Part2 Priority Inversion Problem
과제 목표

- 이번 과제에서는 Priority Inversion Problem을 해결하는 것이 목표이며, 이를 위해 3가지 도네이션 기능을 구현해야 한다. Priority Inversion Problem이 무엇인지 먼저 알아본다.
Priority Inversion Problem
- 우선순위가 높은 스레드가 우선순위가 낮은 스레드를 기다리는 현상을 말한다.
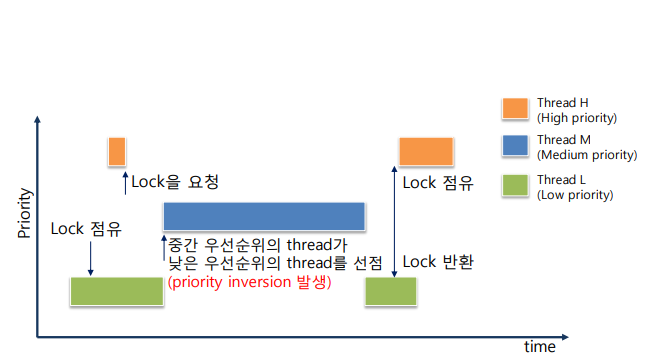
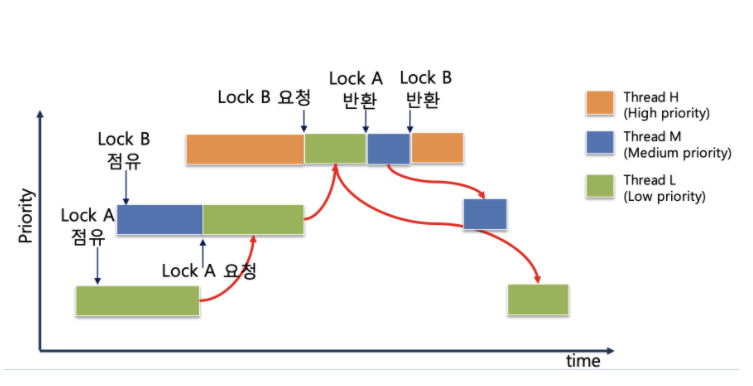
- pintos Documents 에 나와있는 설명을 해석해보자. 우선 priority inversion 이란 위에 그림 같은 상황에서 발생한다. H (high), M (medium), L (low) 라는 세 개의 스레드가 있고 각각의 우선순위는 H > M > L 일 때, H 가 L 을 기다려야 하는 상황(예를 들어, H 가 lock 을 요청했는데 이 lock 을 L 이 점유하고 있는 경우)이 생긴다면 H 가 L 에게 CPU 점유를 넘겨주면 M 이 L 보다 우선순위가 높으므로 점유권을 선점하여 실행되어서 스레드가 마무리 되는 순서가 M->L->H 가 되어서 M 이 더 높은 우선순위를 가진 H 보다 우선하여 실행되는 문제가 발생한다. 이를 잘 나타낸 그림이 있어서 가져와 보았다.
-
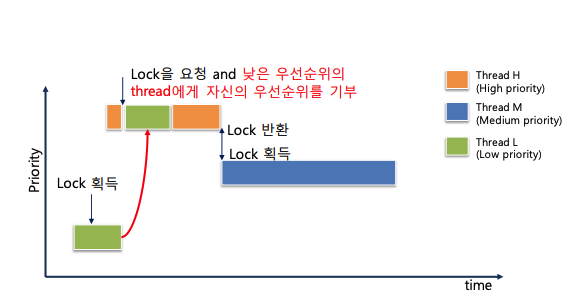
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위한 방법으로 priority donation을 구현하여야 한다. priority donation이란 위의 상황에서 H가 자신이 가진 priority를 L에게 일시적으로 양도하여서 H 자신의 실행을 위해 L이 자신과 동일한 우선순위를 가져서 우선적으로 실행될 수 있도록 만드는 방법이다. priority donation이 작동하면 실행 순서는 위와 같이 바뀐다.
-
pintos documents에서는 priority donation이 일어날 수 있는 모든 상황을 고려해야 한다고 하면서 Multiple donation, Nested donation 두 가지를 언급한다.
Multiple donation
