Data Type : Variable
동적 타입
JavaScript는 느슨한 타입(loosely typed)의 동적(dynamic) 언어입니다. JavaScript의 변수는 어떤 특정 타입과 연결되지 않으며, 모든 타입의 값으로 할당 (및 재할당) 가능합니다
let text = 'hello';
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
text = 1;
//1
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
text = '7' + 5;
//75
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
// 스트링 + 넘버의 조함, 문자열에 +가 있으니까 string으로 인식함! //75
text = '8' / '2';
//
console.log(`value: ${text}, type: ${typeof text}`);
// 스트링 + 스트링의 조합, 나누기 연산자가 있으니 Number로 인식함!
// 4
// JS는 런타임에서 타입이 정해지기 때문에 에러가 발생을 함!
let runTimeError = 'hello';
console.log(runTimeError.charAt(0)); // h
runTimeError = 7 + 5;
console.log(`value: ${runTimeError}, type: ${typeof runTimeError}`); //13, 넘버 + 넘버의 조함
console.log(runTimeError.charAt(0)); // error, 런타임으로 인해 에러가 발생!
// 이것때문에 타임스크립트가 나옴!변수
- primitive, single item: number, string, boolean, unll, underfiend, symbol
- object, box container
function. first-class function
변수 Variable (read/write)
변수란 데이터(data)를 저장하기 위해 프로그램에 의해 이름을 할당받은 메모리 공간을 의미합니다. 즉, 변수란 데이터(data)를 저장할 수 있는 메모리 공간을 의미하며, 이렇게 저장된 값은 변경될 수 있습니다.
var sum = 10 + 20;
- 변수sum에 10 + 20이 평가되어 "숫자값 30이 할당됨"
- 변수에 할당되는 것은 '값'이다.
- 변수는 하나의 값을 저장하기 위해 확보한 "메모리 공간" 또는 "그것의 식별용 이름"상수 Constant (read only)
use const whenever possible.
only use let if variable needs to change.
const count = 17; // integer
const size = 17.1; // decimal number
console.log(`value: ${count}, type: ${typeof count}`);
console.log(`value: ${size}, type: ${typeof size}`);const daysInWeek = 7;
const maxNumber = 5;< Mutable 타입의 let / Immutable 타입의 const >
