JSON이란
복잡한 객체를 서버나 다른 네트워크에 전송해야할 때 객체를 JSON의 문자열 형태로 변환하여 전송한다.
◾️ JSON.stringify – 객체를 JSON으로 바꿔줍니다.
◾️ JSON.parse – JSON을 객체로 바꿔줍니다.
JSON.stringify
let student = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
isAdmin: false,
courses: ['html', 'css', 'js'],
wife: null
};
let json = JSON.stringify(student);
console.log(typeof json);
console.log(json); JSON.stringify(student)를 호출하자 student객체를 문자열 형태로 바꿔 출력된다.
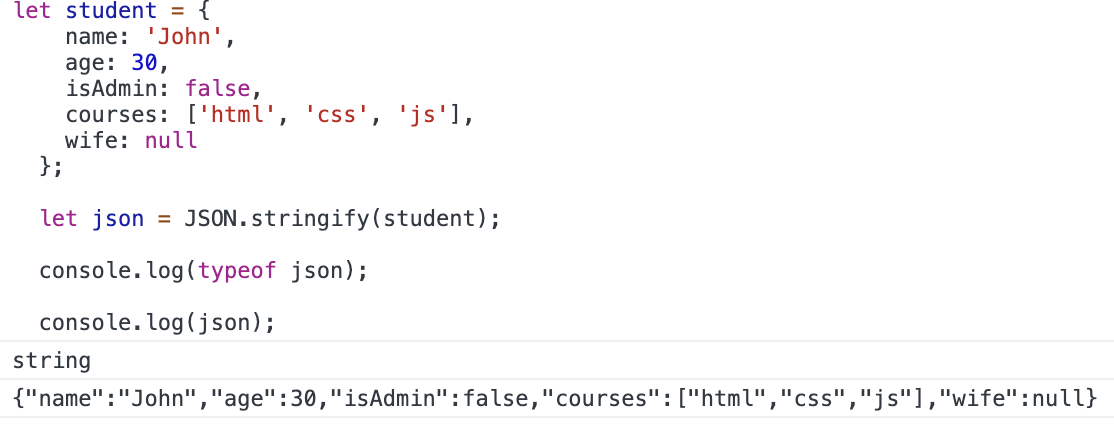
이렇게 JSON으로 바뀐 객체는 문자열로 변환되야 네크워크로 전송되거나 저장소에 저장할 수 있다.
JSON에선 백틱이나 작은 따옴표를 사용할 수 없고 "큰 따옴표로 사용된다. 또한 객체 프로퍼티 이름은 큰따옴표로 감싸져 있어야한다. ("name"="john")
◾️JSON.stringify가 적용할 수 있는 자료형 종류
▪️ 객체{,,,}
let student = {name: 'John',age: 30}
▪️ 배열[,,,]
alert( JSON.stringify([1, 2, 3]) ); // [1,2,3]
▪️ 문자형
alert( JSON.stringify('test') ) // "test"
▪️ 숫자형
alert( JSON.stringify(1) ) // 1
▪️ 불린형(true fals)
alert( JSON.stringify(true) ); // true
▪️ null
◼️ JSON.stringify 호출시 적용되지 않는 프로퍼티
함수 프로퍼티
심볼형 프로퍼티
undefinedet user = { sayHi() { // 무시 alert("Hello"); }, [Symbol("id")]: 123, // 무시 something: undefined // 무시 }; alert( JSON.stringify(user) ); // {} (빈 객체가 출력됨)
JSON.parse
let student = {
name: 'John',
age: 30,
isAdmin: false,
courses: ['html', 'css', 'js'],
wife: null
};
let json = JSON.stringify(student);
let parse = JSON.parse(json);
console.log(json);
console.log(parse); student객체를 json을 통해 문자열로 바꿨다가 다시 객체로 바꾼 출력값이다.
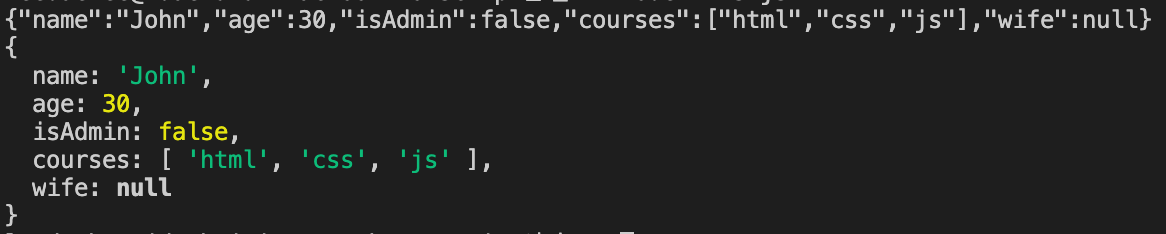
console.log(json)을 결과를 보면 문자열 형태로 출력된 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
let userData = '{ "name": "John", "age": 35, "isAdmin": false, "friends": [0,1,2,3] }';
let user = JSON.parse(userData);
console.log(user.friends[1] );
console.log(userData);console.log(json) 출력 문자열과 같이 userData에 문자열을 저장하여 객체 형태로 출력 할 수 있다.
console.log(user.friends[1] );에 friend배열에 두번째 숫자 1이 출력되고, console.log(userData);를 그대로 출력하면 객체 상태로 출력된다.
