BFS 문제를 풀다가 정리해두고 싶은 문제가 있어서 가져와본 문제!
다음과 같은 그래프가 있다고 해보자

양방향이 아닌 단방향으로 되어있고,
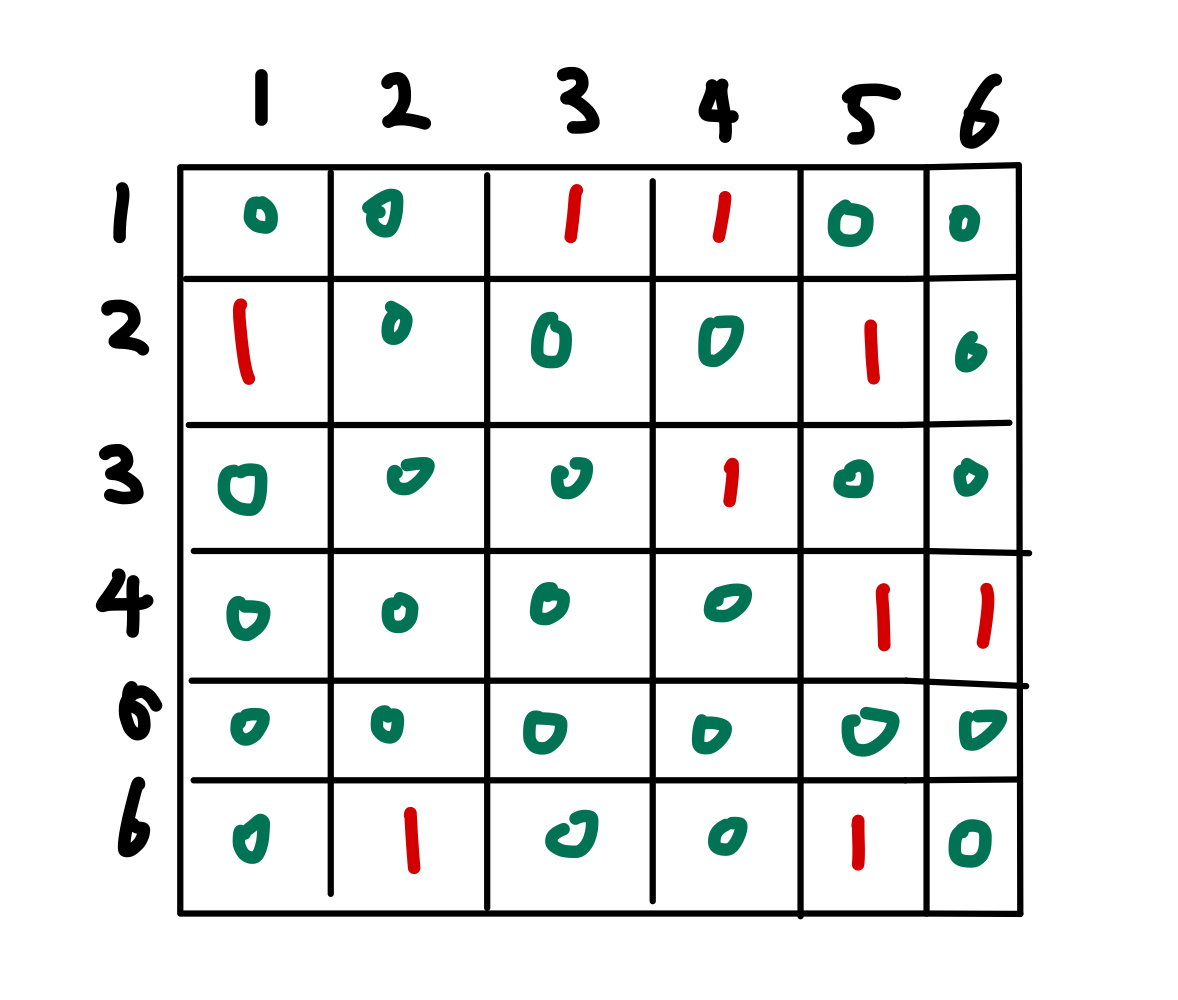
연결을 나타내보면 위처럼 나타낼 수 있다.(1이 연결, 0은 연결x 을 나타내었다.)
