
Unreal 톺아보기
언리얼 엔진 에디터 기본
Step 1. 학습 내용 요약하기
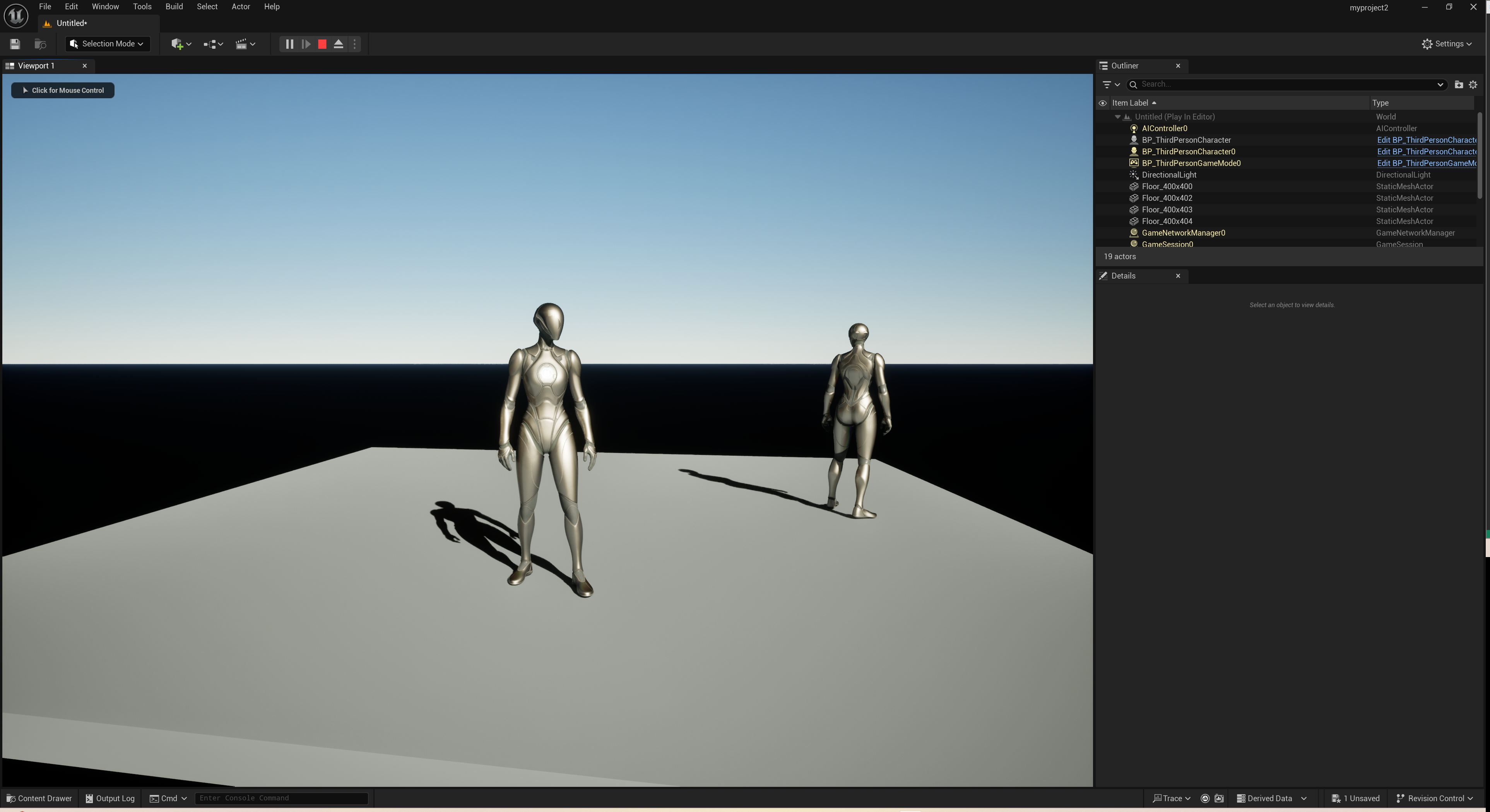
언리얼 엔진의 디폴트 레이아웃, 뷰포트 창, 아웃라이너 패널, 디테일 패널, 콘텐츠 브라우저 및 메인 툴바에 대하여 공부해보자
-
뷰포트
- 뷰포트는 언리얼 엔진에서 가장 큰 부분을 차지하는 패널 또는 창
- 뷰포트에서 레벨을 살펴보고, 액터를 확인할 수 있다.
