논문에서 소개된 모델 아키텍처의 사용법을 간단히 정리하여 소개하는 포스팅입니다.
Introduction
지난 Revisiting Deep Learning Models for Tabular Data 논문에서는 정형 데이터를 위한 ResNet-like 아키텍처(이하 ResNet)를 소개하였습니다. Tabular DL 모델 간 성능 실험 결과를 통해 ResNet이 Deep Tabular Learning에서 효과적인 베이스라인 아키텍처가 될 수 있음을 확인하였습니다.
ResNet은 다음의 수식으로 공식화할 수 있었습니다.

이번 포스팅에서는 rtdl 라이브러리를 통해 정형 데이터를 위한 ResNet 아키텍처의 사용 방법에 대해 간단히 알아보겠습니다. 모델 학습을 위해 PyTorch를 사용하였으며, Optuna 라이브러리를 사용한 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝 예시까지 확인합니다.
사용한 데이터셋은 Adult 데이터셋입니다. 다음과 같은 특징을 가집니다.
- 이진 분류 문제 (소득이 50K 이상인지 판별)
- 숫자형 특성과 범주형 특성이 모두 존재
모든 코드는 Google의 Colaboratory(Colab)에서 구현되었습니다.
Setting
구현에 필요한 패키지를 설치합니다. Colab의 특성상 아래 !pip 코드 블럭을 실행한 후, 런타임을 다시 시작한 뒤 처음부터(!pip 부터) 실행해야 합니다.
# rtdl: ResNet, FT-Transformer
!pip install rtdl
!pip install optunaimport pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import random
from tqdm import tqdm
import rtdl
from typing import Any, Dict
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, LabelEncoder
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import optuna
from optuna import Trial
from optuna.samplers import TPESamplerColab의 GPU를 사용합니다.
# device check
device = ('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f"Using {device} device")출력
Using cuda device
def seed_everything(seed = 21):
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
os.environ["PYTHONHASHSEED"] = str(seed)
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = Truedef read_split_data():
df = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/MyDrive/Data/adult.csv')
X = {}
y = {}
X['train'], X['test'], y['train'], y['test'] = train_test_split(df.iloc[:, :-1], df.income, test_size = 0.10, random_state=21)
X['train'], X['val'], y['train'], y['val'] = train_test_split(X['train'], y['train'], test_size = 0.10, random_state=21)
return X, yread_split_data()는 adult 데이터셋을 불러와 전체 데이터셋을 훈련 / 검증 / 테스트 데이터셋으로 분할합니다. 아래 코드에는 데이터셋이 Google drive에 저장되어 있는데, 직접 실행을 원하신다면 pd.read_csv()에 적절한 경로를 입력하면 됩니다.
def preprocessing(X, y):
cat_index = X['train'].select_dtypes(['object']).columns
num_index = X['train'].select_dtypes(['int64']).columns
# categorical cardinalities for CategoricalFeatureTokenizer
cat_cardinalities = []
# StandardScaler
ss = StandardScaler()
X['train'][num_index] = ss.fit_transform(X['train'][num_index])
X['val'][num_index] = ss.transform(X['val'][num_index])
X['test'][num_index] = ss.transform(X['test'][num_index])
# float64 -> float32 (recommended)
X['train'][num_index] = X['train'][num_index].apply(lambda x: x.astype('float32'))
X['val'][num_index] = X['val'][num_index].apply(lambda x: x.astype('float32'))
X['test'][num_index] = X['test'][num_index].apply(lambda x: x.astype('float32'))
# LabelEncoder
for col in cat_index:
le = LabelEncoder()
X['train'][col] = le.fit_transform(X['train'][col])
# X_val, X_test에만 존재하는 label이 있을 경우
for label in np.unique(X['val'][col]):
if label not in le.classes_:
le.classes_ = np.append(le.classes_, label)
for label in np.unique(X['test'][col]):
if label not in le.classes_:
le.classes_ = np.append(le.classes_, label)
X['val'][col] = le.transform(X['val'][col])
X['test'][col] = le.transform(X['test'][col])
# cardinalities
max_cat = np.max([np.max(X['train'][col]),
np.max(X['val'][col]),
np.max(X['test'][col])]) + 1
cat_cardinalities.append(max_cat)
# y = 1 if > 50K
y['train'] = np.where(y['train']=='>50K', 1, 0).reshape(-1, 1)
y['val'] = np.where(y['val']=='>50K', 1, 0).reshape(-1, 1)
y['test'] = np.where(y['test']=='>50K', 1, 0).reshape(-1, 1)
return X, y, cat_cardinalitiespreprocessing()을 통해 데이터 전처리를 수행합니다. 적용되는 사항은 아래와 같습니다.
- 숫자형 특성: StandardScaler 적용 후 float32 타입으로 변경
- 범주형 특성: LabelEncoder 적용
- 범주형 특성의 경우 특성마다 카디널리티를 계산하여 리턴
- 타겟값 y(income)는 income이 50K를 초과하면 1, 아니면 0
StandardScaler를 사용한 것은 간단히 사용할 수 있기 때문입니다. 다른 전처리 방법을 사용하셔도 무방합니다.
