이번 포스팅에서는 Ansible의 반복문과 조건문에 대해 다뤄보겠다. 기본적으로 언어 사용에 있어서 가장 기본이 되는 문법으로 반복문과 조건문을 꼽을 수 있다. Ansible 환경에서도 자주 사용해야하니 실습을 통해 알아보자.
반복문
Ansible에서는 반복문으로 loop를 사용한다. 바로 실습을 통해 알아보는게 이해가 빠르다.
아래 playbook은 sshd와 rsyslog 프로세스를 시작하는 역할을 한다. name항목만 빼고 다은 내용은 모두 같다.
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Check sshd state
ansible.builtin.service:
name: sshd
state: started
- name: Check rsyslog state
ansible.builtin.service:
name: rsyslog
state: started이런 경우, loop를 통해 코드를 간소화 할 수 있다.
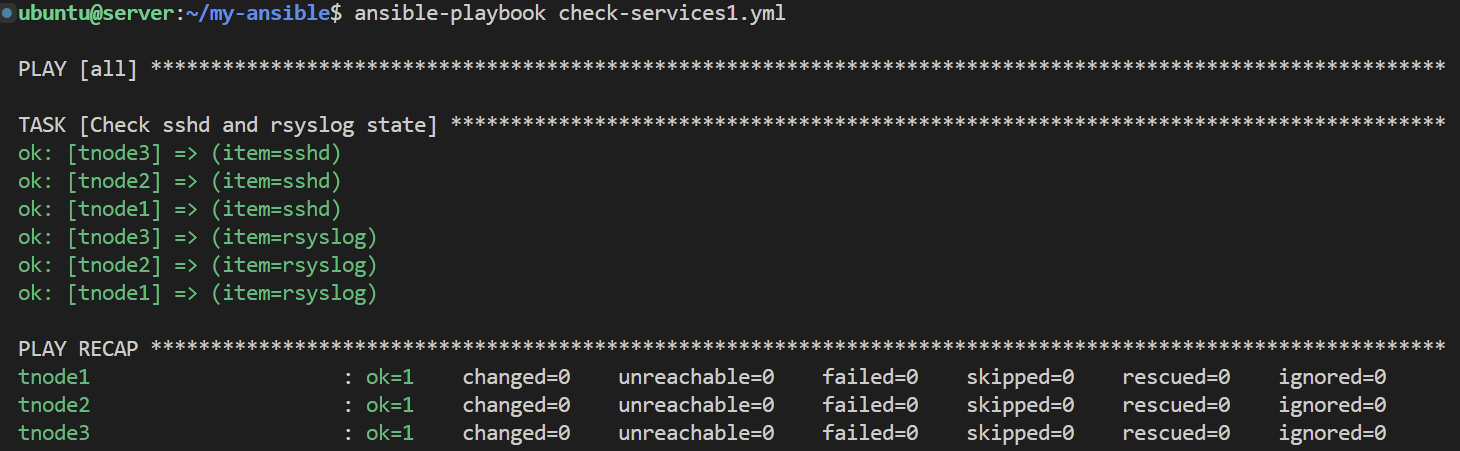
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Check sshd and rsyslog state
ansible.builtin.service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
loop:
- sshd
- rsyslog
register: result
- name: Show result
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: result 참고로, register에 result를 등록한 후 실행결과를 출력도 가능하다.
조건문
Ansible에서는 조건문으로 when을 사용하게된다.
