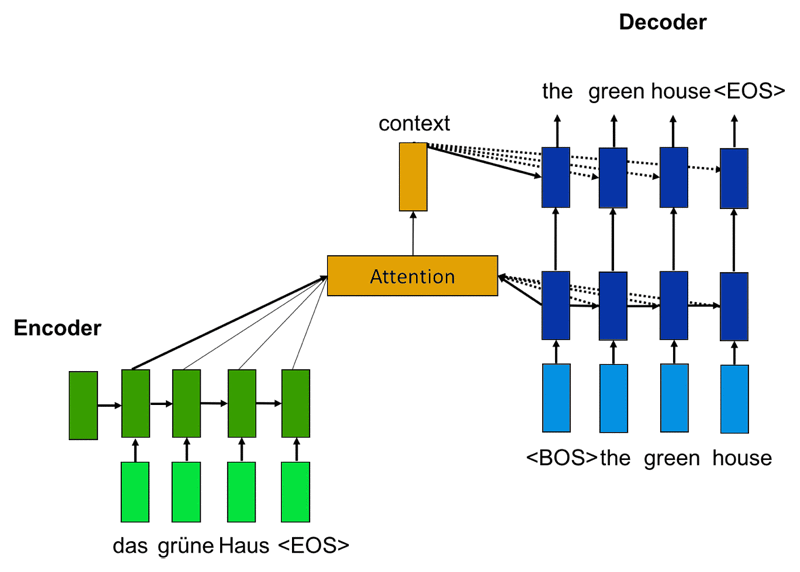
Decoding: 인코딩(encoding)된 벡터를 다시 텍스트로 변환하는 것 (텍스트를 생성하는 과제(text generation)에서는 주어진 토큰 이후에 어떻게 토큰을 출력해야 하는지 방식을 정해야 하므로 디코딩 방법이 필요)
Greedy Search
- 각 타임 스텝마다 다음에 등장할 토큰으로 가장 높은 확률을 가진 토큰 단 하나만을 계산하여 선택하는 방식 (Sequence로서의 전체적인 문장의 확률값을 보는 것 X)
- Usually we decode until the model produces a token
- Problem: 해당 타임 스텝에서 최적의 토큰이 전체 문장에서 최적의 토큰은 아닐 수 있다는 문제가 발생 + 뒤로 돌아갈 수 없음
Exhaustive Search
- 가능한 모든 sequence 경우의 수를 고려하는 방식

-> joint probability 최대가 되는 sequence 선택
-> Complexity is O(V^t) where V is vocabulary size, t means time step
Beam Search
- On each time step of the decoder, we keep track of the k most probable partial translations (which we call hypothesis) where k is the beam size
- A hypothesis y1,...,yt has a score of its log probability:
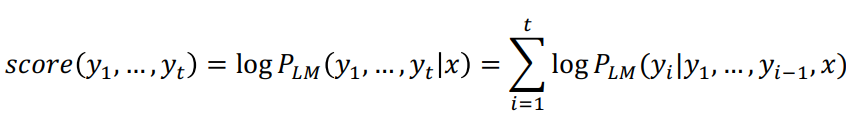
-> joint probability에 log를 취해줌으로써 곱셈이 아니라 덧셈이 됨
-> 이때 log 함수는 단조증가 함수이므로, 확률값과 Score 값이 비례. - For each of the k hypotheses, find top k next words and calculate scores
- If different hypotheses my produce tokens on different timesteps? When a hypothesis produdces , that hypothesis is complete, then place it aside and continue exploring other hypotheses via beam search
(Usually we continue beam search until:- we reach time step T (where T is ome pre-defined cutoff), or
- we have at least n completed hypotheses (where n is the pre-defined cutoff)
- Problem: longer hypotheses have lower scores(항상 -값을 더해주는 형태로 score 계산하므로)
-> Nomalized by length
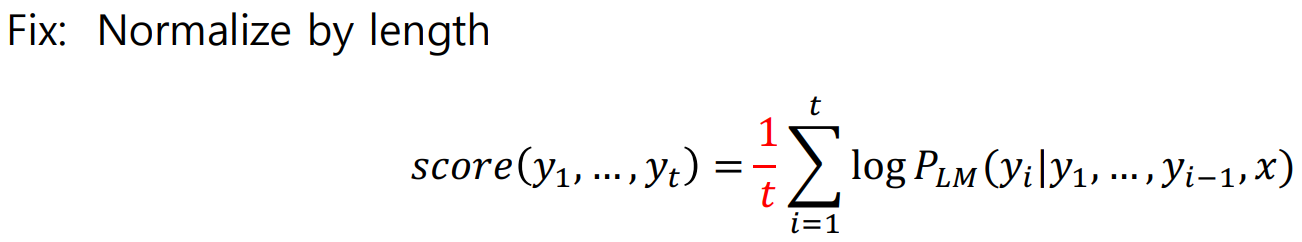
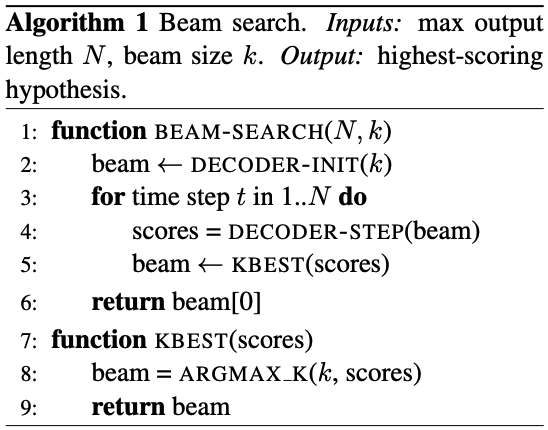
-> beam of size k conatinas a set of active hypotheses
-> At each time step t, the decoder model produce a distribution over the target-language vocabulary V_T. THis produces a large matrix of dimensions k X |V_T|. Conceptually, a (row, column) entry (i,j) in this matrix contains the state obtained from starting from the ith state in the beam and generating the target word corresponding to the jth word of V_T.