범주형 특성의 경우 이후 Embedding layer에 입력하기 위하여 LabelEncoder를 사용해야 하고, 모델 입력 시 범주형 특성에 대한 카디널리티가 필요하기 때문에 따로 계산하여 추가합니다.
def setting_rtdl(data, label):
'''
DataFrame, np.array -> torch.Tensor
ResNet: model(X_num, X_cat) / split X -> X_num, X_cat
'''
cat_index = data['train'].select_dtypes(['int64']).columns
num_index = data['train'].select_dtypes(['float32']).columns
X = {'train': {},
'val': {},
'test': {}}
y = {'train': {},
'val': {},
'test': {}}
X['train']['num'] = torch.tensor(data['train'][num_index].values, device=device)
X['train']['cat'] = torch.tensor(data['train'][cat_index].values, device=device)
X['val']['num'] = torch.tensor(data['val'][num_index].values, device=device)
X['val']['cat'] = torch.tensor(data['val'][cat_index].values, device=device)
X['test']['num'] = torch.tensor(data['test'][num_index].values, device=device)
X['test']['cat'] = torch.tensor(data['test'][cat_index].values, device=device)
# dtype=float for BCELoss
y['train'] = torch.tensor(label['train'], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
y['val'] = torch.tensor(label['val'], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
y['test'] = torch.tensor(label['test'], dtype=torch.float, device=device)
return X, ysetting_rtdl()을 통해 데이터를 torch.Tensor로 변환합니다. ResNet의 경우 입력을 resnet(X_num, X_cat)과 같이 숫자형 특성 데이터와 범주형 특성 데이터를 따로 받기 때문에 이를 분리해 줍니다.
# Dataset with num / cat features (for rtdl)
class TensorData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, num, cat, label):
self.num = num
self.cat = cat
self.label = label
self.len = self.label.shape[0]
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.num[index],self.cat[index], self.label[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.lendef model_train(model, data_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, scheduler=None):
model.train()
running_loss = 0
corr = 0
# for rtdl
for x_num, x_cat, label in tqdm(data_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
x_num, x_cat, label = x_num.to(device), x_cat.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(x_num, x_cat)
output = torch.sigmoid(output)
loss = criterion(output, label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
pred = output >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5]).to(device)
corr += pred.eq(label).sum().item()
running_loss += loss.item() * x_num.size(0)
if scheduler:
scheduler.step()
# Average accuracy & loss
accuracy = corr / len(data_loader.dataset)
loss = running_loss / len(data_loader.dataset)
history['train_loss'].append(loss)
history['train_accuracy'].append(accuracy)
return loss, accuracydef model_evaluate(model, data_loader, criterion, device):
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
running_loss = 0
corr = 0
for x_num, x_cat, label in data_loader:
x_num, x_cat, label = x_num.to(device), x_cat.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(x_num, x_cat)
output = torch.sigmoid(output)
pred = output >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5]).to(device)
corr += pred.eq(label).sum().item()
running_loss += criterion(output, label).item() * x_num.size(0)
accuracy = corr / len(data_loader.dataset)
loss = running_loss / len(data_loader.dataset)
history['val_loss'].append(loss)
history['val_accuracy'].append(accuracy)
return loss, accuracydef model_tune(model, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer, device):
model.train()
# train_loader
for x_num, x_cat, label in train_loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
x_num, x_cat, label = x_num.to(device), x_cat.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(x_num, x_cat)
output = torch.sigmoid(output)
loss = criterion(output, label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# val_loader
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
running_loss = 0
corr = 0
for x_num, x_cat, label in val_loader:
x_num, x_cat, label = x_num.to(device), x_cat.to(device), label.to(device)
output = model(x_num, x_cat)
output = torch.sigmoid(output)
pred = output >= torch.FloatTensor([0.5]).to(device)
corr += pred.eq(label).sum().item()
running_loss += criterion(output, label).item() * x_num.size(0)
val_accuracy = corr / len(val_loader.dataset)
val_loss = running_loss / len(val_loader.dataset)
return val_loss, val_accuracydef plot_loss(history):
plt.plot(history['train_loss'], label='train', marker='o')
plt.plot(history['val_loss'], label='val', marker='o')
plt.title('Loss per epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
def plot_acc(history):
plt.plot(history['train_accuracy'], label='train', marker='o')
plt.plot(history['val_accuracy'], label='val', marker='o')
plt.title('Accuracy per epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()def ready_data():
# data setting
seed_everything()
X, y = read_split_data()
X, y, cardinalities = preprocessing(X, y)
X, y = setting_rtdl(X, y)
# dataset, dataloader
train_data = TensorData(X['train']['num'], X['train']['cat'], y['train'])
val_data = TensorData(X['val']['num'], X['val']['cat'], y['val'])
test_data = TensorData(X['test']['num'], X['test']['cat'], y['test'])
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
return X, y, cardinalities, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader데이터셋과 모델 훈련과 관련된 함수를 정의합니다.