$ vi when_task.yml
---
- hosts: localhost
vars:
run_my_task: false
tasks:
- name: echo message
ansible.builtin.shell: "echo test"
when: run_my_task
register: result
- name: Show result
ansible.builtin.debug:
var: result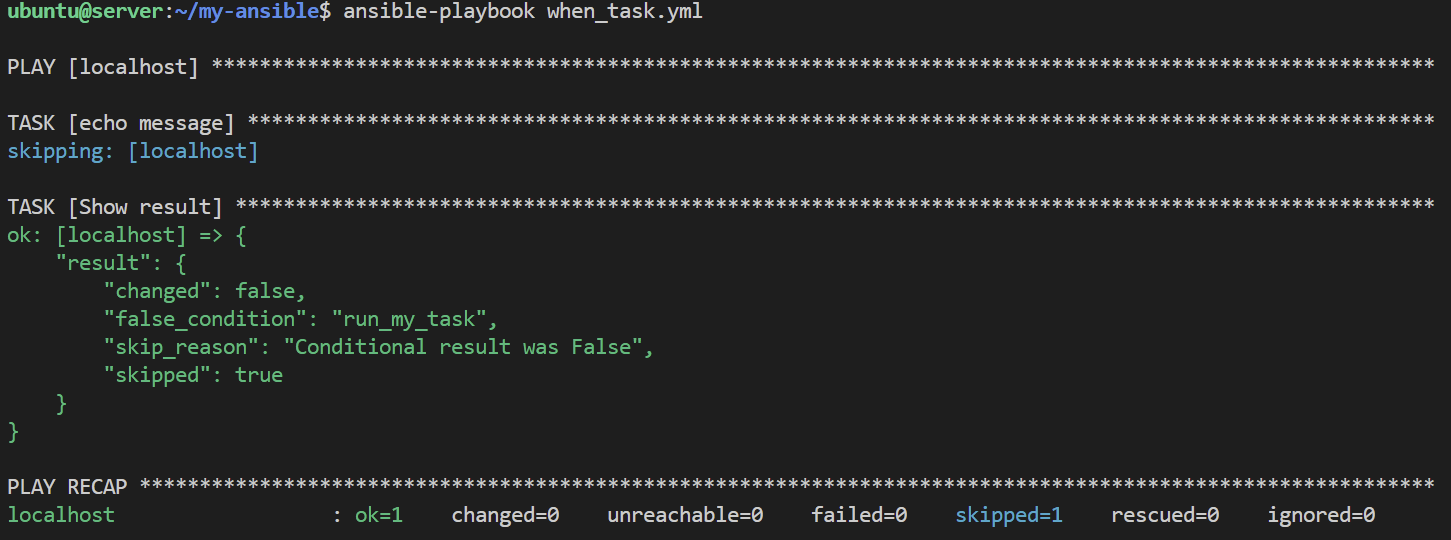
fact 정보 조건문
$ vi check-os1.yml
---
- hosts: all
vars:
supported_distros:
- Ubuntu
- CentOS
tasks:
- name: Print supported os
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "This {{ ansible_facts['distribution'] }} need to use apt"
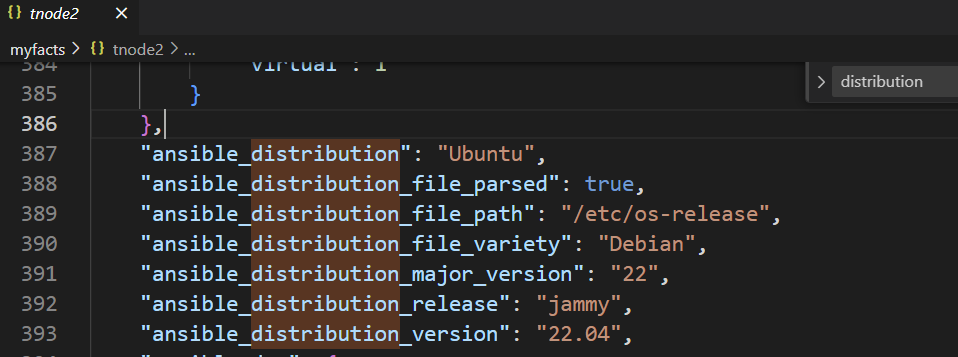
when: ansible_facts['distribution'] in supported_distrosdistribution 이 Ubutu 또는 CentOS 일 때 조건을 거는 방식인데, fact 정보는 이전 포스팅에서 본 fact caching 된 곳에서 확인이 가능하다.
