0. Abstract
- Self-supervised ViT features contain explicit information about the semantic segmentation of an image, which does not emerge as clearly with supervised ViTs, nor with convnets.
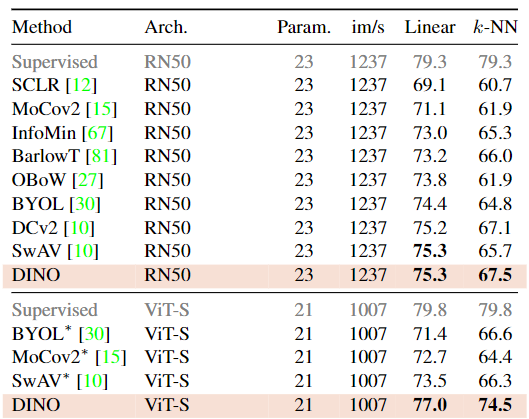
- These features are also excellent k-NN classifiers, reaching 78.3% top-1 on ImageNet with a small ViT.
- Our study also underlines the importance of momentum encoder, multi-crop training, and the use of small patches with ViTs.

1. Introduction
- NLP 에서 BERT, GPT 가 사용하는 self-supervised pretraining objectives 는 문장마다 label 을 예측하는 supervised objective 보다 richer learning signal 을 제공한다.
- 이미지에서도 image-level supervision 은 미리 정의된 카테고리 중 선택하게 함으로서 rich visual information 을 제한한다.
Contribution
- Self-supervised ViT features 는 물체의 바운더리 같은 scene layout 을 explicitly 포함한다. 이는 마지막 블럭의 self-attention 모듈에서 바로 뽑아낼 수 있다.
- Self-supervised ViT features 는 추가적인 fine-tuning, linear classifier, data augmentation 없이 (=zero-shot) k-nn classifier 로 ImageNet에서 78.3% top-1 accuracy 를 달성했다.
- Contribution 1에서 segmentation mask 가 나타나는 것은 self-supervised 방식으로 인한 특성으로 보이고, contribution 2 는 momentum encoder 과 multi-crop augmentation, smaller patches 를 같이 사용해서 나타난 특성으로 보인다.
2. Related work
Self-supervised learning
(1) Instance classification
- how: consider each image a different class and trains the model by discriminating them up to data augmentations.
- caveat: explicitly learning a classifier to discriminate between all images does not scale well with the number of images.
(2) Noise contrastive estimator (NCE)
- how: compare instances instead of classifying them
- caveat: it requires comparing features from a large number of images simultaneously. In practice, this requires large batches or memory banks
(3) W/O discriminating between images
- ex-BYOL: features are trained by matching them to representations obtained with a momentum encoder
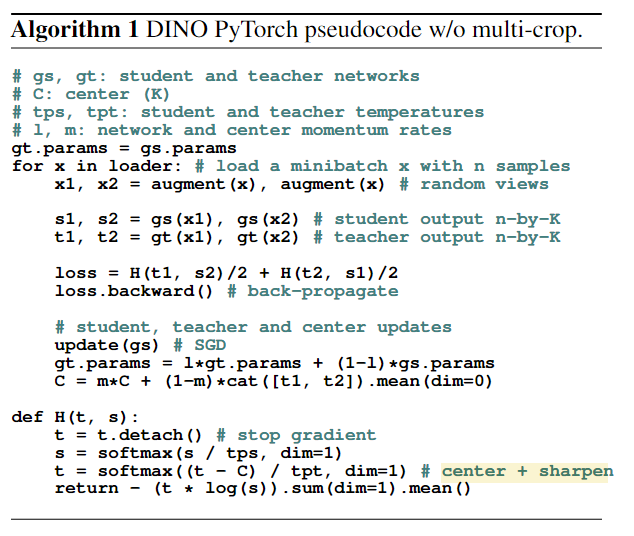
3. Approach
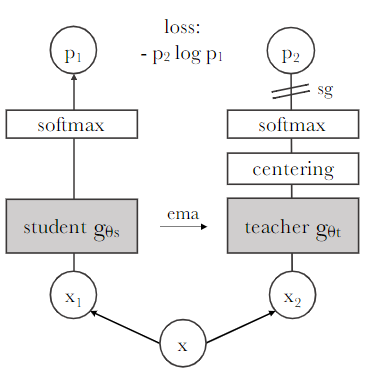
Notation
- student network parameterized by
- teacher network parameterized by
- input image: x
- Each model outputs prob distributions over dimensions denoted by , ( is the output of softmax function)
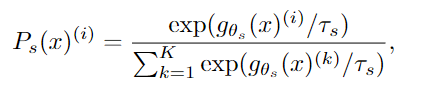
- : temperature parameter that controls the sharpness of the output distribution
-> softmax 는 여기서 normalization 의 효과를 얻기 위해 사용한 것으로 보인다.