# ResNet with Categorical features
class ResNet(nn.Module):
'''
<ResNet>: The ResNet model used in [gorishniy2021revisiting].
ResNet: (in) -> Linear -> Block -> ... -> Block -> Head -> (out)
|-> Norm -> Linear -> Activation -> Dropout -> Linear -> Dropout ->|
| |
Block: (in) ------------------------------------------------------------> Add -> (out)
Head: (in) -> Norm -> Activation -> Linear -> (out)
Examples:
.. testcode::
x = torch.randn(4, 2)
module = ResNet.make_baseline(
d_in=x.shape[1],
n_blocks=2,
d_main=3,
d_hidden=4,
dropout_first=0.25,
dropout_second=0.0,
d_out=1
)
assert module(x).shape == (len(x), 1)
n_num_features: # of numeric features
cat_tokenizer: CategoricalFeatureTokenizer(cardinalities, d_token, bias, initialization)
d_token: embedding size, bias = True or False, initialization = 'uniform' or 'normal'
resnet_kwargs:
n_blocks: the number of Blocks
d_main: the input size (or, equivalently, the output size) of each Block
d_hidden: the output size of the first linear layer in each Block
dropout_first: the dropout rate of the first dropout layer in each Block.
dropout_second: the dropout rate of the second dropout layer in each Block.
'''
def __init__(self,
n_num_features: int,
cat_tokenizer: rtdl.CategoricalFeatureTokenizer,
resnet_kwargs: Dict[str, Any],):
super().__init__()
self.cat_tokenizer = cat_tokenizer
self.model = rtdl.ResNet.make_baseline(d_in=n_num_features + cat_tokenizer.n_tokens * cat_tokenizer.d_token, **resnet_kwargs,)
def forward(self, x_num, x_cat):
return self.model(torch.cat([x_num, self.cat_tokenizer(x_cat).flatten(1, -1)], dim=1))마지막으로 ResNet 클래스를 정의합니다. 데이터셋이 숫자형 특성만 가지고 있다면 rtdl.ResNet.make_baseline()을 사용하여 간단히 모델을 구성할 수 있습니다. Adult 데이터셋의 경우 범주형 특성을 가지고 있기 때문에 새로운 클래스를 정의하여 범주형 입력을 받을 수 있게 수정합니다.
Run
이제 모델을 생성하고 훈련합니다. 모델의 하이퍼파라미터는 임의로 설정하였습니다.
X, y, cardinalities, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = ready_data()
# categorical embedding dimension = 32
d_token = 32
# hyperparameters
resnet_kwargs = {'n_blocks': 2,
'd_main': 64,
'd_hidden': 128,
'dropout_first': 0.25,
'dropout_second': 0.1,
'd_out': 1}
resnet = ResNet(n_num_features=X['train']['num'].shape[1],
cat_tokenizer=rtdl.CategoricalFeatureTokenizer(cardinalities, d_token, True, 'uniform'),
resnet_kwargs=resnet_kwargs).to(device)
print(resnet)출력
ResNet(
(cat_tokenizer): CategoricalFeatureTokenizer(
(embeddings): Embedding(102, 32)
)
(model): ResNet(
(first_layer): Linear(in_features=262, out_features=64, bias=True)
(blocks): Sequential(
(0): Block(
(normalization): BatchNorm1d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(linear_first): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=128, bias=True)
(activation): ReLU()
(dropout_first): Dropout(p=0.25, inplace=False)
(linear_second): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=64, bias=True)
(dropout_second): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
(1): Block(
(normalization): BatchNorm1d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(linear_first): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=128, bias=True)
(activation): ReLU()
(dropout_first): Dropout(p=0.25, inplace=False)
(linear_second): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=64, bias=True)
(dropout_second): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
)
)
(head): Head(
(normalization): BatchNorm1d(64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(activation): ReLU()
(linear): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
)
)모델 훈련을 진행합니다. 간단한 예시를 보는 것이므로 15 에포크만 훈련하고, 검증 손실이 가장 낮은 모델을 'ResNet_Best.pth'로 저장합니다.
논문에서는 AdamW 옵티마이저를 사용하였는데, 실험 결과 AdamW를 사용하면 loss와 accuracy가 이리저리 튀어서 Adam 옵티마이저를 사용하였습니다.
