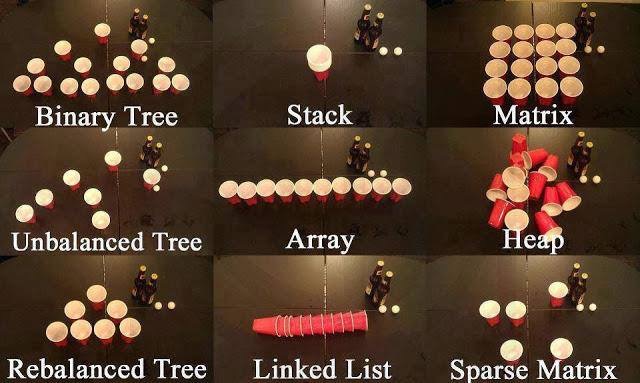
Stack
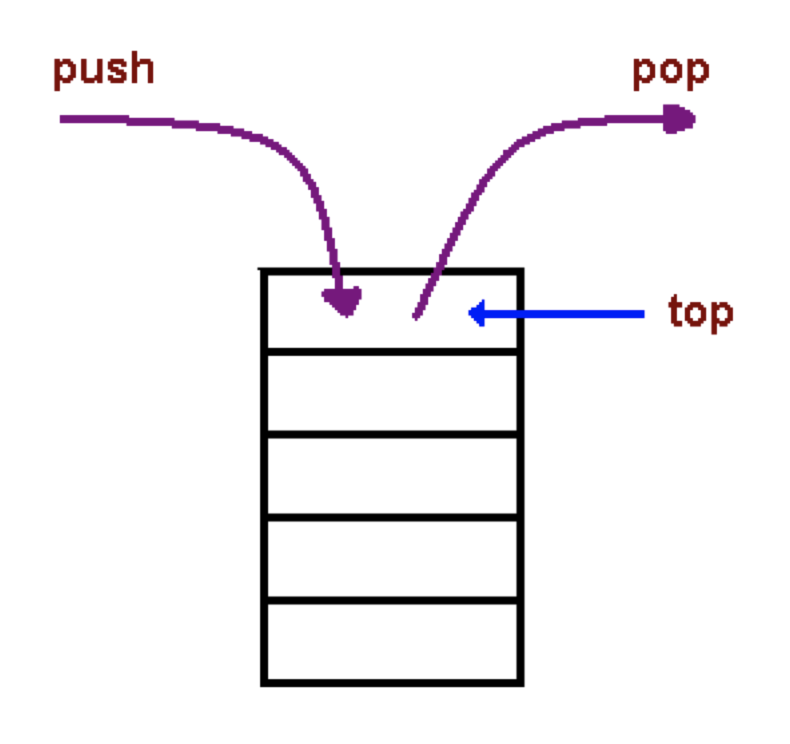
- 스택은 자료구조의 한 종류이며, 데이터의 삽입과 삭제는 last-in, first-out(LIFO)를 따른다(후입선출).
- 스택에서 자료의 삽입과 삭제는 스택의
top(맨 위)에서 단 두개 push pop만 허용된다.
push: 스택의 탑에 아이템을 삽입.pop: 스택의 탑에서 아이템을 삭제.- 쌓여있는 여러개의 접시들을 상상하면 비슷하다, 맨 위의 접시를 먼저쓰고 맨 위에다가 접시를 추가할 수 있다.
- 대표적인 사용 예시
- 문자열의 역순 구하기.
- 주어진 문자열의 캐릭터를 하나씩 순서대로
push후, 다시 pop.
- text editor에서
undo기능.