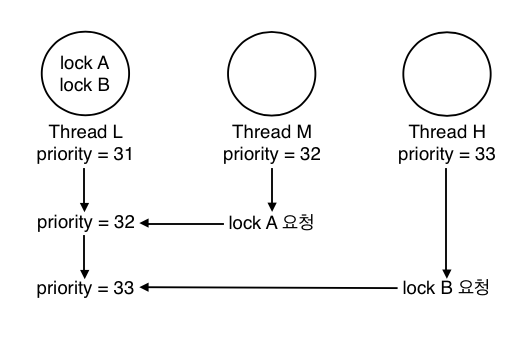
-
단어에서 알 수 있듯이 여러번의 donation이 일어난 상황이라고 볼 수 있다. 위의 예시에서 L이 lock A, lock B라는 두 가지 lock을 점유하고 있다고 가정한다. H가 lock B를, M이 lock A를 각각 요청하였을 때, L은 자신이 가지고 있는 lock을 요청한 모든 스레드에게 priority를 양도받고, 이 중 가장 높은 priority를 일시적으로 자신의 priority로 갖는다.
-
이 경우에 L이 lock B를 release 해도 아직 M에게 양도받은 priority 가 있기 때문에 31 이 아닌 32의 priority 를 가지게 된다.
Nested donation
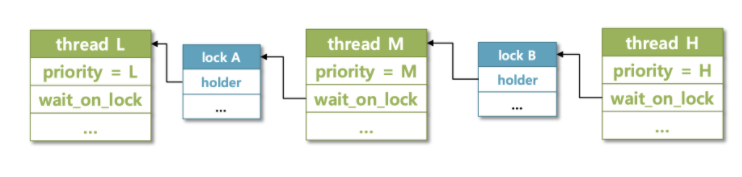
- Nested donation은 마치 체인처럼 H, M, L이 서로 연결되어 우선순위를 기부하는 상황이다. (H-> M -> L)
-
L 스레드가 Lock A를 점유하고서 작업 중인 상황에서 M 스레드가 들어온다. M 스레드의 우선순위가 더 높고 다른 Lock을 점유하고 있으니 CPU 제어권은 M이 잡는다.
-
이어서 M이 Lock A를 요청한다. 그러면 donation이 일어나 L의 우선순위가 M과 동등해진다. 여기서 lock A는 L이 잡고 있었으니 CPU 제어권은 L에게 넘어오고 L 이 작업을 시도할 것이다.
-
그 사이에 H가 들어온다. H는 처음에 아무런 Lock도 요청하지 않았기에 바로 CPU를 잡고 작업을 한다. 그러다 중간에 Lock B를 요청하는데, Lock B는 M 스레드가 잡고 있었다. 하지만 M 스레드는 Lock A를 요청하고 기다리던 상황이었기 때문에 M 스레드가 H한테 Lock B를 넘겨주기 위해서는 가장 먼저 L 스레드가 Lock A를 반환해야 이 순환고리가 끝이 난다. 따라서 M과 L 둘다 H의 우선순위를 물려받는다.
-
그러면 L 스레드가 작업을 끝내고 A를 반환하고, 이어서 M이 lock B를 반환한다. 마지막으로 H가 작업을 끝내며 모든 것이 종료된다.
- 위의 설명이 부족하다고 느껴진다면 Priority Inversion Problem를 좀더 자세히 설명한 사이트 링크를 참고하길 바란다. Priority Inversion Problem 참고글
구현