복수 조건문
$ vi check-os2.yml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Print os type
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg: "OS Type {{ ansible_facts['distribution'] }}"
when: ansible_facts['distribution'] == "CentOS" or ansible_facts['distribution'] == "Ubuntu"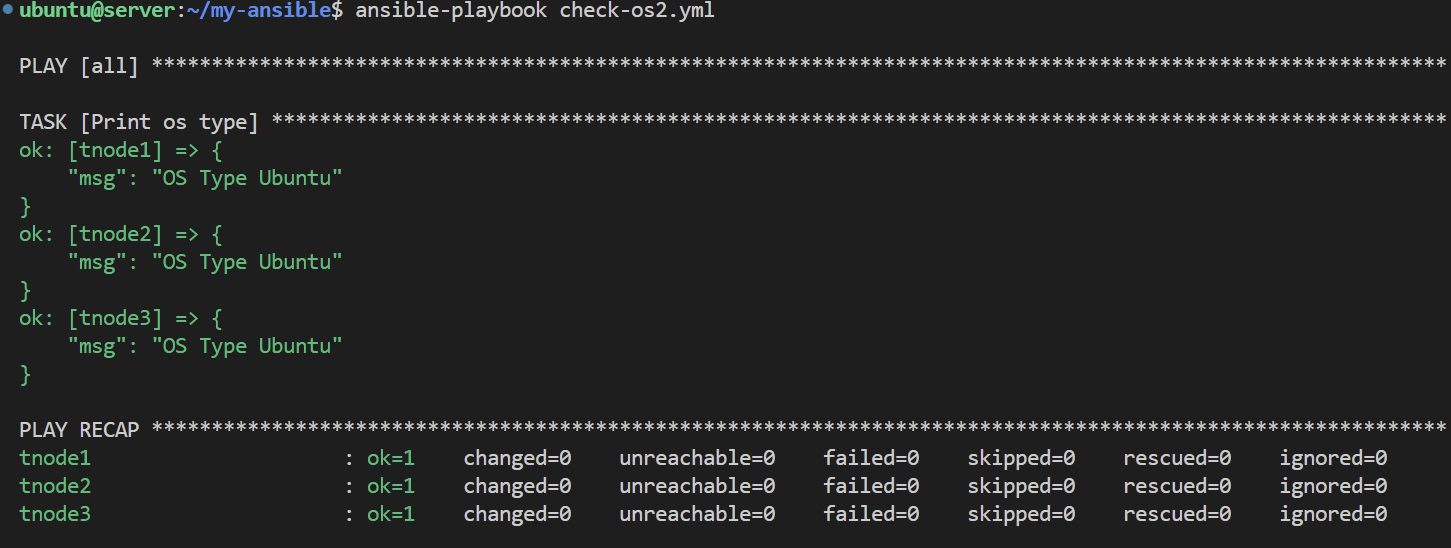
도전과제
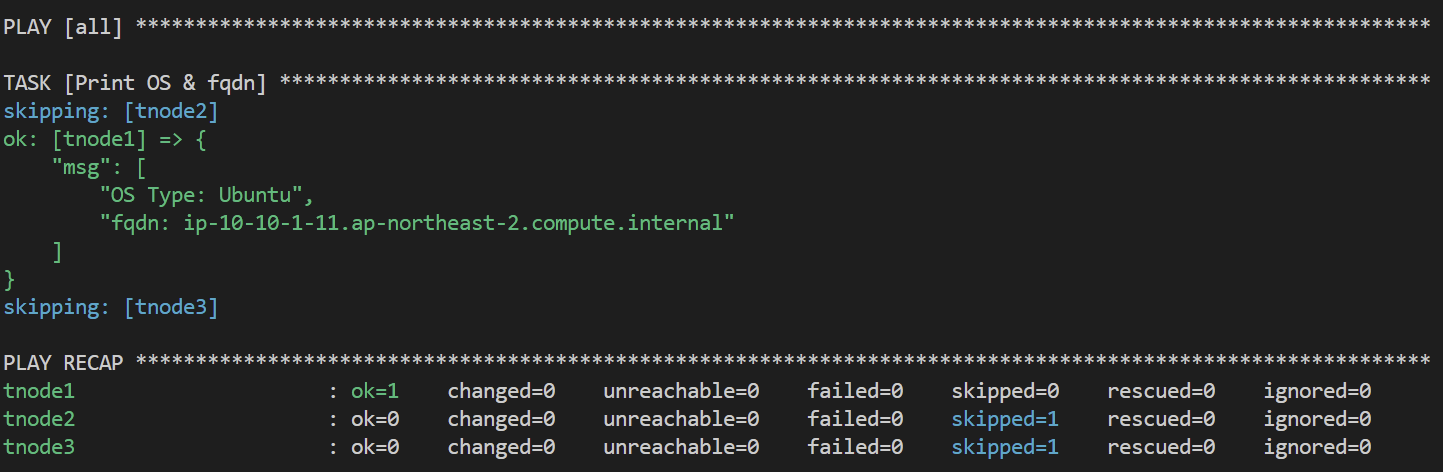
Ubuntu OS이면서 fqdn으로 tnode1 인 경우, debug 모듈을 사용하여 OS 정보와 fqdn 정보를 출력해보자
$ vi check-os-fqdn.yml
---
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Print OS & fqdn
ansible.builtin.debug:
msg:
- "OS Type: {{ ansible_facts['distribution'] }}"
- "fqdn: {{ ansible_facts['fqdn'] }}"
when: ansible_facts['distribution'] == "Ubuntu" and ansible_facts['fqdn'] == "ip-10-10-1-11.ap-northeast-2.compute.internal"