Object
- one of the JavaScript's data types
- a collection of related data and/or functionality
- Nearly all objects in JavaScript are instance of Object
const object = { key : value};
1. Literals and properties
object 생성 방법
'object literal' syntax
const obj1 = {};
'object constructor' syntax
- 클래스, 생성자 활용
- 같은 형식의 객체를 여러번 생성할 때
const obj2 = new Object();
-> 생성자 함수는 4번으로
-> 생성자 함수
function print1(person) {
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
}
const ellie4 = {
name: "ellie",
age: 4,
};
print1(ellie4);
- with JS magic (dynamically typed language)
- can add properties later
ellie4.hasJob = true;
console.log(ellie4.hasJob);
- can delete properties later
delete ellie4.hasJob;
console.log(ellie4.hasJob);
console.log("------------------------------");

2. Computed properties
-
key should be always string
-
["key"] -
정확하게 어떤 키가 필요한지 모를 때, 런타임에서 결정될 때
-
실시간으로 원하는 키를 받아올 때
console.log(ellie4.name);
console.log(ellie4["name"]);
ellie4["hasJob"] = true;
console.log(ellie4.hasJob);
✨✨📢. vs. []

- ✨✨
.: 객체의 속성에 직접 접근 - ✨✨
[]: 변수로 접근
- 출처 : 링크텍스트
function printValue(obj, key) {
console.log(obj.key); //undefined
//**`.` : 객체의 속성에 접근
//obj 엔 key 가 없어서 undefined
console.log(obj[key]);
//**`[]` : 변수로 접근
//key로 넘어온 "name", "age"로 객체의 속성을 찾음
}
printValue(ellie4, "name");
printValue(ellie4, "age");
3. Property value shorthand
const person1 = { name: "bob", age: 2 };
const person2 = { name: "steve", age: 3 };
//...
const person3 = makePerson("wowow", 4);
console.log(person3);
function makePerson(name, age) {
return {
//이게 property shorthand
name, //name: name,
age, //age: age,
};
}
//class 같은 것. 템플릿. 예전에 class가 없었을 때 이런 식으로 object를 만들었다.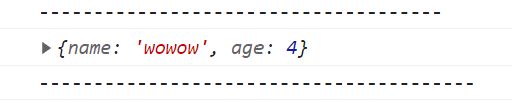
4. Constructor Function 생성자 함수
- 생성자 함수의 업그레이드 버전 => class
const person4 = new Person1("dave", 30);
console.log(person4);
function Person1(name, age) {
//this = {}
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
//return this;
}
//생성자 함수의 업그레이드 버전 => class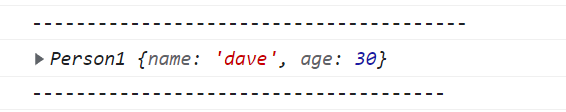
5. in 연산자
- property existence check (
key in obj)
console.log("name" in ellie4);
console.log("age" in ellie4);
console.log("random" in ellie4);
console.log(ellie4.random);
6. for..in vs. for..of
✨for (key in obj)
- 객체의 모든 ✨key
for (const key in ellie4) {
console.log(key);
}
//객체의 모든 key 출력
✨for (value of iterable)
- 배열, 리스트 ... 에서의 ✨값value 출력
for (const iterator of object) { ... }
const array = [1, 2, 4, 5];
for (const value of array) {
console.log(value);
}
7. cloning
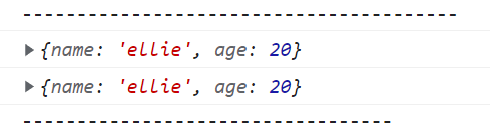
const user = { name: "ellie", age: 20 };old way
const user2 = {};
for (const key in user) {
user2[key] = user[key];
}
console.log(user2);✨Object.assign()
Object.assign(dest, [obj1, obj2, obj3...])
const user3 = Object.assign({}, user);
console.log(user3);
another example
const fruit1 = { color: "red" };
const fruit2 = { color: "blue", size: "big" };
const mixed = Object.assign({}, fruit1, fruit2);
console.log(mixed.color);
//같은 속성이면 최근 걸로 덮음
console.log(mixed.size);