- 기본적으로 하나가 표시되고(Perspective View) 한눈에 레벨이 어떤 모습인지 볼 수 있게 되어있음
- 윈도우에서 여러 개 추가 가능ㅈ
- 뷰포트의 옵션에는 실시간 렌더링, FPS도 표시, 통계 표시등 다양한 옵션이 있음
- 뷰포트의 레이아웃의 패널을 변경함으로써 상하좌우 다른 시점에서 뷰포트를 볼 수 있음
- 뷰포트는 언리얼 엔진에서 가장 큰 부분을 차지하는 패널 또는 창
-
아웃라이너
- 아웃라이너는 현재 월드 또는 레벨에 있는 모든 항목이 계층 구조로 표시
- 아웃라이너는 월드에 있는 액터를 작업할 때 사용하는 인터페이스
- 액터 선택, 그룹화, 검색, 부모-자식 관계 설정해 복잡한 레벨을 효율적으로 관리 가능
-
디테일 패널
- 특정 액터를 선택했을 때 활성화 됨
- 디테일한 속성이나 설정 값들이 들어있음
-
콘텐츠 브라우저
- 콘텐츠 브라우저는 패널 또는 창으로써 프로젝트에 포함된 모든 콘텐츠를 여기서 볼 수 있음.
- 블루프린트, 이미지 등 커스텀 콘텐츠가 전부 들어있다.
- 콘텐츠 브라우저는 프로젝트에 포함된 에셋에 액세스하는 창이고 아웃라이너는 월드에 있는 액터에 액세스 하는 창
-
에디터 개인 설정
- 에디터 테마나 키보드 숏컷등 개인 설정을 변경할 수 있고, 지역/언어 설정으로 에디터 언어나 프리뷰 게임 언어 설정까지 가능
- 플레이에서 어떤 해상도에서 플레이할지 설정 할 수도 있음, 게임의 오디오도 비활성화 가능하고, 테스트 할 때도 유용하게 사용 가능
- wasd 설정, look and feel옵션
-
프로젝트 세팅
- 디폴트 맵 세팅, 렌더링 세팅, 엔진 세팅등
- 엔진세팅에서 콜리전이 상당히 중요한데 다양한 콜리전 프리셋들을 제공하며 커스텀 콜리전도 생성할 수 있다.
- 입력세션,, 레거시 인풋 -> 향상된 인풋으로 대체됨
- 렌더링 세팅에서는 프로젝트의 렌더링 부분과 관련된 모든 세팅을 변경할 수 있음, 모바일에 적용되는 부분도 있고, 레이트레이싱 옵션이나 글로벌 일루미네이션 메서드, 리플렉션 메서드 등이 있다.
- 플랫폼 세팅에서는 플랫폼 지원을 활성화
-
월드세팅
- 게임모드나 중력 오버라이드가 가능하여 현재 레벨에서만 다르게 오버라이드 가능
- 킬Z (적용해놓은 값에서 벗어나면 액터가 파괴됨)
Step 2. 실습 프로젝트 따라하기
-
기본 캐릭터와 삼인칭 템플릿
-
박스 추가
-
박스 충돌 무시
-
프로젝트를 진행하면서 어려웠던 점
- 요소나 옵션이 어느 위치에 있는지 익숙치가 않아서 액터 추가하는것도 버벅이면서 진행했습니다.
- 카메라 이동이나 액터 이동도 아직은 조금 어색한 느낌
- 전체적으로 언리얼 엔진에 익숙해지지 않은 점
-
새로운 기능이나 툴
- 메인 툴바에서 액터를 추가하는 것
- 창에서 아웃라이너, 디테일 패널 추가하는것
- 디테일 패널에서 콜리전프리셋을 NoCollision으로 설정해본 것
-
다음 프로젝트에서 도전하고 싶은 아이디어?
- 다른 액터들도 다뤄보기
- 조명 추가??