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
# using Adam instead of AdamW(in paper)
optimizer = optim.Adam(resnet.parameters(), lr = 1e-4)
history = {'train_loss' : [],
'val_loss': [],
'train_accuracy': [],
'val_accuracy': []}
EPOCHS = 15
max_loss = np.inf
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
train_loss, train_acc = model_train(resnet, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, None)
val_loss, val_acc = model_evaluate(resnet, val_loader, criterion, device)
if val_loss < max_loss:
print(f'[INFO] val_loss has been improved from {max_loss:.5f} to {val_loss:.5f}. Save model.')
max_loss = val_loss
torch.save(resnet.state_dict(), 'ResNet_Best.pth')
print(f'epoch {epoch+1:02d}, loss: {train_loss:.5f}, accuracy: {train_acc:.5f}, val_loss: {val_loss:.5f}, val_accuracy: {val_acc:.5f} \n')출력
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:10<00:00, 119.46it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from inf to 0.33440. Save model.
epoch 01, loss: 0.39882, accuracy: 0.82513, val_loss: 0.33440, val_accuracy: 0.85100
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:05<00:00, 212.29it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.33440 to 0.32271. Save model.
epoch 02, loss: 0.33136, accuracy: 0.84639, val_loss: 0.32271, val_accuracy: 0.85350
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:09<00:00, 132.25it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.32271 to 0.31843. Save model.
epoch 03, loss: 0.32522, accuracy: 0.84932, val_loss: 0.31843, val_accuracy: 0.85191
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:17<00:00, 71.52it/s]
epoch 04, loss: 0.32013, accuracy: 0.84985, val_loss: 0.32101, val_accuracy: 0.85214
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:09<00:00, 125.29it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31843 to 0.31757. Save model.
epoch 05, loss: 0.31675, accuracy: 0.85359, val_loss: 0.31757, val_accuracy: 0.85146
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 161.32it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31757 to 0.31634. Save model.
epoch 06, loss: 0.31858, accuracy: 0.85316, val_loss: 0.31634, val_accuracy: 0.85259
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 198.08it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31634 to 0.31621. Save model.
epoch 07, loss: 0.31564, accuracy: 0.85511, val_loss: 0.31621, val_accuracy: 0.85441
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 177.02it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31621 to 0.31278. Save model.
epoch 08, loss: 0.31382, accuracy: 0.85579, val_loss: 0.31278, val_accuracy: 0.85555
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:05<00:00, 212.71it/s]
epoch 09, loss: 0.31113, accuracy: 0.85698, val_loss: 0.31686, val_accuracy: 0.85555
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 167.01it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31278 to 0.31170. Save model.
epoch 10, loss: 0.31122, accuracy: 0.85549, val_loss: 0.31170, val_accuracy: 0.85441
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:05<00:00, 210.14it/s]
epoch 11, loss: 0.31107, accuracy: 0.85607, val_loss: 0.31632, val_accuracy: 0.85305
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 166.65it/s]
epoch 12, loss: 0.31153, accuracy: 0.85625, val_loss: 0.31682, val_accuracy: 0.85373
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:05<00:00, 209.86it/s]
epoch 13, loss: 0.30981, accuracy: 0.85779, val_loss: 0.31836, val_accuracy: 0.85100
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 180.14it/s]
epoch 14, loss: 0.30902, accuracy: 0.85812, val_loss: 0.31425, val_accuracy: 0.85350
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 190.72it/s]
epoch 15, loss: 0.30704, accuracy: 0.85832, val_loss: 0.31184, val_accuracy: 0.85487 plot_acc(history)출력
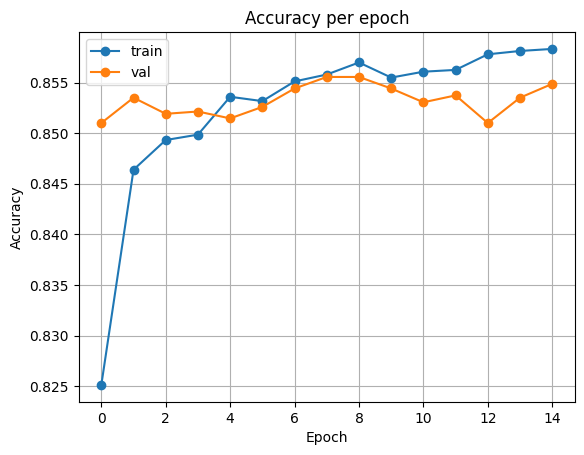
plot_loss(history)출력
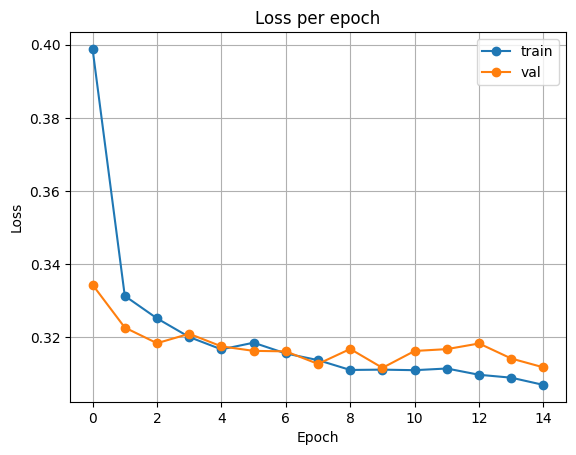
검증 손실이 가장 적었던 모델을 불러와 테스트 데이터셋에서 평가를 진행합니다.