-
struct list donation : A thread가 B thread에 의해 priority가 변경되었다면 A thread의 list donations에 B thread를 기억해놓는다. 이는 차후에 쓰일 것이다. (자신에게 기부한 기부자 목록이라고 생각하자.)
-
struct list_elem donation_elem : 또한 B thread는 A thread의 기부자 목록 (list donations)에 자신의 이름을 새겨놓아야한다. 이를 donation_elem을 통해 새겨놓는다.

- 위에 struct thread에 선언해준 4개의 값에 대해 초기화를 해준다
static void init_thread(struct thread *t, const char *name, int priority)
{
ASSERT(t != NULL);
ASSERT(PRI_MIN <= priority && priority <= PRI_MAX);
ASSERT(name != NULL);
memset(t, 0, sizeof *t);
t->status = THREAD_BLOCKED;
strlcpy(t->name, name, sizeof t->name);
t->tf.rsp = (uint64_t)t + PGSIZE - sizeof(void *);
t->priority = priority;
t->magic = THREAD_MAGIC;
/* Priority donation관련 자료구조 초기화 */
t->init_priority = priority;
t->wait_on_lock = NULL;
list_init(&t->donations);
}
lock_acquire()함수는 스레드가 CPU 제어권을 잡고나서 lock을 요청할 때 실행된다. sema_down()을 실행해 lock을 얻기 위해 세마포어를 waiters 리스트에 줄세운 다음 해당 스레드를 blocked 상태로 전환한다. 그러다 앞서 lock을 점유하던 애가 반환하면 sema_down()에서 sema->value 값을 1 빼고(여기까지 sema_down) 다시 lock_acquire()로 와서 lock을 받는다 (lock->holder).
void lock_acquire(struct lock *lock)
{
ASSERT(lock != NULL);
ASSERT(!intr_context());
ASSERT(!lock_held_by_current_thread(lock));
struct thread *curr = thread_current();
/* 해당 lock의 holder가 존재 한다면 */
if (lock->holder != NULL)
{
/* 현재 스레드의 wait_on_lock 변수에 획득 하기를 기다리는 lock의 주소를 저장 */
curr->wait_on_lock = lock;
/* multiple donation 을 고려하기 위해 이전상태의 우선순위를 기억,
donation 을 받은 스레드의 thread 구조체를 list로 관리한다. */
list_insert_ordered(&lock->holder->donations, &curr->donation_elem, cmp_donation_priority, NULL);
/* priority donation 수행하기 위해 donate_priority() 함수 호출 */
donate_priority();
}
sema_down(&lock->semaphore);
curr->wait_on_lock = NULL;
/* lock을 획득 한 후 lock holder 를 갱신한다. */
lock->holder = thread_current();
}-
lock->holder는 현재 lock을 소유하고 있는 스레드를 가리킨다. 현재 lock을 소유하는 스레드가 없다면 (if(lock->holder)) if 문을 건너 뛰고 바로 sema_down()을 실행한 뒤, lock을 점유(lock->holder = thread_current())할 것이다.
-
현재 스레드가 lock_acquire()를 실행했다는 건 이미 이전에 lock을 점유하고 있는 스레드보다 우선순위가 높기 때문에 CPU 제어권을 선점한 것이다. 따라서 lock을 점유하고 있던 CPU와 우선순위 크기를 비교할 필요가 없다. 현재 스레드의 우선순위가 높기 때문에 lock_acquire를 실행할 수 있는 것이기 때문이다.
-
반면 lock을 누군가 점유하고 있다면 현재 스레드의 wait_on_lock 멤버에 기다려야 할 lock을 추가한다. 이어서 현재 lock을 들고 있는 스레드의 donations 리스트에 자신의 donation_elem을 달아준다. 이때, list_push_back이 아닌 list_insert_ordered 방식으로 달아주는데, 이는 donations 리스트에 들어있는 스레드들이 우선순위를 기부한 순서가 아니라 가장 높은 우선순위부터 lock을 들고 기부 리스트에서 빠져나가는 구조기 때문이다.
-
cmp_donation_priority 함수
bool cmp_donation_priority(const struct list_elem *a, const struct list_elem *b, void *aux UNUSED)
{
struct thread *da = list_entry(a, struct thread, donation_elem);
struct thread *db = list_entry(b, struct thread, donation_elem);
return da->priority > db->priority;
}
donate_priority()함수는 자신의 priority를 스레드에게 빌려주는 함수다. 여기서 주의해야 할 점은, nested donation 케이스처럼 lock에 연결된 모든 스레드에 donation이 일어난다는 점이다. 따라서 wait_on_lock에서 기다리고 있는 lock을 현재 점유하고 있는 holder들을 순회하면서 모두에게 자신의 우선순위를 기부한다.
void donate_priority(void)
{
struct thread *holder = thread_current()->wait_on_lock->holder;
int count = 0;
while (holder != NULL)
{
holder->priority = thread_current()->priority;
count++;
if (count > 8 || holder->wait_on_lock == NULL)
break;
holder = holder->wait_on_lock->holder;
}
}- 과제에서 nested donation의 깊이를 최대 8로 정해놨기 때문에 depth 값을 설정해준다. 맨 처음에는 현재 스레드가 기다리고 있는 lock의 holder 스레드로 가서 걔한테 우선순위를 기부한다. 그러면 cur을 그 holder 스레드로 변경하고, 다음 for문에서 그 스레드가 기다리는 또다른 lock을 현재 들고 있는 holder 스레드에도 우선순위를 기부하는 식. 그러다 더이상 연결된 wait_on_lock이 없다면 종료한다.