Implementation
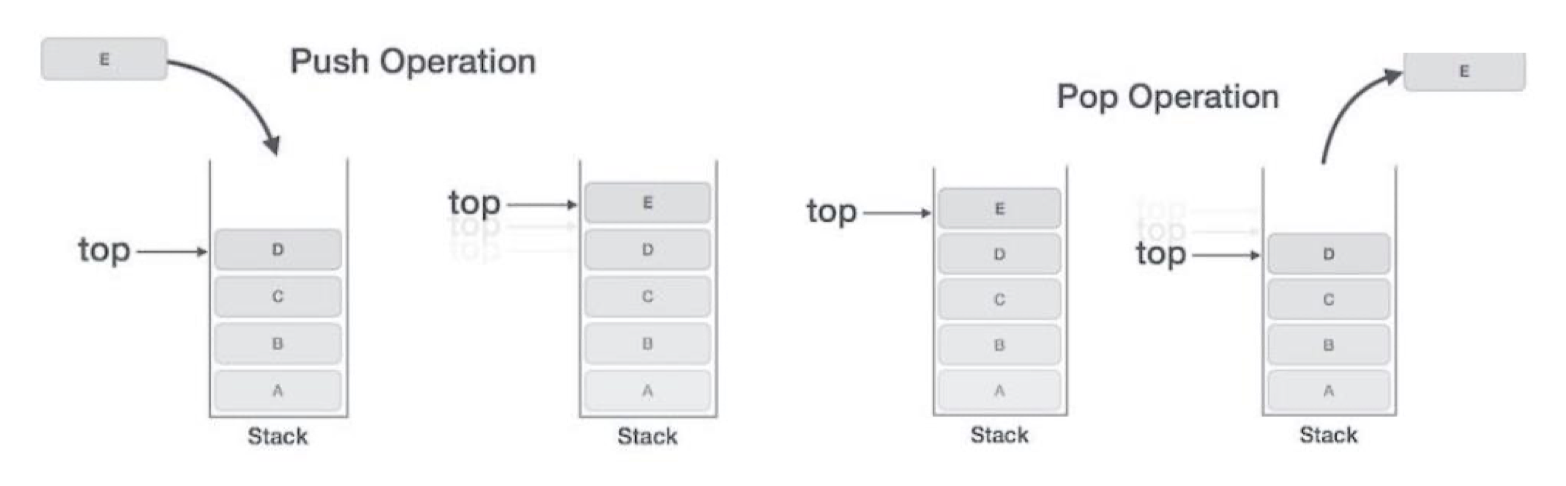
Array-based
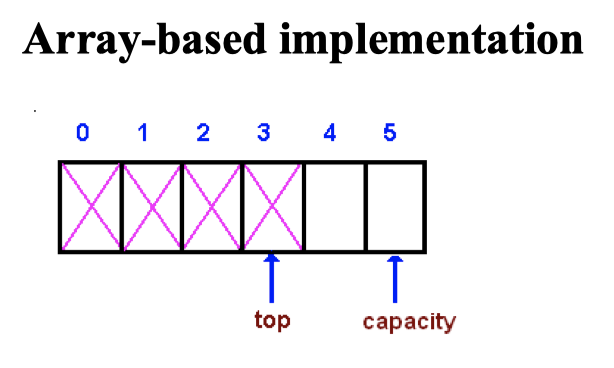
- 스택의 사이즈는 1보다 크거나 같다.
top: 스택의 맨 위 요소를 가르킨다.capacity: 스택의 사이즈를 가르킨다.top은 -1부터 capacity-1까지의 값을 취할수 있다.
if top == -1: a stack is empty.top == capacity-1: a stack is full.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int stack[100], n=100, top=-1;
void push(int val) {
if(top>=n-1) cout<<"Stack Overflow"<<endl;
else {
top++;
stack[top] = val;
}
}
void pop() {
if(top<=-1) cout<<"Stack Underflow"<<endl;
else {
cout<<"The popped element is "<< stack[top] <<endl;
top--;
}
}
void display() {
if(top>=0) {
cout<<"Stack elements are:";
for(int i=top; i>=0; i--) cout<<stack[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
} else cout<<"Stack is empty";
}
int main() {
int ch, val;
cout<<"1) Push in stack"<<endl;
cout<<"2) Pop from stack"<<endl;
cout<<"3) Display stack"<<endl;
cout<<"4) Exit"<<endl;
do {
cout<<"Enter choice: "<<endl;
cin>>ch;
switch(ch) {
case 1: {
cout<<"Enter value to be pushed:"<<endl;
cin>>val;
push(val);
break;
}
case 2: {
pop();
break;
}
case 3: {
display();
break;
}
case 4: {
cout<<"Exit"<<endl;
break;
}
default: {
cout<<"Invalid Choice"<<endl;
}
}
} while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}
Linked List-based
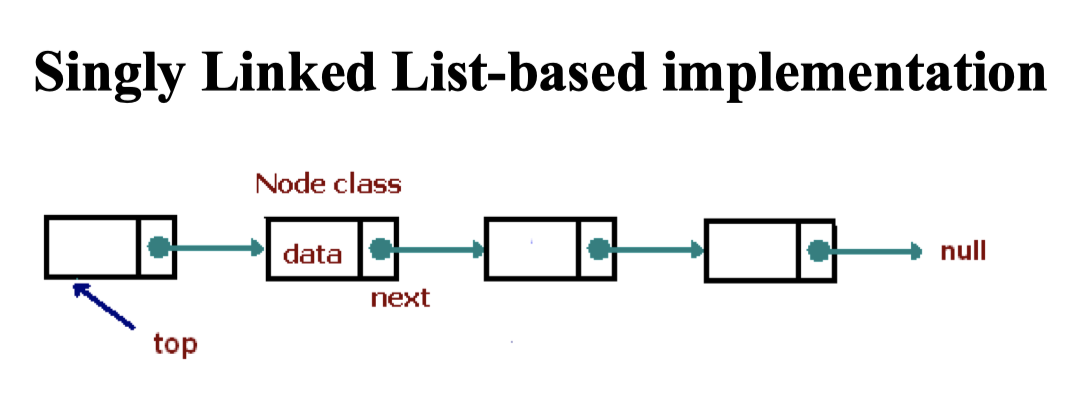
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node* top = NULL;
void push(int val) {
struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newnode->data = val;
newnode->next = top;
top = newnode;
}
void pop() {
if(top==NULL) cout<<"Stack Underflow"<<endl;
else {
cout<<"The popped element is "<< top->data <<endl;
top = top->next;
}
}
void display() {
struct Node* ptr;
if(top==NULL) cout<<"stack is empty";
else {
ptr = top;
cout<<"Stack elements are: ";