# test evaluate
resnet.load_state_dict(torch.load('ResNet_Best.pth'))
test_loss, test_acc = model_evaluate(resnet, test_loader, criterion, device)
print('Test loss:', test_loss, '\nTest acc:', test_acc)출력
Test loss: 0.31441132257880305
Test acc: 0.8536335721596725
Tuning
Optuna 라이브러리를 사용하여 하이퍼파라미터 튜닝을 수행합니다. Optuna 사용 방법에 대해서는 Optuna 튜토리얼을 참고해 주세요.
데이터를 준비한 뒤, optuna objective 함수를 정의합니다. 탐색할 하이퍼파라미터의 범위는 해당 논문을 참고하였습니다.
X, y, cardinalities, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = ready_data()
# optuna objective
# hyperparameter space from Revisiting Deep Learning Models for Tabular Data
# suggest_uniform, suggest_loguniform -> suggest_float, suggest_float(log=True)
def objective(trial, train_loader, val_loader):
d_token = trial.suggest_int('d_token', 64, 512, log=True)
resnet_kwargs = {'n_blocks': trial.suggest_int('n_blocks', 1, 8, log=True),
'd_main': trial.suggest_int('d_main', 64, 512, log=True),
'd_hidden': trial.suggest_int('d_hidden', 64, 2048, log=True),
'dropout_first': trial.suggest_float('dropout_first', 0, 0.5),
'dropout_second': trial.suggest_float('dropout_second', 0, 0.5),
'd_out': 1}
lr = trial.suggest_float('lr', 1e-5, 1e-2, log=True)
weight_decay = trial.suggest_float('weigth_decay', 1e-6, 1e-3, log=True)
model = ResNet(X['train']['num'].shape[1],
rtdl.CategoricalFeatureTokenizer(cardinalities, d_token, True, 'uniform'),
resnet_kwargs).to(device)
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
EPOCHS = 10
min_loss = np.inf
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
val_loss, val_acc = model_tune(model, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer, device)
if val_loss < min_loss:
min_loss = val_loss
# minimize minimun loss
return min_loss10 에포크 동안 모델을 훈련한 뒤, 10 에포크 중 가장 작았던 검증 손실(min_loss)을 리턴합니다. 에포크 수, 리턴 값 종류는 임의로 설정한 것이니 다른 방법으로 수정할 수 있습니다.
n_trials=15를 전달하여 15회 탐색을 수행합니다. 최적의 방법은 아닐 수 있습니다.
study = optuna.create_study(study_name='ResNet', direction='minimize', sampler=TPESampler(seed=21))
study.optimize(lambda trial: objective(trial, train_loader, val_loader), n_trials=15)
print()
print("Best Score:", study.best_value)
print("Best trial:", study.best_trial.params)출력
[I 2023-09-03 14:30:37,482] A new study created in memory with name: ResNet
[I 2023-09-03 14:31:29,227] Trial 0 finished with value: 0.3111502611713045 and parameters: {'d_token': 70, 'n_blocks': 1, 'd_main': 286, 'd_hidden': 68, 'dropout_first': 0.10296138263371951, 'dropout_second': 0.0253866283476884, 'lr': 8.068925058345682e-05, 'weigth_decay': 9.8113977880839e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:32:57,047] Trial 1 finished with value: 0.3124179112249553 and parameters: {'d_token': 121, 'n_blocks': 3, 'd_main': 73, 'd_hidden': 1292, 'dropout_first': 0.06662025962587387, 'dropout_second': 0.08906233077974918, 'lr': 0.00030746001885481724, 'weigth_decay': 0.000390030826829326}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:35:41,597] Trial 2 finished with value: 0.31428985122770914 and parameters: {'d_token': 310, 'n_blocks': 8, 'd_main': 310, 'd_hidden': 241, 'dropout_first': 0.20435916472186627, 'dropout_second': 0.35668021394223937, 'lr': 6.4864835049475e-05, 'weigth_decay': 0.00036501323850154823}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:37:16,463] Trial 3 finished with value: 0.31154074351065153 and parameters: {'d_token': 428, 'n_blocks': 4, 'd_main': 187, 'd_hidden': 114, 'dropout_first': 0.14934614580443284, 'dropout_second': 0.14197152251531692, 'lr': 9.586006736497123e-05, 'weigth_decay': 2.4011594547390928e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:38:08,474] Trial 4 finished with value: 0.31694241238247817 and