GBS(Grid Beam Search)
≒ adding an additional dimension to the beam (base bim size k X the number of constraints)
- For C constraints, this is accomplished by maintaining C+1 separate beams OR banks, B_0, B_1, ..., B_C, wehre B_i groups together hypotheses that have generated (or met) i of the constraints.
- Decoding proceeds as with standard beam search, but with the addition of bookkeeping that tracks the number of constraints met by each hypothesis, such that each bank is filled at each time step.
- When beam search is complete, the hypothesis returned is the highest-scoring one in bank B_C.
=> Impractical. B/c the beam size changes for every sentence
=> Decoding complexity is linear in the numer of constraints. B/c the effective beam size is k * (C+1)
DBA (fast lexically-constrained decoding via Dynamic Beam Allocation for NMT)
-
We maintain a single beam of size k, as with unconstrained decoding, and dynamically allocate the slots of this beam across the constraint banks at each time step.
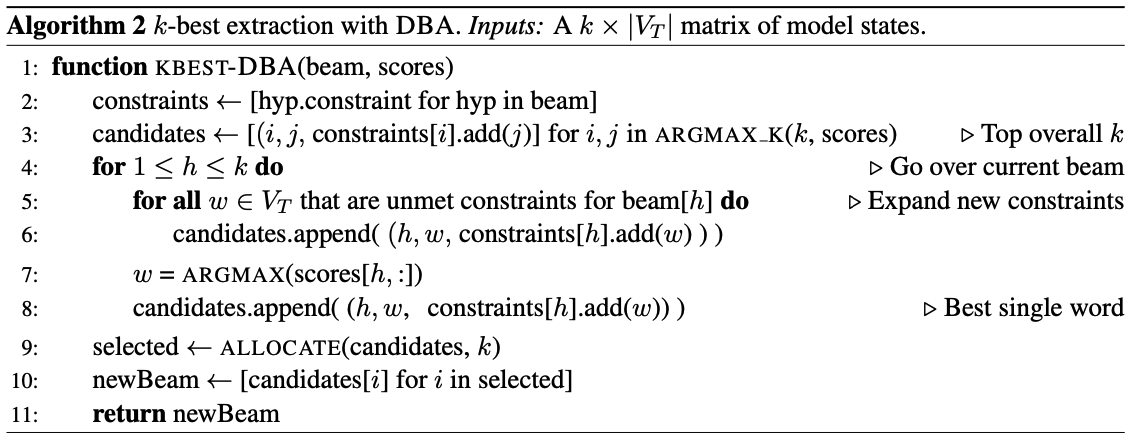
-> Algorithm 1의 KBEST function을 다음과 같이 대체
-> candidates = (current beam, new word, expected constraints set)
-> candidates (1) from the k best items, (2) from extending each hypothesis with all unfilled constraints, (3) from its single-best token (to ensure consideration of partially-completed hypotheses)
-> When allocating a size-k beam across C+1 constraint banks(the portion of the beam reserved for items having met the same number of constraints), where C may be greater than k, we use a simple allocation strategy, setting each bin size to [k/C], irrespective of the timestep. Any remaining slots are assigned to the "topmost" or maximally constrained bank, C. But! There is bank adjustment. An overfilled bank is one that has been allocated more slots than it has candidates to fill. Each such overfilled bank, in turn, gives its extra allotments to banks that have more candidates than slots, looking first to its immediate neighbors, and moving outward until it has distributed all of its extra slots. In this way, the beam is filled, up to the minimumu of the beam size or the number of candidates. -
Hypotheses are not allowed to generate the end-of-sentence token, , unless they have met all of their constraints. when beam search is finished, the highest-scoring completed item is returned.