while (ptr != NULL) {
cout<< ptr->data <<" ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int ch, val;
cout<<"1) Push in stack"<<endl;
cout<<"2) Pop from stack"<<endl;
cout<<"3) Display stack"<<endl;
cout<<"4) Exit"<<endl;
do {
cout<<"Enter choice: "<<endl;
cin>>ch;
switch(ch) {
case 1: {
cout<<"Enter value to be pushed:"<<endl;
cin>>val;
push(val);
break;
}
case 2: {
pop();
break;
}
case 3: {
display();
break;
}
case 4: {
cout<<"Exit"<<endl;
break;
}
default: {
cout<<"Invalid Choice"<<endl;
}
}
}while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}
Queue

- 큐는 자료구조의 한 종류이며, 데이터의 삽입과 삭제는 first-in, first-out(FIFO)를 따른다(선입선출).
- 큐에서 자료의 삽입은 큐의
back에서만 허용되며 삭제는 큐의 front에서만 허용된다.
enqueue: 큐의 맨 뒤에 아이템 삽입. dequeue: 큐의 맨 앞 아이템 삭제.- 마트 계산대의 계산을 기다리는 대기열과 비슷하다, 제일 먼저온 손님이 계산을 먼저하고 나가며 새로운 손님은 대기열의 맨 뒤에 추가된다.
- 대표적인 사용 예시
- IO Buffers.
- Job scheduling.
- In shared resource management.
Implementation
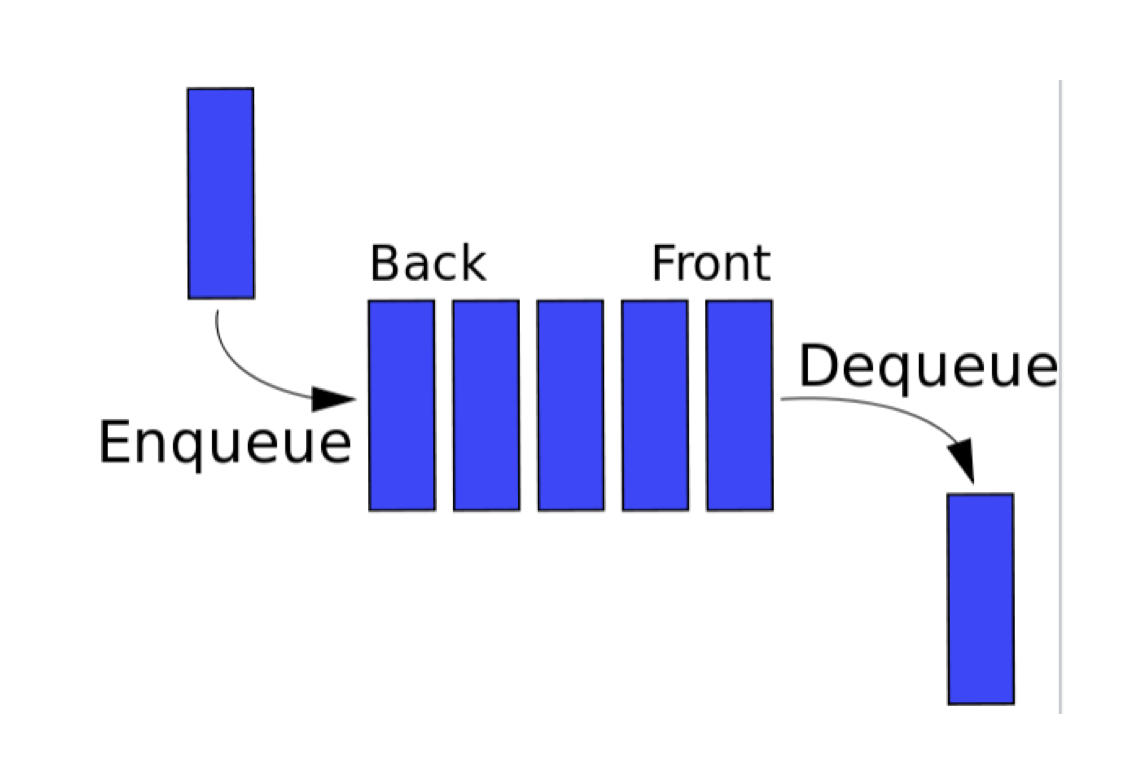
Array-based
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int queue[100], n = 100, front = -1, rear = -1;
void Insert() {
int val;
if (rear == n-1) cout<<"Queue Overflow"<<endl;
else {
if (front == -1) front = 0;
cout<<"Insert the element in queue : "<<endl;
cin>>val;
rear++;
queue[rear] = val;
}
}
void Delete() {
if (front == -1 || front > rear) {
cout<<"Queue Underflow ";
return ;
} else {
cout<<"Element deleted from queue is : "<< queue[front] <<endl;
front++;;
}
}
void Display() {
if (front == -1) cout<<"Queue is empty"<<endl;
else {
cout<<"Queue elements are : ";
for (int i = front; i <= rear; i++) cout<<queue[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
}
int main() {
int ch;
cout<<"1) Insert element to queue"<<endl;
cout<<"2) Delete element from queue"<<endl;
cout<<"3) Display all the elements of queue"<<endl;