parameters: {'d_token': 198, 'n_blocks': 1, 'd_main': 337, 'd_hidden': 793, 'dropout_first': 0.42464635669560846, 'dropout_second': 0.13376090229103615, 'lr': 0.0006989951034134576, 'weigth_decay': 9.083813718648172e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:39:18,066] Trial 5 finished with value: 0.32026535305139475 and parameters: {'d_token': 142, 'n_blocks': 2, 'd_main': 345, 'd_hidden': 511, 'dropout_first': 0.44917016929234715, 'dropout_second': 0.245016112524509, 'lr': 0.0030546003462430396, 'weigth_decay': 0.000377284022269761}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:41:31,395] Trial 6 finished with value: 0.3170844090999095 and parameters: {'d_token': 329, 'n_blocks': 6, 'd_main': 273, 'd_hidden': 308, 'dropout_first': 0.15295758239442775, 'dropout_second': 0.4100422024629634, 'lr': 2.62418208491809e-05, 'weigth_decay': 1.599151079011668e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:42:54,658] Trial 7 finished with value: 0.3205868454007695 and parameters: {'d_token': 103, 'n_blocks': 3, 'd_main': 404, 'd_hidden': 198, 'dropout_first': 0.4023048260098239, 'dropout_second': 0.39872641973399076, 'lr': 0.0009933011615357063, 'weigth_decay': 5.3993003907165594e-06}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:44:04,192] Trial 8 finished with value: 0.3208724130707724 and parameters: {'d_token': 351, 'n_blocks': 2, 'd_main': 297, 'd_hidden': 315, 'dropout_first': 0.4320428747864871, 'dropout_second': 0.3510821460020566, 'lr': 3.1909883622776933e-05, 'weigth_decay': 3.4493671208006622e-06}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:44:54,171] Trial 9 finished with value: 0.32169066208183383 and parameters: {'d_token': 375, 'n_blocks': 1, 'd_main': 141, 'd_hidden': 73, 'dropout_first': 0.3170815384573714, 'dropout_second': 0.4020891712225652, 'lr': 0.004919700819400421, 'weigth_decay': 3.8396394716123356e-06}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:45:45,932] Trial 10 finished with value: 0.31238244642063745 and parameters: {'d_token': 78, 'n_blocks': 1, 'd_main': 448, 'd_hidden': 68, 'dropout_first': 0.0013221072775810028, 'dropout_second': 0.013516481246185822, 'lr': 1.1137780707344282e-05, 'weigth_decay': 7.623746090570489e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:46:36,467] Trial 11 finished with value: 0.313731754634248 and parameters: {'d_token': 495, 'n_blocks': 1, 'd_main': 198, 'd_hidden': 110, 'dropout_first': 0.14373720565363307, 'dropout_second': 0.009585553939793268, 'lr': 0.00013178662211098122, 'weigth_decay': 2.5158402039876266e-05}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:48:09,874] Trial 12 finished with value: 0.3129236849467249 and parameters: {'d_token': 70, 'n_blocks': 4, 'd_main': 176, 'd_hidden': 127, 'dropout_first': 0.2527907610405756, 'dropout_second': 0.15412323275581827, 'lr': 0.00010989756665468876, 'weigth_decay': 1.2121329904905024e-06}. Best is trial 0 with value: 0.3111502611713045.
[I 2023-09-03 14:49:18,923] Trial 13 finished with value: 0.30996863016548537 and parameters: {'d_token': 227, 'n_blocks': 2, 'd_main': 500, 'd_hidden': 140, 'dropout_first': 0.09382503031023116, 'dropout_second': 0.08519248250739686, 'lr': 0.0003181781772281558, 'weigth_decay': 8.381275137828959e-05}. Best is trial 13 with value: 0.30996863016548537.
[I 2023-09-03 14:50:26,894] Trial 14 finished with value: 0.31938375626183074 and parameters: {'d_token': 195, 'n_blocks': 2, 'd_main': 454, 'd_hidden': 163, 'dropout_first': 0.05899430015521513, 'dropout_second': 0.4980679512673059, 'lr': 0.00028888934139216916, 'weigth_decay': 9.692391574276788e-05}. Best is trial 13 with value: 0.30996863016548537.