lock_release()함수는 해당 스레드가 lock 안에서 작업을 끝마치면 현재 스레드가 갖고 있던 lock을 NULL 상태로 바꾸고 sema_up을 실행한다. 그러면 다음 차례에서 기다리고 있던 스레드가 해당 lock을 잡을 것이다.
void lock_release(struct lock *lock)
{
ASSERT(lock != NULL);
ASSERT(lock_held_by_current_thread(lock));
lock->holder = NULL;
remove_with_lock(lock);
refresh_priority();
sema_up(&lock->semaphore);
}- 여기서 스레드가 priority를 양도받아서 작업을 마치고 lock을 반환할 때의 경우를 만들어줘야 한다. 즉, sema_up 하여 lock 점유를 반환하기 전에 lock을 사용하기 위해 나한테 priority를 빌려준 스레드들을 donations 리스트에서 전부 제거하고 priority를 재설정해주는 작업을 추가한다. 이를 위해 두 가지 새로운 함수를 짠다. 바로 remove_with_lock(lock) (priority 빌려준 스레드를 donations 리스트에서 제거)와 refresh_priority() (priority 재설정)이다.

void remove_with_lock(struct lock *lock)
{
struct list_elem *curr_donation_elem = list_begin(&thread_current()->donations);
/* donations 리스트에서 지울 lock을 찾아서 삭제한다. */
while (curr_donation_elem != list_tail(&thread_current()->donations))
{
struct thread *curr_donation_thread = list_entry(curr_donation_elem, struct thread, donation_elem);
if (curr_donation_thread->wait_on_lock == lock)
{
curr_donation_elem = list_remove(curr_donation_elem);
}
else
{
curr_donation_elem = list_next(curr_donation_elem);
}
}
}lock_release()를 실행하면 해당 lock을 사용하기 위해서 자신의 우선순위를 기부하고 기다리고 있던 스레드는 이제 priority를 빌려줄 이유가 없어지니 donation 리스트로부터 자신을 지운다. 이를 위해 remove_with_lock()에서는 donations 리스트에 달려 있는 list_elem으로부터 thread를 불러온다. 현재 점유가 풀린 lock에 대해 donations 리스트에 있는 스레드가 해당 lock을 원하는 애라면 donations 리스트에서 제거한다.

- donations 리스트의 우선순위를 재설정한다. 만약 donations 리스트가 비었다면 init_priority로 설정하고 도네이션 리스트 중 가장 높은 priority를 가져온다.
void refresh_priority(void)
{
/* 현재 스레드의 우선순위를 기부받기 전의 우선순위로 초기화 */
thread_current()->priority = thread_current()->init_priority;
if (!list_empty(&thread_current()->donations))
{
struct thread *front_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&thread_current()->donations),
struct thread,
donation_elem);
if (thread_current()->priority < front_thread->priority)
{
thread_current()->priority = front_thread->priority;
}
}
}
void thread_set_priority(int new_priority)
{
thread_current()->priority = new_priority;
thread_current()->init_priority = new_priority;
refresh_priority();
test_max_priority();
}- 현재 스레드의 우선순위를 인자로 받은 new_priority로 init_priority도 변경해준 뒤, 우선순위가 변경되었으므로 재정렬(refresh_priority)를 해준뒤, test_max_priority()로 ready 리스트 맨 앞에서 기다리고 있던 스레드와 우선순위를 비교해 만약 ready 리스트에 기다리고 있던 스레드의 우선순위가 더 높다면 현재 작업 중인 스레드가 CPU를 기다리고 있던 애한테 양보한다.
결과
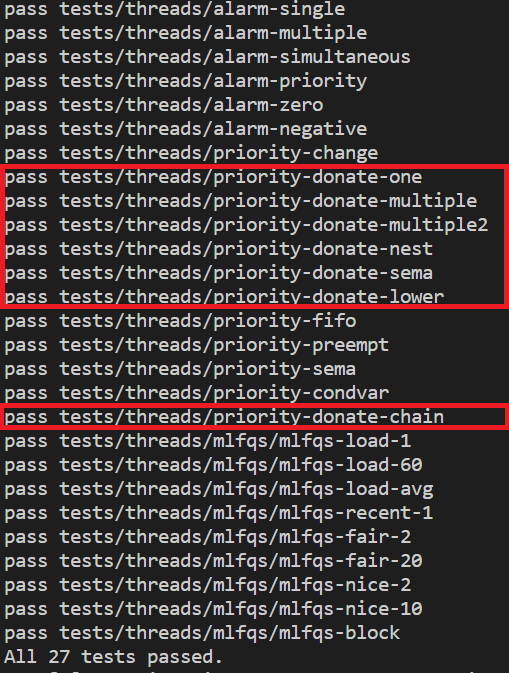
요약
- 추가 함수 및 자료구조 수정

- 수정 함수

PintOS Project1 GIthub 주소 PintOS