Immutable data types :
imitive types, frozen objects (i,e. object.freeze())
Mutable data typed :
all objects by default are mutable in JS
"favor immutable data type" always for a few reasons
- security (해커가 값을 변경해서 코드 변경하는것을 방지)
- thread safety (어플리케이션에 연동된 변수가 변경되면 위험하므로 안정성을 위해 constants 사용)
- reduce human mistakes (훗날 코드 변경할때 실수 방지할 수 있음)
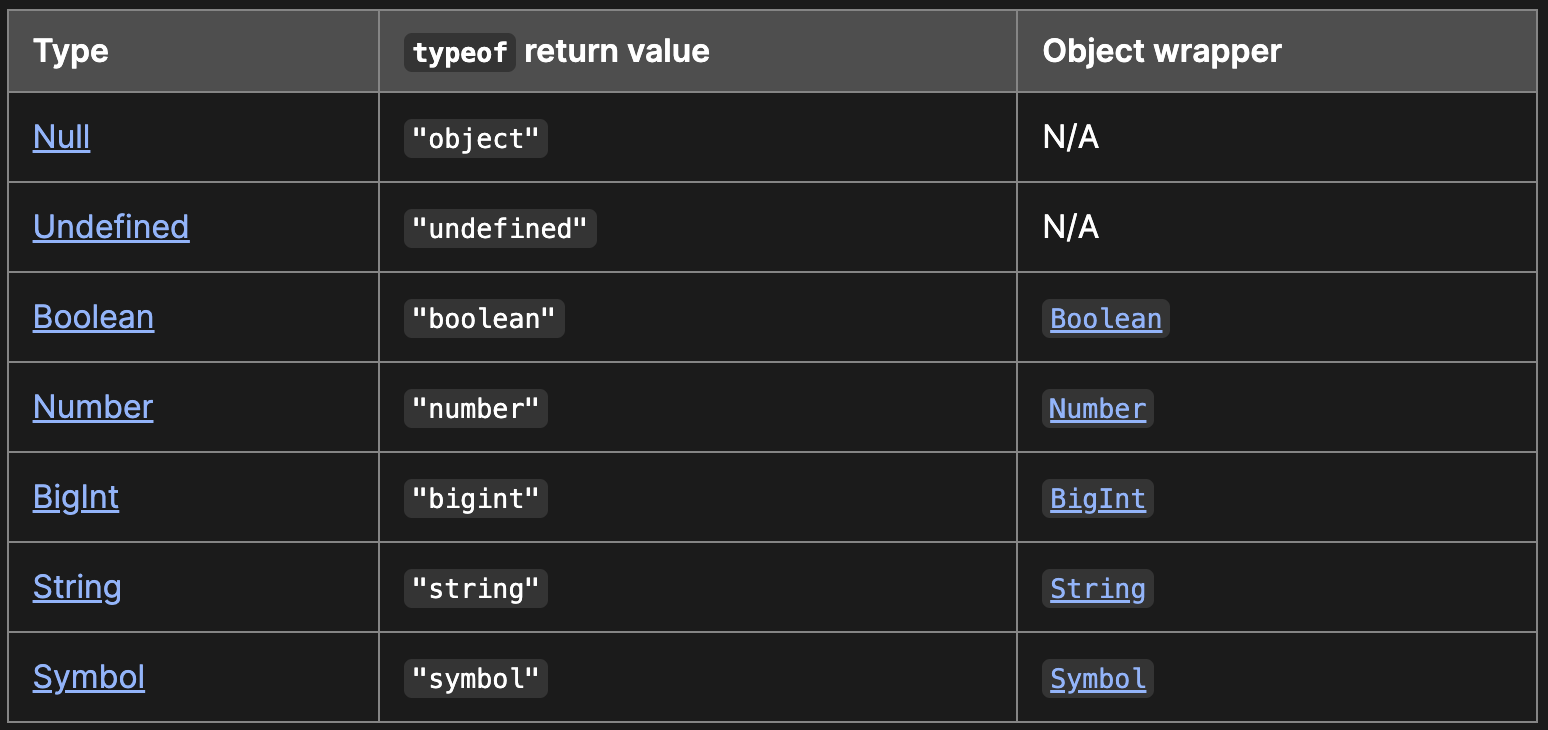
데이터 타입
자바스크립트 Data types
JavaScript 언어의 타입은 원시 값과 객체로 나뉩니다.
컴퓨터 과학에서의 객체란 식별자로 참조할 수 있는 메모리 상의 값을 말함.
모든 값은 '데이터 타입'을 가짐!
다만 데이터 타입에 따라 메모리에 저장된 값은 다르게 헤석됨!
1️⃣ number(숫자)
speical numeric values: infinity, -infinity, NaN
자바스크립트는 '실수' 하나의 숫자 타입으로만 처리됨! (10, 10.5, -10)
cf) C언어/자바는 '정수'와 '실수'구분 사용. 여러 숫자 타입 처리!
const infinity = 1 / 0;
const negativeInfinity = -1 / 0;
const nAn = 'not a number' / 2;
console.log(infinity);
console.log(negativeInfinity);
console.log(nAn);
// bigInt (fairly new, don't use it yet)
const bigInt = 12345678901234567890123456789012345n;//
console.log(`value: ${bigInt}, type: ${typeof bigint}`);2️⃣ string(문자열)
텍스트 데이터를 나타내는데 사용. (16비트 유니코드 문자 /UTF-16)
작은 따옴표'', 큰따옴표"", 또는 백틱으로 텍스트를 감쌈!
const char = 'c'; // 단일 문자
const brendan = 'brendan'; // 복수의 문자
const greeting = 'hello ' + brendan; // 문자 + 변수 조합도 가능!!
console.log(`value: ${greeting}, type: ${typeof greeting}`);
const helloBob = `hi ${brendan}!`; // template literals (srting)
console.log(`value: ${helloBob}, type: ${typeof helloBob}`);
// > 백틱으로 콘솔 작성하면 편함. 따옴표로 하면 아래와 같음
console.log('value: '+ helloBob + 'type: ' + typeof helloBob);3️⃣ boolean(블리언)
논리적 참/거짓을 가릴때 사용되어 주로 조건문에서 많이 활용한다!