Best Score: 0.30996863016548537
Best trial: {'d_token': 227, 'n_blocks': 2, 'd_main': 500, 'd_hidden': 140, 'dropout_first': 0.09382503031023116, 'dropout_second': 0.08519248250739686, 'lr': 0.0003181781772281558, 'weigth_decay': 8.381275137828959e-05}optuna.visualization.plot_optimization_history(study)출력
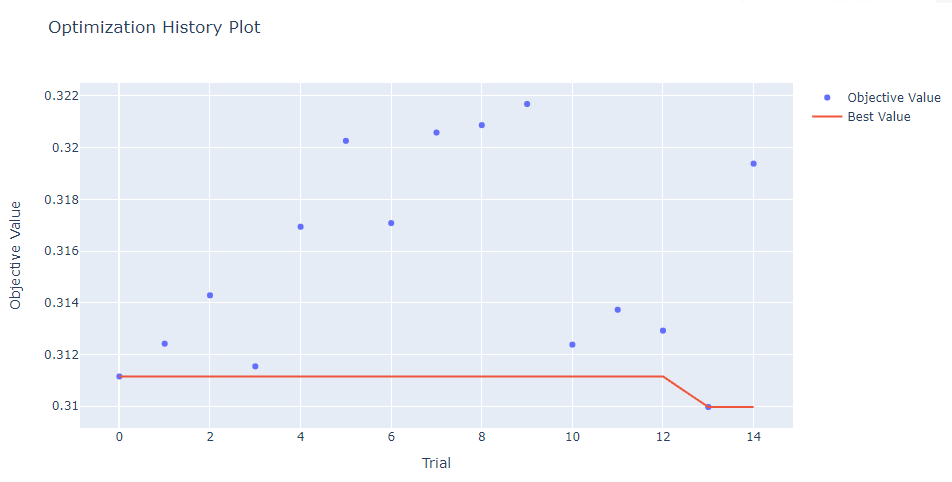
optuna.visualization.plot_param_importances(study)출력
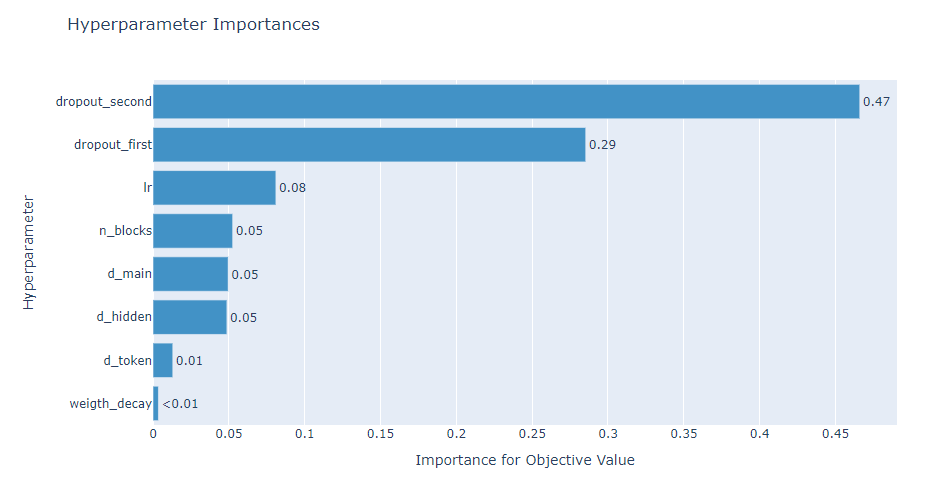
study.best_trial.params출력
{'d_token': 227,
'n_blocks': 2,
'd_main': 500,
'd_hidden': 140,
'dropout_first': 0.09382503031023116,
'dropout_second': 0.08519248250739686,
'lr': 0.0003181781772281558,
'weigth_decay': 8.381275137828959e-05}최적의 하이퍼파라미터 조합으로 모델을 다시 훈련합니다. 검증 손실이 가장 작은 모델을 'ResNet_Best_tuned.pth'로 저장합니다.
X, y, cardinalities, train_loader, val_loader, test_loader = ready_data()
d_token = study.best_trial.params['d_token']
resnet_kwargs = {'n_blocks': study.best_trial.params['n_blocks'],
'd_main': study.best_trial.params['d_main'],
'd_hidden': study.best_trial.params['d_hidden'],
'dropout_first': study.best_trial.params['dropout_first'],
'dropout_second': study.best_trial.params['dropout_second'],
'd_out': 1}
resnet = ResNet(n_num_features=X['train']['num'].shape[1],
cat_tokenizer=rtdl.CategoricalFeatureTokenizer(cardinalities, d_token, True, 'uniform'),
resnet_kwargs=resnet_kwargs).to(device)
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.AdamW(resnet.parameters(), lr = study.best_trial.params['lr'], weight_decay=study.best_trial.params['weigth_decay'])
history = {'train_loss' : [],
'val_loss': [],
'train_accuracy': [],
'val_accuracy': []}
EPOCHS = 15
max_loss = np.inf
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
train_loss, train_acc = model_train(resnet, train_loader, criterion, optimizer, device, None)
val_loss, val_acc = model_evaluate(resnet, val_loader, criterion, device)
if val_loss < max_loss:
print(f'[INFO] val_loss has been improved from {max_loss:.5f} to {val_loss:.5f}. Save model.')
max_loss = val_loss
torch.save(resnet.state_dict(), 'ResNet_Best_tuned.pth')
print(f'epoch {epoch+1:02d}, loss: {train_loss:.5f}, accuracy: {train_acc:.5f}, val_loss: {val_loss:.5f}, val_accuracy: {val_acc:.5f} \n')출력
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 150.61it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from inf to 0.32505. Save model.
epoch 01, loss: 0.33805, accuracy: 0.84320, val_loss: 0.32505, val_accuracy: 0.84918
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 184.00it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.32505 to 0.31666. Save model.