문제 해결 전, 그냥 BFS 문제이니까 큐를 이용하고 단순한 배열만을 이용하여 문제를 풀어왔었는데, 그렇게하면 처음 1->3 노드로 접근을 했을 때는 상관이 없는데, 4-> 5,6 노드로 접근하는게 문제였다.
4노드를 poll() 하고 4노드와 연결된 노드를 찾은 후, 거리를 구하러면 거리를 저장을 할 방법이 필요했는데, 그 해결방법에 처음엔 접근하지 못했었다.
고민을 하다가 원하는 노드까지 거리를 구하기 위해 배열을 하나 생성하고(dis[]), 노드 1의 거리를 0으로 생각했을 때 노드 1에서 한 노드씩 더 갔다고 하기위해 +1 을 하여 그것을 배열에 저장했다.
( 즉, 1->3 까지 거리는 1노드의 거리가 0이니까 dis[1] = 0, 그러면 dis[3] = dis[1] + 1 을 하면 dis[3] = 2 가 되고 그것을 저장해주는 방법을 사용했다.)
그리고 문제에서 사용한 ArrayList !!
✅ArrayList 특징
java-arraylist 📝 참고링크
- 연속적인 데이터의 리스트 (데이터는 연속적으로 리스트에 들어있어야 하며 중간에 빈공간이 있으면 안된다)
- ArrayList 클래스는 내부적으로 Object[] 배열을 이용하여 요소를 저장
- 배열을 이용하기 때문에 인덱스를 이용해 요소에 빠르게 접근할 수 있다.
- 크기가 고정되어있는 배열과 달리 데이터 적재량에 따라 가변적으로 공간을 늘리거나 줄인다.
- 그러나 배열 공간이 꽉 찰때 마다 배열을 copy하는 방식으로 늘리므로 이 과정에서 지연이 발생하게 된다.
- 데이터를 리스트 중간에 삽입/삭제 할 경우, 중간에 빈 공간이 생기지 않도록 요소들의 위치를 앞뒤로 자동으로 이동시키기 때문에 삽입/삭제 동작은 느리다.
- 따라서 조회를 많이 하는 경우에 사용하는 것이 좋다.
.
.
📝 문제-그래프최단거리(BFS)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Inflearn54 {
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> graph;
static int n,m; // 6 9
// 방문배열
static boolean[] visited;
// 최단거리를 저장할 배열
static int[] dis;
static void bfs(int v) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited[v] = true;
dis[v] = 0;
queue.offer(v);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int current = queue.poll();
for(int find : graph.get(current)) {
if(!visited[find]) {
visited[find] = true;
dis[find] = dis[current] + 1;
queue.offer(find);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
m = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
// 실수 //
// int i=1 부터 헸었는데, 생각해보면 visited,dis 배열 모두
// 인덱스 번호를 1 부터 시작하기위해 n+1 한 크기의 배열이다.
// 그러므로 list의 크기를 맞춰줘야 한다.
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
// ArrayList 에 n 만큼의 비어있는 공간 할당
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}
visited = new boolean[n+1];
dis = new int[n+1];
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(bf.readLine());
int u = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// u 인덱스에 v를 저장
graph.get(u).add(v);
}
bfs(1);
for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
System.out.println(i + " : " +dis[i]);
}
}
}<입력>
6 9
1 3
1 4
2 1
2 5
3 4
4 5
4 6
6 2
6 5
<출력>
2:3
3:1
4:1
5:2
6:2
✍️ 내가 한 실수
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++) {
// ArrayList 에 n 만큼의 비어있는 공간 할당
graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
}이 부분에서
int i=1 로 시작을 했었는데, 생각해보면 visited[],dis[] 배열 모두
인덱스 번호를 1 부터 시작하기위해 n+1 한 크기의 배열이다.
그러므로 list의 크기를 맞춰줘야 한다.
