1. 파이썬 여러개 입력받기
num1, num2 = *map*(*int*, *input*().split())
int 대신 원하는 타입형 쓰면됨
2.2차원 리스트 입력값으로 생성
graph = []
for i in range(num1):
graph.append(list(map(int,input()))) # 붙여서 쓸땐 split 쓰면 안된다
#입력값
2 2
11
22
[[1, 1], [2, 2]]
3. key, value값으로 있으면 원래 추가하고 없으면 새로 key 만들어서 해당값 추가하기
def solution(clothes):
answer = 1
db = dict()
for ele in clothes:
cat = ele[1]
name = ele[0]
if cat in db:
db[cat].append(name)
else:
db[cat] = [name]
for key in db.keys():
answer = answer * (len(db[key]) + 1)
return answer-1key error 발생시
for i in range(T):
for j in range(len(arr[i])):
#print(arr[i][j][1])
try:
db[arr[i][j][1]].append(arr[i][j][0])
except KeyError:
db[arr[i][j][1]] = [arr[i][j][0]]4 . 빈 배열 생성하기
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
만든 빈 배열에 값 받기
for _ in range(m):
a,b = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append(b)
#[[], [2, 3], [3, 4], [], []]5 처음과 끝 문자 잘라서 리스트 로 반환
u = "abcdefga"
u = list(u[1:-1])
print(u)6 최대값, 최소값 지정
minv = 1e9
maxv = -1e97 입력값으로 리스트 노드로 연결
for _ in range(m):
a,b = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append(b)8 key를 활용한 정렬
array=[('바나나',2),('사과',5),('당근',3)]
def setting(data):
return data[1]
#key = 함수가 들어가야됨
result = sorted(array, key=setting)
print(result)sorted
result = sorted(array) : 리스트를 입력 받아 정렬된 결과를 출력(새로운 리스트 반환
sort
array.sort() : 리스트를 입력 받지 않고, 원래의 리스트를 그대로 정렬
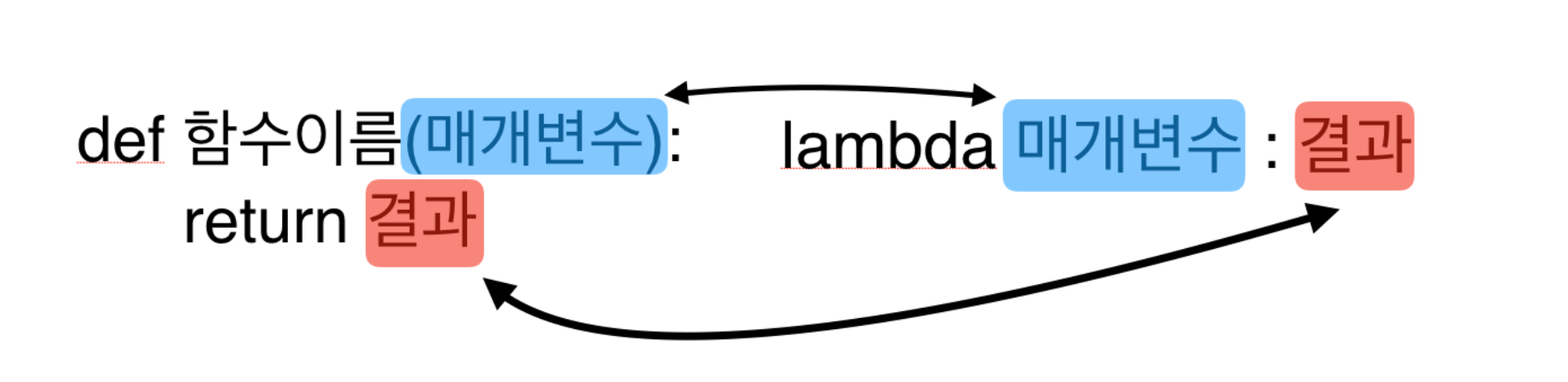
9 람다 사용
10 리스트로 입력 받기
listA = list(map(int, input().split()))
listB = list(map(int, input().split()))1 2 5 4 3
5 5 6 6 5
listA [1, 2, 5, 4, 3]
listB [5, 5, 6, 6, 5]11 빠르게 입력 받기
import sys
#하나의 문자열 데이터 입력받기
input_data = sys.stdin.readline().rstrip()
#입력받은 문자열 그대로 출력
print(input_data)12 특정원소값을 제외하고 입력 받기
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5]
remove_set = {3,5}
#remove_set에 포함되지 않은 값만을 저장
result = [i for i in a if i not in remove_set]13 집합 자료형 정리
a = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
b = set([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
#중복 허용 안함, 순서 없음
print(a | b) #합집합 1,2,3,4,5,6,7
print(a $ b) #교집합 3,4,5
print(a - b) #차집합 1,214 같은 원소가 몇개 들어가 있는지 dict 형태로 반환
from collections import Counter
counter = Counter([1,1,1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,5])
print(dict(counter))15 딕셔너리 정렬 하기
1) key를 이용한 정렬(역순)
res = sorted(db.items(), reverse=True)2) value를 이용한 정렬 (역순)
1.operator.itemgetter 이용
res = sorted(db.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
2.ramda이용
res = sorted(db.items(), key = lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
7
15 11 4 8 5 2 4
{0: 15, 1: 11, 2: 4, 3: 8, 4: 5, 5: 2, 6: 4} -> 정렬전
[(0, 15), (1, 11), (3, 8), (4, 5), (2, 4), (6, 4), (5, 2)] -> value값을 기준으로 정렬됨16 f string 입력
소수점 3자리까지 출력
ss = round(above/students * 100, 3)
print(f'{ss:.3f}%')
40.000%
57.143%
33.333%
66.667%
55.556%17. 리스트내 두 원소 비교
a=[1,3,2,5,4]
for p1, p2 in zip(a,a[1:]):
print(p1, p2)
# 1 3
# 3 2
# 2 5
# 5 418. 리스트 조건 여러개 정렬
sdict = sorted(check.items(), key = lambda x: (-x[1], x[0]))
처음 람다 조건으로 정렬후 그 값 고정한후
두번째람다 조건으로 다시 정렬19.파이썬 정규표현식
# ([\S]*) -> 이렇게 소괄호 해준 부분이 그룹핑 1번 부분 전체가 그룹핑 0번부분
url = re.search(r'<meta[^>]*content="https://([\S]*)"/>',lp).group(1)[PYTHON] 매칭 점수(kakao 2019 프로그래머스)
https://whatisthenext.tistory.com/116
20. 리스트 안에 T 갯수별로 각각 리스트 받기
T = int(input())
arr = []
for _ in range(T):
many = int(input())
arr_in = []
for i in range(many):
arr_in.append(list(map(str, input().split())))
arr.append(arr_in)
print(arr)21. 1~ 36까지의 숫자를 2차원 배열에 column 만큼 나눠서 넣기
board = [[]*columns for _ in range(rows)]
each = []
idx = []
for i in range(1, rows * columns+1):
each.append(i)
for j in range(0, len(each) - 1, columns):
idx.append(j)
for i in range(rows):
board[i] = each[idx[i]:idx[i] + columns]22. 최대힙
q = []
for i in range(T):
heapq.heappush(q, -int(input()))
print(-heapq.heappop(q))넣을때 - 붙여서 넣고, 뺄때도 -붙여서 빼줌