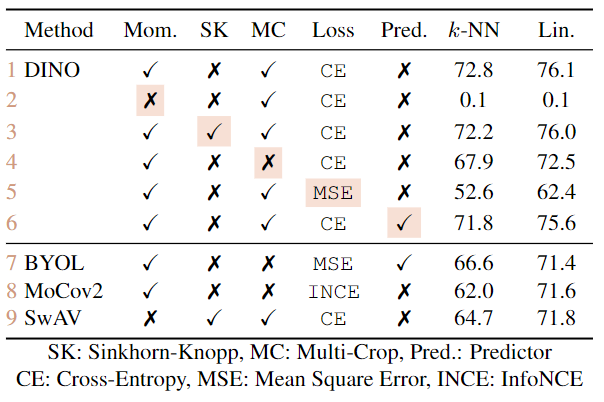
(1) Loss: cross-entropy
Given a fixed teacher network , we learn to match these distributions by minimizing the cross-entropy loss w.r.t. the parameters of the student network
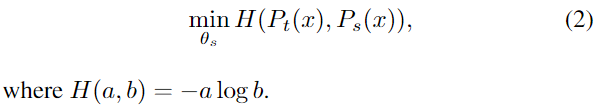
특이하게도 cross-entropy 를 사용하였다.
* loss: CE vs MSE vs INCE
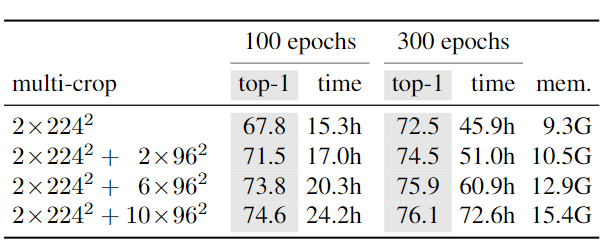
(2) Augementation: multi-crop
cross entropy 에 들어가는 x 의 augmentation 방식을 짚고 넘어가야한다.
- 큰 resolution (224x224) 인 gloabl view, 작은 resolution (96x96) 인 local view 로 multi-crop
- student 한테는 local view, teacher 한테는 gloabl veiw 를 통과시켜서
- “local-to-global” correspondences 를 배우도록 시킨다.
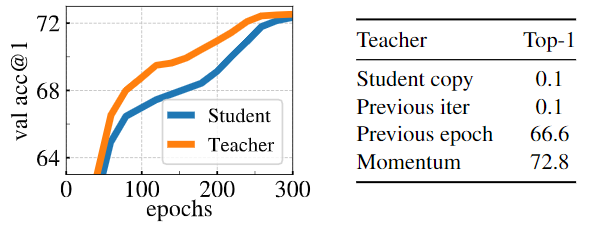
(3) Teacher network: EMA
- Using an exponential moving average (EMA) on the student weights, i.e., a momentum encoder, is particularly well suited for our framework.
- We observe that this teacher has better performance than the student throughout the training, and hence, guides the training of the student by providing target features of higher quality.
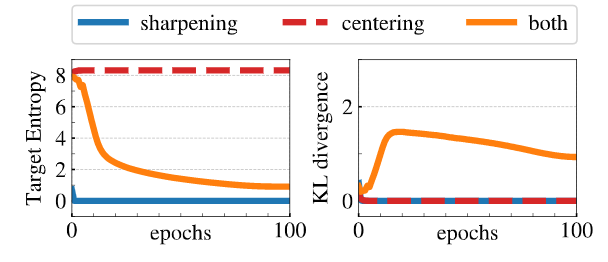
(4) Avoiding collapse: centering & sharpening
- It can also work with only a centering and sharpening ofthe momentum teacher outputs to avoid model collapse.
- Centering prevents one dimension to dominate but encourages collapse to the uniform distribution,
- while the sharpening has the opposite effect
Implementation
4. Results