이중연결리스트란?
각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 가지며, 두 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조
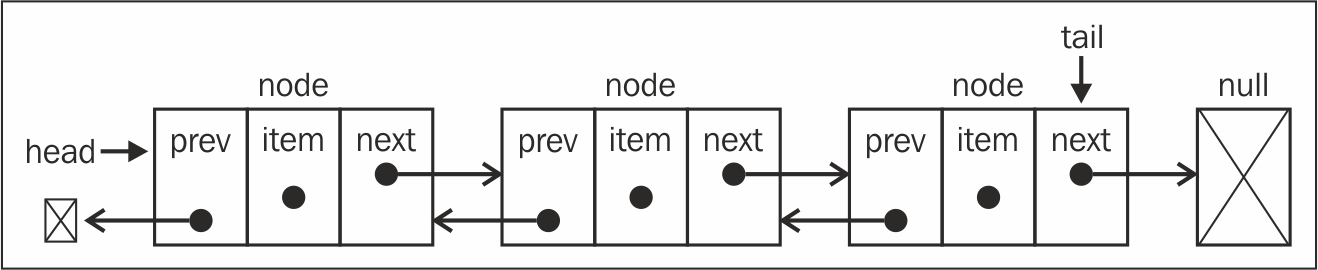
일반 연결 리스트와 다른점
- prev를 저장할 수 있는 장소가 있다는 것
- head 외에 tail도 존재한다는 것
구현 메서드
- 노드 개수 / 비어 있는지 확인: DoubleLinkedList.size(), DoubleLinkedList.isEmpty()
- 순차 출력 / 역 출력: DoubleLinkedList.printNode(), DoubleLinkedList.printNodeInverse()
- 노드 추가: DoubleLinkedList.append(), DoubleLinkedList.insert()
- 노드 삭제: DoubleLinkedList.remove(), DoubleLinkedList.removeAt()
- 데이터 위치 확인: DoubleLinkedList.indexOf()
1. data와 point를 가지고 있는 node 선언
LinkedList와 다르게 prev도 가지고 있다.
function Node(data) {
this.data = data;
this.prev = null;
this.next = null;
}2. head, tail과 length를 가지고 있는 DoubleLinkedList 선언
function DoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}3. size와 empty 확인
size와 empty의 경우, 이전에 구현 했던 LinkedList와 크게 다르지 않다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.size = function() {
return this.length;
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function() {
return this.length === 0;
}4. 노드를 출력 (DoubleLinkedList.printNode(), DoubleLinkedList.printNodeInverse())
일반 LinkedList와 다르게 역방향의 node도 출력 가능하다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.printNode = function() {
for (let node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next) {
process.stdout.write(`${node.data} -> `);
}
console.log("null");
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.printNodeInverse = function() {
for (let node = this.tail; node != null; node = node.prev) {
process.stdout.write(`${node.data} -> `);
}
console.log("null");
}5. 연결리스트 끝에 노드를 추가 (DoubleLinkedList.append(value))
- 새로운 노드를 생성한다.
- head가 null일 경우, 즉 node가 하나도 없을 경우 head와 tail은 모두 새로 생성한 node가 된다.
- head가 존재할 경우, head.next는 node가 되며, node.prev는 head, tail은 node가 된다.
- length를 증가시킨다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.append = function(value) {
let node = new Node(value);
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.head.next = node;
node.prev = this.head;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}6. position 위치에 노드를 추가 (DoubleLinkedList.insert(value, position))
- 새로운 노드를 생성한다.
- current. index, prev를 선언한다.
- position이 0일 때, DoubleLinkedList가 비었을 경우와 비어있지 않을 경우로 나누어 준다.
- position이 마지막 위치일 때, tail을 꼭 설정해줘야 한다.
- position이 중간에 있을 때, next와 prev를 업데이트 해준다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.insert = function (value, position = 0) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return false;
}
let node = new Node(value);
let current = this.head, index = 0, prev;
if (position === 0) {
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else if (position === this.length) {
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
prev.next = node;
node.next = current;
node.prev = prev;
current.prev = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}7. 해당하는 value를 삭제(DoubleLinkedList.remove(value))
- current.data가 찾고자하는 value가 아니거나, current의 next가 null이 아니면, 계속해서 prev = current, current = current.next한다.
- 결국 current.data가 찾고자하는 value가 아니면 null을 리턴한다.
- current가 현재 head일 때, head는 current.next를 가리키게 되는데, length가 1일 경우, 기존의 current가 사라지기 때문에 this.tail은 null이 된다.
- length가 1이 아닐 경우, current가 사라지기 때문에 this.head.prev = null이 된다.
- current가 tail에 있다면 tail은 current.prev, tail.next는 null이 되면서 current가 사라진다.
- 둘 다 아니라면 LinkedList와 동일하게 prev.next는 current.next, current.next.prev는 prev가 된다.
- length를 줄인다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.remove = function(value) {
let current = this.head, prev = current;
while (current.data != value && current.next != null) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current.data !== value) {
return null;
}
if (current === this.head) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.length === 1) this.tail = null;
else this.head.prev = null;
} else if (current === this.tail) {
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return current.data;
}8. position 위치 노드 삭제 (DoubleLinkedList.removeAt(position))
value가 position으로 변경되었다는 것 이외에 remove와 크게 차이는 없다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(position = 0) {
if (position < 0 || position > this.length) {
return null;
}
let current = this.head, index = 0, prev;
if (position === 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.length === 1) this.tail = null;
else this.head.prev = null;
} else if (position === this.length) {
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return current.data;
}10. value값을 갖는 node의 위치를 반환 (DoubleLinkedList.indexOf(value))
기존 LinkedList의 indexOf와 동일하다.
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function(value) {
let current = this.head, index = 0;
while (current != null){
if (current.data === value) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}관련 전체 코드는 Git에 업로드 해두었습니다.
github_DoubleLinkedList