false : 0, null, undefined. NaN, ''
true : any other value
const canRead = true;
const test = 3 < 1; //false
console.log(`value: ${canRead}, type: ${typeof canRead}`);
console.log(`value: ${test}, type: ${typeof test}`);4️⃣ null
프로그래밍 언어에서 변수값이 없다는것을 의도적으로 명시할 때 사용
변수에 null 할당-> 이전에 할당된 값에 참조를 명시적으로 제거!
(* 자바스크립트 엔진은 참조하지 않는 메모리 공간에 가비지 콜렉션을 수행할 것임!)
let nothing = null;
console.log(`value: ${nothing}, type: ${typeof nothing}`);5️⃣ undefined
이 값은 undefined가 유일함
var(let) 키워드로 변수 선언 => 확보된 메모리 공간을 초기화(undefined)함
var y;
console.log(y);
//undefined
let x;
console.log(`value: ${x}, type: ${typeof x}`);
//undefined6️⃣ smybol
변경 불가 원시 타입! 타 값와 중복되지 않는 유일무이한 값!
smybol, create unique idenrifiers for objects
- 심벌 외 원시값 = 리터럴을 통해 생성
- 심벌 값 = 심벌 함수 통해 표현
const symbol1 = Symbol('id');
const symbol2 = Symbol('id');
console.log(symbol1 === symbol2); //flase
const gsymbol1 = Symbol.for('id');
const gsymbol2 = Symbol.for('id');
console.log(gsymbol1 === gsymbol2); //true
// symbole은 .description을 적어 스트링으로 변환해야 출력됨! 그냥은 안됨!
console.log(`value: ${symbol1.description}, type: ${typeof symbol1}`);7️⃣ object