- 다양한 기능 사용해보기
언리얼 엔진 5와의 첫 시간
Step 1. 학습 내용 요약
-
언리얼 엔진을 실행하면 에디터가 실행 되며 템플릿이나 기본 프로젝트 생성 가능
-
프로젝트 생성 시 뷰포트가 보이고 이를 통해 월드를 볼 수 있음
- 카메라 wasd qe로 이동하여 월드 탐색 가능
-
오브젝트를 이동 회전 늘리기 줄이기 등 조작 가능
-
콘텐츠 브라우저에서 자유롭게 뷰포트로 에셋 추가 가능
-
Fab에서 필요한 에셋들을 프로젝트에 추가
- 기존 프로젝트에 추가하는 에셋 팩
- 새 프로젝트 생성에 사용하는 전체 프로젝트
- 다른 프로젝트로 콘텐츠를 이주(migrate)할 수 있음
-
첫 레벨 생성
- 스태틱 메시 생성 (가장 기본적인 3D 모델 유형, 정적인 오브젝트를 의미)
- 라이팅이 없으면 material과 object가 라이트에 반응할 수 없어 아무것도 안 보임
- 라이팅 없이 레벨 작업을 하려면 뷰모드를 Unlit 으로 설정해 라이트 없이 작업 가능
- scale로 크기 조정 및 alt를 통해 복사, Ctrl, Shift기능 다 먹음
- Unlit모드는 에디터에서만 사용하므로 라이트를 추가해야 함
- directional light추가 (태양처럼 작동)
- 이제 플레이하면 캐릭터와 스태틱 메시가 보이지만 캐릭터가 카메라의 위치에서 스폰됨
- player start 지정
- 캐릭터가 요소들과 겹치거나 충돌하게끔 설정하면 (콜리전) bad size라고 나옴
- 키보드의 end키를 누르면 지면에 가장 가까이 설정 가능 (수직으로 가장 가까운 항목에 스냅)
- 플레이어의 스폰 위치가 이상하다면 플레이 버튼 옆 점 세 개에서 default player start인지 확인하기
- 대기 추가
- visual effect에서 sky Atmosphere추가
- directional light와 연동 ( Atmosphere sunlight 체크되어있는지 확인 )
- directional light를 회전시킬 때마다 그에맞게 대기가 변함 (석양이 진다던지)
- directional light와 연동 ( Atmosphere sunlight 체크되어있는지 확인 )
- 안개나 구름 등등 많은거 추가해보자
- visual effect에서 sky Atmosphere추가
- 강도 설정, 라이트 컬러
- Sky light(앰비언트 라이트, 그림자에 비춰지는 라이트)
- 언리얼 엔진은 인간의 눈을 모방하려고 하기 때문에 어두운 곳에서 밝은 곳으로 가면 라이팅이 서서히 밝아지는 등 시각적응이 있다.
- PostProcessVolume에서 Min, Max Brightness로 수정가능
- 다시 directional light로 와서 Light Shaft Occlusion, Light Shaft Bloom 효과를 키면 블룸 효과가 나타남
- 모빌리티
- Static, Stationary, Movable
- Stationary가 둘의 중간, 움직일 수는 없지만 다이나믹 섀도우가 있음
- Static을 설정할 경우 Build > Build Lightning only 에서 라이팅을 빌드하면 퍼포먼스가 개선되며 모바일 기기에서 도움이 된다.
- Lumen
- 언리얼엔진 5에서 도입
- Movable 라이트 필
- 실시간으로 라이트 바운스 계산, 실제 빛의 작동 방식을 모방하는 기능
-
Unreal Engine 5에서 '프로젝트 생성' 단계의 주요 흐름
- 템플릿 선택 -> 프로젝트 세팅 -> 프로젝트 시작
-
'에디터 인터페이스'의 핵심요소 3가지
- 뷰포트
- 레벨의 모습을 보여주는 작업 공간
- 액터를 직접 조작하여 배치 수행가능
- 아웃라이너
- 현재 레벨의 모든 액터의 목록을 보여줌
- 폴더를 체계적으로 정리하여 관리하기 좋음
- 디테일 패널
- 액터를 선택했을때 세부속성이 나타남
- 위치, 충돌 등 제어
- 뷰포트
-
Unreal Engine에서 'Actor'란?
