
-
DDL 은 테이블, DML 에서는 튜플을 관리한다.
-
테이블을 정의한다는 것?
-
스키마 / 어트리뷰트의 도메인 / 참조무결성 정의 / 뷰와 인덱스 / 보안, 권한 정보 / 물리적 저장 구조.
Domain Types in SQL
- 학년 어트리뷰트 > 타입은 integer.
- 도메인 타입을 정의한다라고 한다.
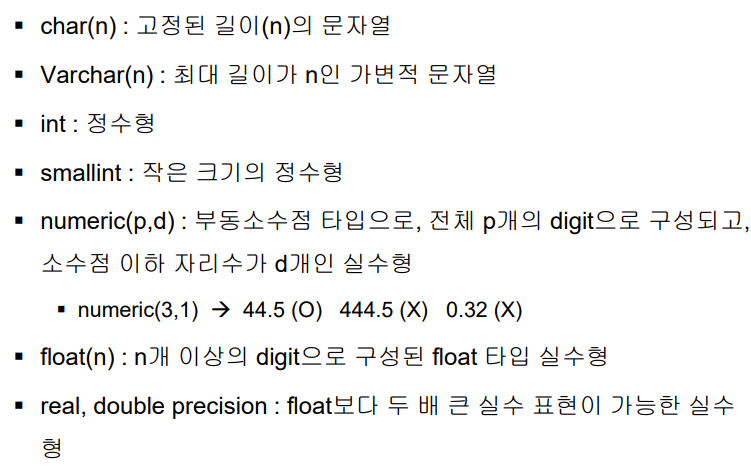
- numeric(전체 자리수, 이하자리수)
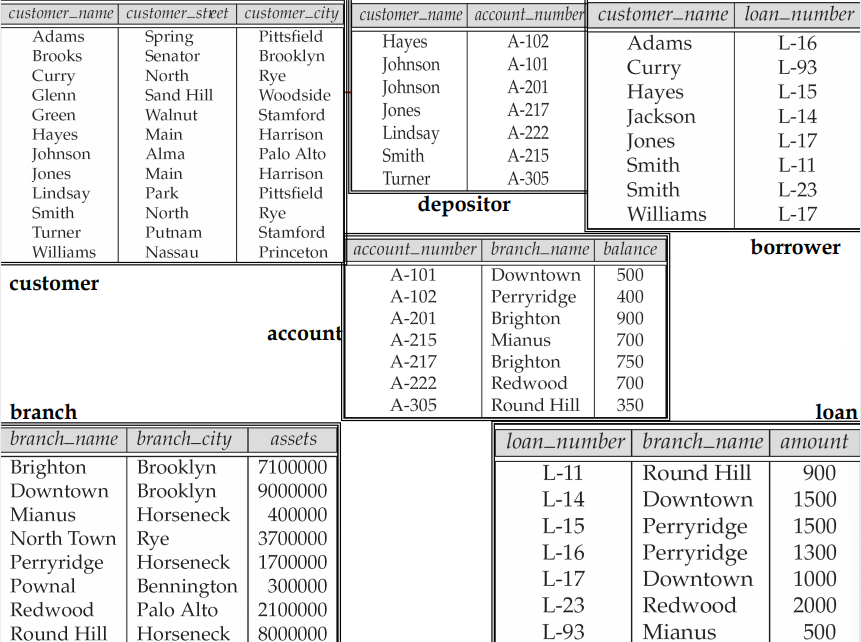
- account_number 은 char(5) 이 적합하다.
- branch_name 은 Varchar
- balance 는 int
- 타입과 맞지 않는 튜플이 들어오면 오류를 일으킨다.
- 메모리 효율적 관리 (바이트를 정할 수 있기 때문에)
Data Definition 작업의 종류
- 스키마 정의 / 어트리뷰트의 도메인을 정의(타입 포함) / 어트리뷰트별 제약 조건 정의
- 기존 테이블 아예 제거 또는 변형(여기선 튜플이 아닌 스키마의 변형을 의미한다.)
- Data Manipulation 에서의 변형은 튜플의 변형을 이야기한다. (구분하자.)
Create Table

어트리뷰트 (데이터타입)를 먼저 정의, (integrity-constraint 를 정의: 도메인 제약, 참조무결성 등)
- r은 테이블의 이름 / A는 i번째 어트리뷰트 / D는 Ai의 데이터타입.
실제로 보면 다음과 같다.