자바는 객체 지향 프로그래밍이고 기본으로 제공하는 (Primitive Type)이 아닌 나머지는 모두 객체(object)로 구성되어 있다.
object, real-life object, data structure
const kse = {name: 'kse', age: 20};
kse.age = 21;
//.을 이용해 새로운 변수값 지정가능! 새로운 메모리에 다른 값으로 할당할 수 있게 된다!
Data type의 추가 예시는 아래에서 확인하자.
Data Type : String / Number
문자열과 숫자
문자열은 문자의 배열이다. “abc”라는 문자열은 ‘a’,‘b’,‘c’라는 문자를 나열한 배열인 것이다. 예를 들어 다음과 같은 것들이 문자열이다.
"Happy Java"
"a"
"123"자바에서 문자열을 나타내는 자료형은 String 이다. 위의 문자열을 자바에서 표현하려면 다음과 같이 사용해야 한다.
String a = "Happy Java";
String b = "a";
String c = "123";
---
<string 문자>
"1"= 문자열
"1"+"1" = "11"
<string 숫자>
1 = 숫자
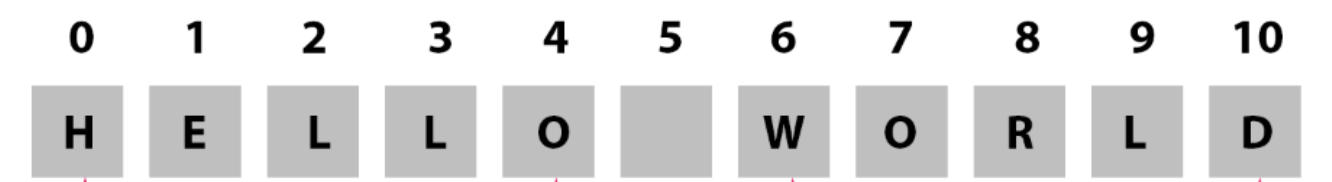
1+1 = 2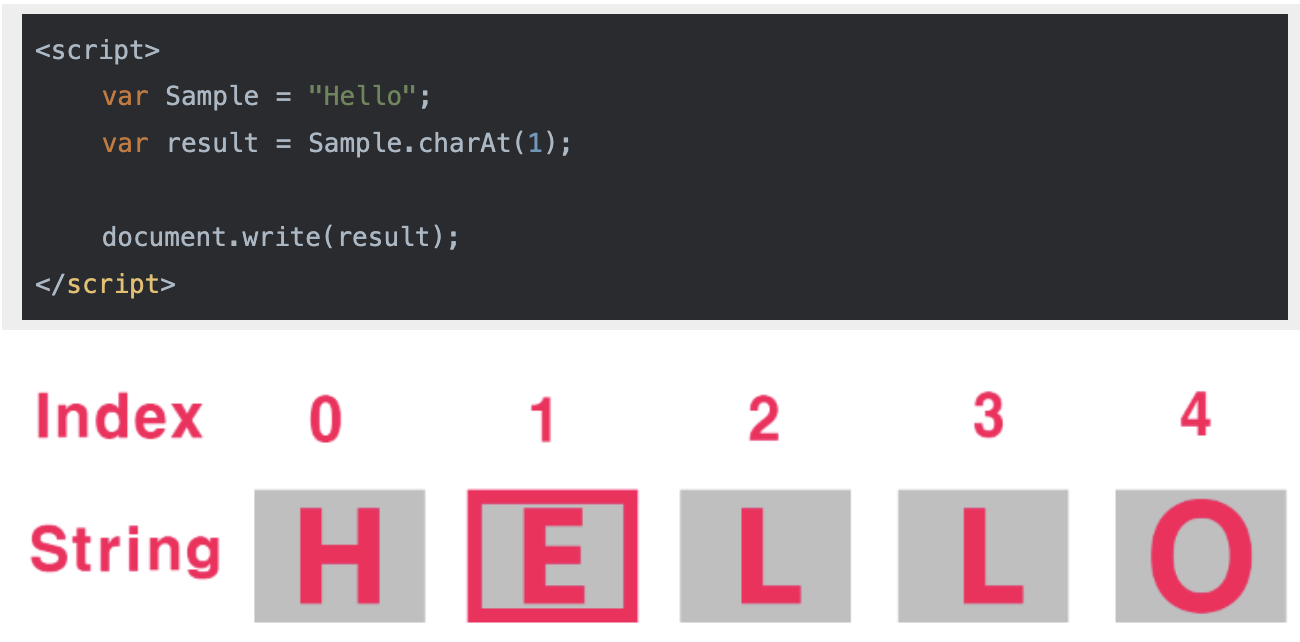
연산자
산술연산자 (ex.사칙연산)
문자열 내장 메서드
String 자료형의 내장 메서드 중에서 자주 사용하는 것들에 대해서 알아보자.
1) string length
'Hello world'.length
// 11
문자 갯수 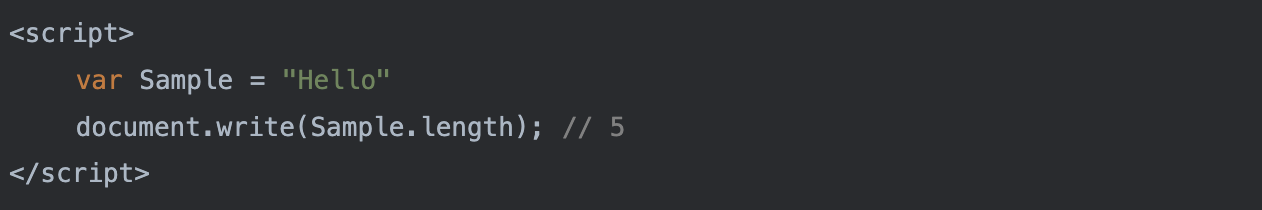 2) string toupperCase()
2) string toupperCase()
'Hello world'.toUpperCase()
// 'HELLO WORLD'
문자열을 모두 대문자로 변경할 때 사용한다.
(모두 소문자로 변경할때는 toLowerCase를 사용한다.)3) indexOf
'Hello world'.indexOf('O')
// -1
'Hello world'.indexOf('o')
// 4
'Hello world'.indexOf('world')
// 6
indexOf는 문자열에서 특정 문자열이 시작되는 위치(인덱스)를 리턴한다. (숫자는 0부터 센다!!0,1,2...)