- 레벨에 배치될 수 있는 모든 오브젝트의 기본
- 눈에 보이거나 보이지 않는 부분까지 레벨을 구성하는데 사용됨
Step 2. 실습
- floor, light, atmosphere, 캐릭터 설정
C++
- 메서드들 사용해보기
int main() {
string input = "2025_KIM";
string year = input.substr(0, 4);
string name = input.substr(5);
cout << "년도 : " << year << endl;
cout << "이름 : " << name << endl;
cout << "원본 : " << input << endl;
input.replace(0, 4, "2026_");
cout << "변경 후 : " << input << endl;
size_t find_underbar = input.find("_");
size_t find_underbar2 = input.find("_", find_underbar + 1);
size_t find_2025 = input.find("2025");
cout << "첫번째 언더바 위치 : " << find_underbar << endl;
cout << "두번째 언더바 위치 : " << find_underbar2 << endl;
if (find_2025 == string::npos) {
cout << "2025는 변경되었다." << endl;
}
cout << "문자열이 비어있는가? " << input.empty() << endl;
input.clear();
cout << "input 출력: " << input << " 없다! " << endl;
cout << "clear()후 문자열이 비어있는가? " << input.empty() << endl;
input.append("hi");
cout << input << endl;
input += " hello";
cout << input << endl;
input.insert(0, "everyone ");
cout << input << endl;
input.erase(0, 9);
cout << input << endl;
cout << input.compare("gi") << endl;
// 완전일치 0, 양수 반환 (input의 첫번째 인자가 gi의 첫번째 인자보다 사전순으로 뒤에오므로 양수, 음수반환은 그 반대
input.push_back('z');
cout << input << endl;
input.pop_back();
cout << input << endl;
input.resize(2);
cout << input << endl;
input.resize(5, 'o');
cout << input << endl;
string input2 = "swappp!!!";
input.swap(input2);
cout << "input : " << input << endl;
cout << "input2 : " << input2 << endl;
char lowA = 'a';
char changeA = toupper(lowA);
cout << "lowA : " << changeA << endl;
changeA = tolower(changeA);
cout << "lowA : " << changeA << endl;
return 0;
}
STL
-
STL이란
- C++ 표준 라이브러리 일부
- 코드 재사용성이 높다.
- 컨테이너
- 데이터를 저장하고 관리하는 객체
- vector, map, list
- 알고리즘
- sort(), next_permutation();
- 반복자
- 컨테이너의 요소 순회, 접근방법 제공
- 포인터처럼 동작
- 반복자는 컨테이너 요소에 접근하고 순회하는 수단이며 알고리즘은 반복자를 통해 컨테이너 내부 데이터를 처리, 이것이 STL의 중요한 설계 원칙인 "알고리즘과 컨테이너의 분리"
-
순방향 반복자
- begin(), end()
- 반복자가 가리키는 곳을 읽거나 수정가능
- ++는 지원, -- 미지원 , 한 방향으로만 움직일 수 있음
-
역방향 반복자
- rbegin(), rend()
- 반복자가 가리키는 곳을 읽거나 수정가능
- ++, -- 둘 다 지원 , 양 방향으로 움직일 수 있음
-
vector
- vector v(5, 10) : 크기5 + 10으로 초기화된 벡터 생성
- push_back(), insert(), clear() { O(N) }, pop_back(), erase()
- 중간 삽입 삭제가 빈번하면 덱을 고려해보자 -> 시간복잡도로 인해 pass fail이 갈릴 수가 있다.
- 벡터의 원소개수가 내부 용량보다 커지면 벡터는 재할당을 하는(2배씩) 이게 O(N)의 시간복잡도를 가지므로 원소개수를 알고있다면 reserve()로 미리 할당하는게 좋다.
- vector는 =로 할당가능한데 왜 그냥 정적배열들은 불가? (vector는 =로 깊은복사(값 복사를 위해 새로 메모리 확보하고 내용 전부 복사, 얕은 복사는 주소값만 복사함 (사본과 원본이 같은 메모리 공유)) 가능,
vector 내부(클래스)에서 =를 오버로딩해서 사용하고 있기 때문
-
set
- 중복되지 않는 원소들을 정렬된 상태로 저장하는 컨테이너
- 헤더를 포함해야 한다.
- set도 =로 기존 셋 복사해서 사용 가능 set s2 = s1;
- insert(), erase(), clear() { O(N) }
- 셋은 레드/블랙 트리 사용하므로 삽입/삭제에서 O(log N)
- 정렬상태 유지하려는 속성으로 인해 수정을 하려면 기존 값을 삭제하고 새로 삽입
- 정렬상태유지하며 중복도 필요하면 multiset사용
- 정렬이 필요없고 빠른탐색이 중요한 경우에는 unordered_set사용
- 바로 정렬하는 특성탓에 삽입순서가 유지되지 않음 필요한 경우 vector나 list사용
- set은 인덱스를 지원하지 않는다.
-
map
- 키-값 쌍으로 이룬 컨테이너
- 중복 키 불가, 키를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬
- 헤더파일 포함
- map<keyType, valType> m;
- 얘또한 = 로 기존 맵 복사 가능
- m[key] = newVal (key가 없으면 자동으로 key-val쌍 추가) , m.at(key) = newVal; ( []와 달리 key가 존재하지 않으면 out_of_range 예외 발생)
- insert(), erase() {O(log N)}, clear() {O(N)}
- 키는 명확해야해서 부동소수점 같은거 사용하지말자
- insert는 key값이 이미 있는경우 삽입에 실패한다.