- not null 이란 값은, 해당 어트리뷰트에서만큼은 null 값을 허용하지 않는다는 것이다.
Integrity Constraints in Create Table
- not null
- primart key 를 설정해준다. (여러 어트리뷰트 셋으로 구성될 수 있다.)
- null 값을 가지면 안된다!

create table branch
(branch_name Varchar(15),
branch_city Varchar(30),
assets int,
primary key(branch_name))Drop Table and Alter Table
drop table r: r이라는 테이블 통째로 삭제
alter table r add A D: r 테이블에 A어트리뷰트 타입 D 추가
- 새로 추가되는 속성의 값을 null 로 할당
alter table r drop A: r 테이블에서 어트리뷰트 A 삭제 - 삭제되는 속성이 다른 테이블에서 참조되고 있을 수 있음.
- 🤔 참조무결성: 참조하는 속성의 값은 참조되는 속성에 존재하는 값만 저장할 수 있다.
이들은 모두 Data Definition 의 범위이다.
Data Manipulation in SQL
- 튜플단위 조작의 종류: Select, Insert, Delete, Update
Basic Query Strcture for Select
-
select 쿼리의 표현
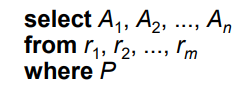
-
특정 어트리뷰트를 뽑아내는 것.
-
모든 테이블을 하나로 합친 후 조건을 만족하는 튜플을 뽑음.
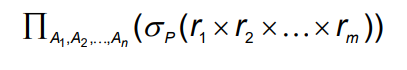
-
결과는 테이블 형태. (그냥 보여주고 끝남.)
The select Clause

select branch_name
from loan
where : 조건이 없으므로 생략
프로젝션_branch_name(loan)
사실관계
SQL은 중복된 튜플을 제거하지 않음.(이전 algebra와는 다름.)
중복을 제거하기 위해 select 구문에 distinct 키워드 사용.
Relation 속한 모든 속성을 나열하는 경우 * 를 사용 (특정 테이블의 모든 속성)
select loan *
from loanSelect 구문에서는 산술 표현식을 쓸 수 있다. (갱신이 아닌 JUST 출력, 갱신은 update 임!)
select loan_number, branch_name, amount * 100 # amount 에는 각 값에 100을 곱해서 추출.
from loanwhere Clause
찾고자 하는 조건을 명시하는 게 where 이다.
ex) Perryridge 지점에서 개설된 모든 대출 계좌 중 금액이 1200 보다 많은 계좌를 찾으시오. (대출은 amount)
select loan_number
from loan
where branch_name = 'Perryridge' and amount > 1200- between 키워드
대출금액이 90000 이상, 100000 이하라면?
select loan_number
from loan
where amount between 9000 and 1000009000 이상, 100000 이하를 제외하고 싶다면?
select loan_number
from loan
where amount not between 9000 and 100000The from Clause
select 가 속성, where 은 조건이라면 from 은 테이블 이름을 쓰면 된다.
from 절의 테이블이 2개 이상이라면 Cartesian product 를 수행한다. = 하나의 테이블로 합친다.
ex) Perryridge 지점에서 대출 계좌를 개설한 모든 고객의 이름(customer_name)과 대출 계좌 번호(loan_number), 그리고 대출 금액(amount)을 찾으시오.

select customer_name, borrower.loan_number, amount
from borrower, loan
where borrower.loan_number = loan.loan_number and branch_name = 'Perryridge' 이때 select 에 loan_number 가 아닌 borrower.loan_nubmer 또는 loan.loan_number 가 들어가야 한다는 점을 명심하자. 합친 이상 loan_number 은 없다!