cout<<"4) Exit"<<endl;
do {
cout<<"Enter your choice : "<<endl;
cin>>ch;
switch (ch) {
case 1: Insert();
break;
case 2: Delete();
break;
case 3: Display();
break;
case 4: cout<<"Exit"<<endl;
break;
default: cout<<"Invalid choice"<<endl;
}
} while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}
Linked List-based
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* front = NULL;
struct node* rear = NULL;
struct node* temp;
void Insert() {
int val;
cout<<"Insert the element in queue : "<<endl;
cin>>val;
if (rear == NULL) {
rear = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
rear->next = NULL;
rear->data = val;
front = rear;
} else {
temp=(struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
rear->next = temp;
temp->data = val;
temp->next = NULL;
rear = temp;
}
}
void Delete() {
temp = front;
if (front == NULL) {
cout<<"Underflow"<<endl;
return;
}
else
if (temp->next != NULL) {
temp = temp->next;
cout<<"Element deleted from queue is : "<<front->data<<endl;
free(front);
front = temp;
} else {
cout<<"Element deleted from queue is : "<<front->data<<endl;
free(front);
front = NULL;
rear = NULL;
}
}
void Display() {
temp = front;
if ((front == NULL) && (rear == NULL)) {
cout<<"Queue is empty"<<endl;
return;
}
cout<<"Queue elements are: ";
while (temp != NULL) {
cout<<temp->data<<" ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int ch;
cout<<"1) Insert element to queue"<<endl;
cout<<"2) Delete element from queue"<<endl;
cout<<"3) Display all the elements of queue"<<endl;
cout<<"4) Exit"<<endl;
do {
cout<<"Enter your choice : "<<endl;
cin>>ch;
switch (ch) {
case 1: Insert();
break;
case 2: Delete();
break;
case 3: Display();
break;
case 4: cout<<"Exit"<<endl;
break;
default: cout<<"Invalid choice"<<endl;
}
} while(ch!=4);
return 0;
}
References