epoch 02, loss: 0.32212, accuracy: 0.85132, val_loss: 0.31666, val_accuracy: 0.85055
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 151.89it/s]
epoch 03, loss: 0.31704, accuracy: 0.85203, val_loss: 0.31921, val_accuracy: 0.84964
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 181.44it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31666 to 0.31646. Save model.
epoch 04, loss: 0.31728, accuracy: 0.85377, val_loss: 0.31646, val_accuracy: 0.85191
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 150.40it/s]
epoch 05, loss: 0.31434, accuracy: 0.85380, val_loss: 0.31839, val_accuracy: 0.85305
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 184.34it/s]
epoch 06, loss: 0.31252, accuracy: 0.85511, val_loss: 0.31893, val_accuracy: 0.85282
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 151.39it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31646 to 0.31143. Save model.
epoch 07, loss: 0.31158, accuracy: 0.85395, val_loss: 0.31143, val_accuracy: 0.85373
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 177.75it/s]
epoch 08, loss: 0.30929, accuracy: 0.85632, val_loss: 0.31401, val_accuracy: 0.85669
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 152.09it/s]
epoch 09, loss: 0.30777, accuracy: 0.85627, val_loss: 0.31582, val_accuracy: 0.85077
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:06<00:00, 178.54it/s]
epoch 10, loss: 0.30757, accuracy: 0.85746, val_loss: 0.31208, val_accuracy: 0.85282
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 153.30it/s]
epoch 11, loss: 0.30452, accuracy: 0.85903, val_loss: 0.31358, val_accuracy: 0.85487
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 173.93it/s]
epoch 12, loss: 0.30536, accuracy: 0.85928, val_loss: 0.31284, val_accuracy: 0.85191
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:08<00:00, 154.19it/s]
[INFO] val_loss has been improved from 0.31143 to 0.31039. Save model.
epoch 13, loss: 0.30437, accuracy: 0.85784, val_loss: 0.31039, val_accuracy: 0.85714
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 176.24it/s]
epoch 14, loss: 0.30356, accuracy: 0.85855, val_loss: 0.31417, val_accuracy: 0.85146
100%|██████████| 1237/1237 [00:07<00:00, 156.12it/s]
epoch 15, loss: 0.30431, accuracy: 0.85817, val_loss: 0.31190, val_accuracy: 0.85282 plot_acc(history)출력
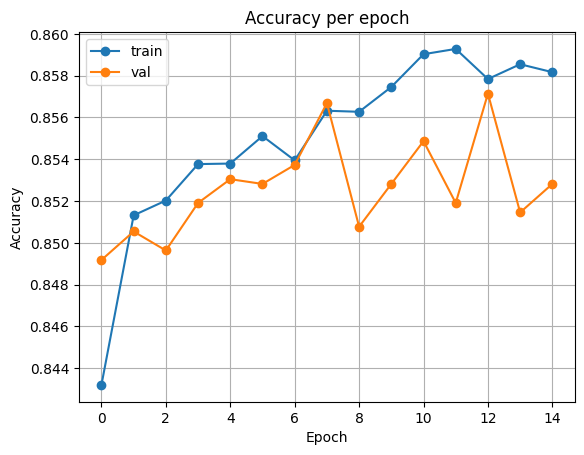
plot_loss(history)출력
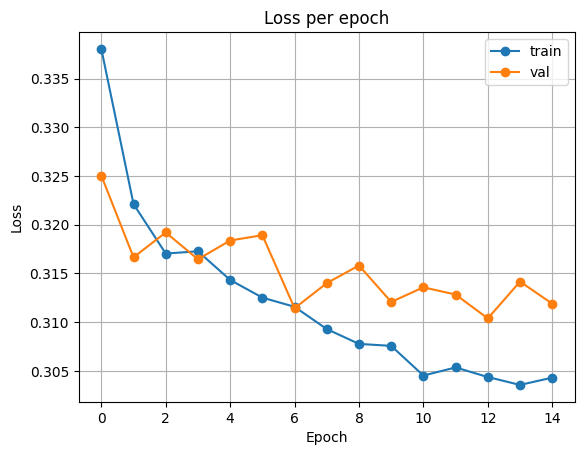
테스트 데이터셋에서 최종 평가를 진행합니다.
# test evaluate
resnet.load_state_dict(torch.load('ResNet_Best_tuned.pth'))
test_loss, test_acc = model_evaluate(resnet, test_loader, criterion, device)
print('Test loss:', test_loss, '\nTest acc:', test_acc)출력
Test loss: 0.3126100196748087
Test acc: 0.8562947799385875
이상으로 ResNet 아키텍처의 간단한 사용 방법에 대해 알아보았습니다. 위의 방법이 모델 성능을 위한 최적의 방법이 아닐 수 있습니다. 하이퍼파라미터 탐색 범위 수정, 모델 훈련 시 scheduler 사용 등 추가적인 방법으로 더 좋은 성능을 달성할 수도 있습니다.
해당 아키텍처에 대해 더 많은 정보를 확인하시려면 rtdl의 github를 참고해 주세요.
감사합니다.