-
sort
- 기본적으로 오름차순, sort(first, second)
- sort(first, second, comp) 처럼 사용할 수 도 있다.
- comp는 비교함수, comp(a,b)에서 true면 a가 b보다 먼저 와야한다는 뜻
-
find()
- first, last 내에서 특정 값과 일치하는 첫 번째 원소를 선형 탐색한다. 일치하는 값이 있으면 해당 원소를 가리키는 반복자를 반환하고, 없으면 last반복자를 반환
- find(first, last, value), 시간복잡도는 O(N);
-
count()
- first, last내에서 특정 값이 몇 번 등장하는지를 계산하여 반환
- count(first, last, value); 시간복잡도 O(N)
-
unique()
- first, last내에서 연속된 중복 제거
- 실제로 컨테이너에서 원소가 삭제되는것은 아니고, 첫번째 발생만 유지되도록 원소들을 앞쪽으로 덮어씌움
- erase()와 함께 사용해 완전히 제거
- unique(first, last); O(N)
- 중복 제거 후 마지막 고유 원소의 다음 위치를 가리키는 반복자를 반환한다.
- 잊지 말아야 할것이 unique는 바로 옆의 중복(연속된)만 제거한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> filled(5, 100);
for (int val : filled) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
filled.insert(filled.begin() + 2, 99);
for (int val : filled) {
cout << val << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 중간삽입은 기존 원소들은 뒤로 다 밀어야해서 O(N)으로 비효율적
cout << "size : " << filled.size() << ", capacity : " << filled.capacity() << endl;
// capacity()는 용량 -> 초과시 2배씩 늘어남 O(N), 대충 크기알면 reserve()사용하는게 효과적
set<int> s = { 3, 1, 3, 2, 5 };
for (int v : s) {
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s.insert(2);
s.insert(8);
for (int v : s) {
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s.erase(2);
s.erase(3);
for (int v : s) {
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s.clear();
cout << "Size after clear : " << s.size() << endl;
float a1 = 0.3;
float a2 = 0.2;
a2 += 0.1;
bool a3 = a1 == a2;
cout << a3 << endl; // float라 1출력
double b1 = 0.3;
double b2 = 0.2;
b2 += 0.1;
bool b3 = b1 == b2;
cout << b3 << endl; // double이라 정밀 오차값으로 인해 0출력
map<string, int> myMap = { {"Apple", 1}, {"Banana", 2}, {"Cherry", 3} };
myMap.at("Banana") = 20;
try {
myMap.at("Durian") = 4;
}
catch (out_of_range& e) {
cout << "예외 발생 : " << e.what() << endl;
}
for (auto& p : myMap) {
cout << p.first << ": " << p.second << endl;
}
auto result = myMap.insert({ "Banana", 10 });
if (!result.second) {
cout << "insert 실패 !" << endl;
}
for (auto& p : myMap) {
cout << p.first << ": " << p.second << endl;
}
vector<string> names = { "Alice", "Dan", "Bob", "Christina" };
sort(names.begin(), names.end(), comp);
for (const string& name : names) {
cout << name << endl;
}
vector<int> vec = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
auto it = find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 30);
if (it != vec.end()) {
cout << "찾은 값 : " << *it << endl;
}
auto it2 = find(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 99);
if (it2 == vec.end()) {
cout << "값이 없습니다" << endl;
}
vec.push_back(10);
vec.push_back(10);
vec.push_back(10);
int res = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 10);
cout << "10의 개수 : " << res << endl;
int res2 = count(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 1);
cout << "1의 개수 : " << res2 << endl;
vector<int> v = { 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3 };
v.erase(unique(v.begin(), v.end()), v.end());
for (int val : v) {
cout << val << " ";
}
return 0;
}
부동소수점
부동소수점은 실수를 이진수만 사용하는 컴퓨터에 저장하는 방식 이 과정에서 오차가 조금씩 생김
예를들어 js에서 0.3 === 0.2+0.1은 다름
- c++에서
float a1 = 0.3;
float a2 = 0.2;
a2 += 0.1;
bool a3 = a1 == a2;
cout << a3 << endl;이렇게 구성하니 출력이 1이나옴 왜그럴까???
C++에서 소수점 리터럴(0.3, 0.1 같은)은 기본적으로 double 타입으로 취급되는데 이것을 float로 타입으로 받았기 때문에 float로 변환하는 과정에서 double의 정밀한 오차값이 사라짐
double a1 = 0.3;
double a2 = 0.2;
a2 += 0.1;
bool a3 = a1 == a2;
cout << a3 << endl;double로 변경하니 의도한대로 0출력함