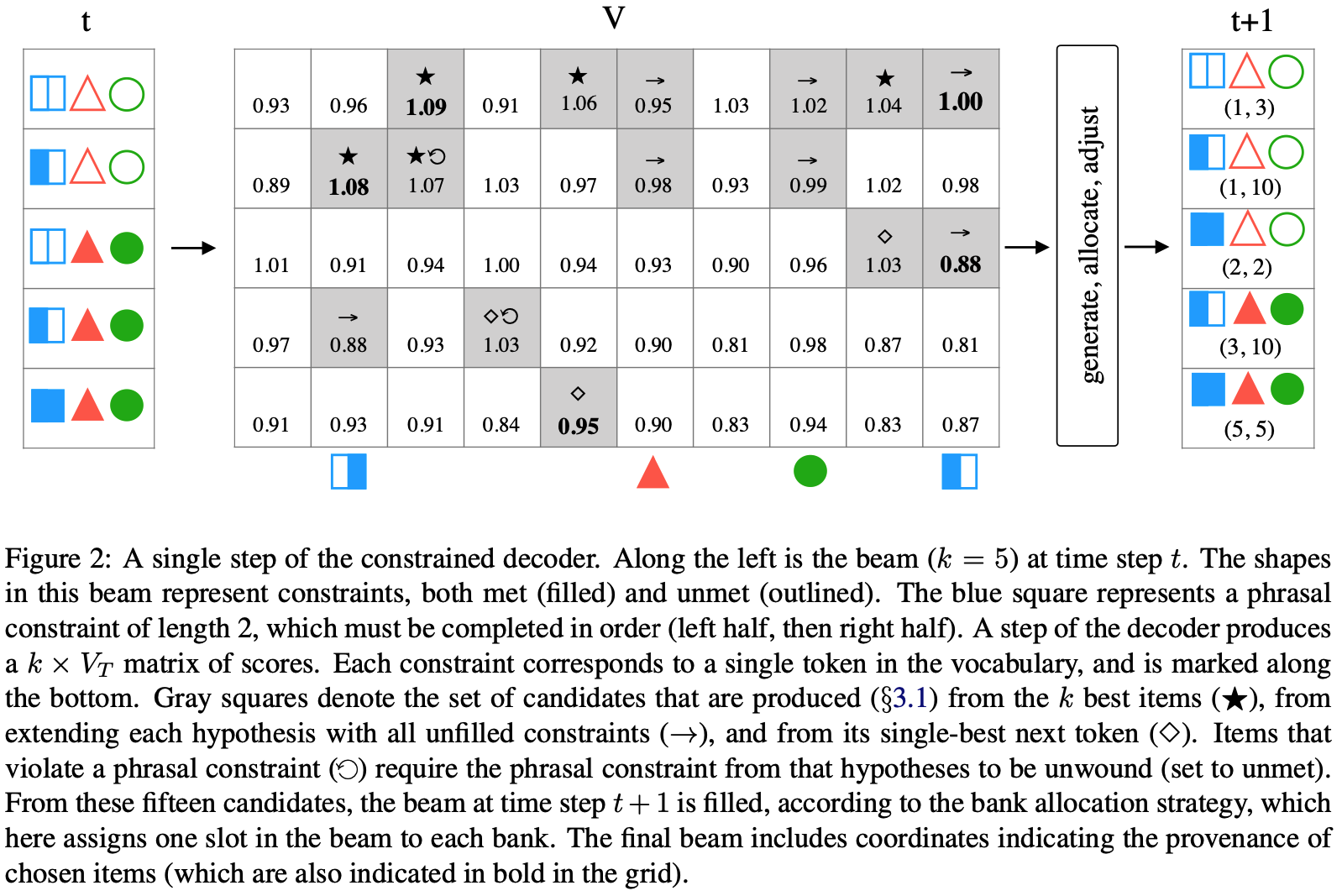
-> 회색으로 칠해진 word가 KBEST-DBA에서 candidates list에 포함한 beam h의 후보 word
<참고>
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/train-neural-machine-translation-models-with-sockeye/
https://terms.naver.com/entry.naver?docId=6653720&cid=69974&categoryId=69974
https://blog.naver.com/eungang0301/223242740713
https://www.boostcourse.org/ai330/lecture/1455757?isDesc=false
https://showmiso.tistory.com/156
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.06609.pdf