배열을 문자열로
join('구분자')
//1. make a string out of an array : join('구분자')
{
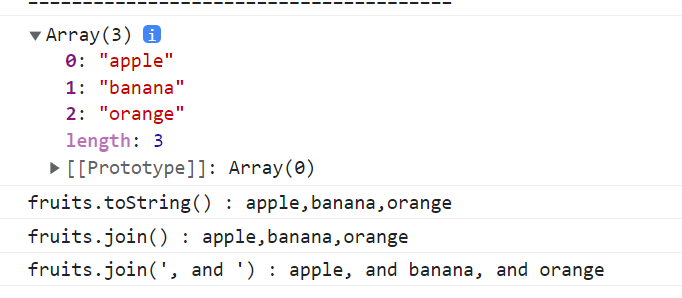
const fruits = ["apple", "banana", "orange"];
console.log(fruits);
console.log(`fruits.toString() : ${fruits.toString()}`);
console.log(`fruits.join() : ${fruits.join()}`);
console.log(`fruits.join(', and ') : ${fruits.join(", and ")}`);
}
문자열을 배열로
split('구분자', 개수)
//2. make an array out of a string : split('구분자', 개수)
{
const fruits = "사과, 키위, 바나나, 체리";
console.log(fruits);
const result = new Array(fruits);
console.log(result); //땡!! 전체가 하나의 요소로 된다(length == 1)
console.log("------------------------------------------");
const result2 = fruits.split(",");
console.log(result2);
const result3 = fruits.split(",", 2);
console.log(result3);
}
배열을 거꾸로
🤞reverse()
//3. make this array look like this: [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] : reverse()
//원본 변화
{
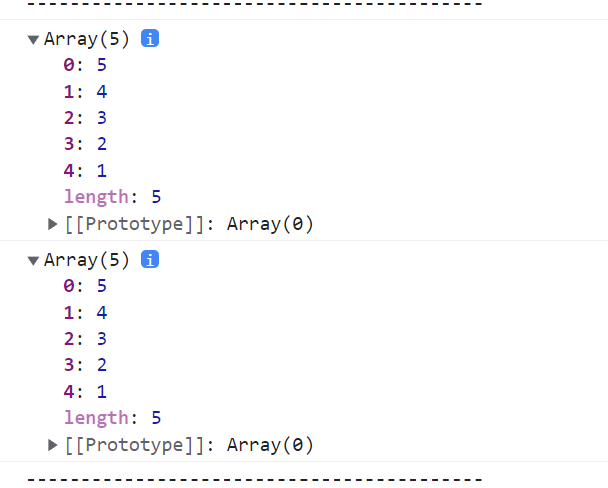
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(array.reverse());
console.log(array);
}
배열 잘라내서 새 배열 만들기
slice(시작인덱스, 끝인덱스)
- 원본 그대로!!!
//4. make new array without the first two elements : slice(시작인덱스, 끝인덱스)
//***원본 그대로!!!
{
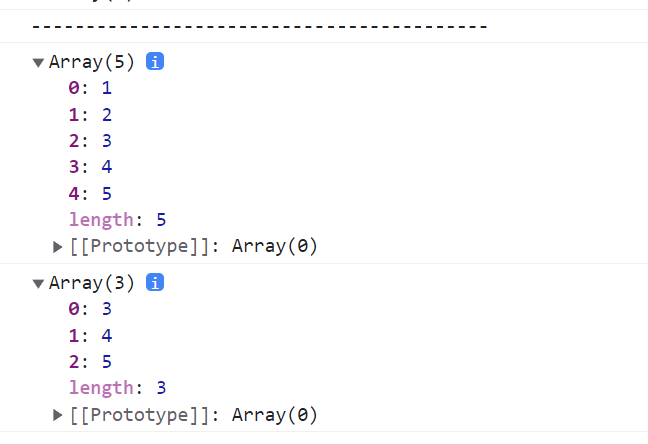
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const array2 = array.slice(2, 5);
console.log(array);
console.log(array2);
}
class 예제
class Student {
constructor(name, age, enrolled, score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.enrolled = enrolled;
this.score = score;
}
}
const students = [
new Student("A", 29, true, 45),
new Student("B", 28, false, 88),
new Student("C", 30, true, 90),
new Student("D", 40, false, 66),
new Student("E", 18, true, 88),
];
find(콜백함수)
//5. find a student with the score 90 : find(콜백함수)
//콜백함수 : 배열의 요소들마다 호출하고, 각 value, index 등을 인자로 받고, boolean 타입을 반환한다.
//find() : 콜백함수가 true를 반환하게 하는 첫 요소를 반환한다.
{
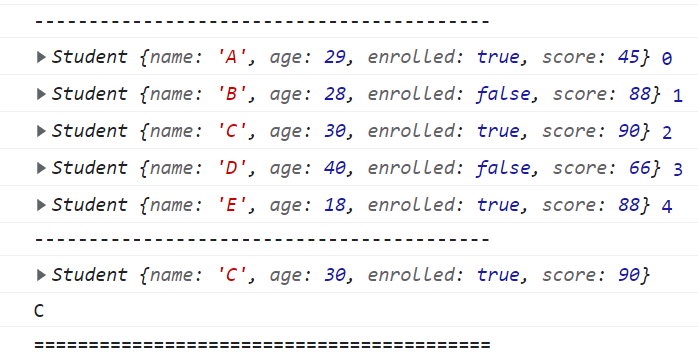
const result = students.find(function (student, index) {
//모든 요소가 true가 됨
console.log(student, index);
});
console.log("------------------------------------------");
const result1 = students.find((student) => student.score === 90);
console.log(result1);
console.log(result1.name);
}
filter(콜백함수)
- ✨✨✨새로운 배열을 만든다!!!
//6. make an array of enrolled students : filter(콜백함수)
//filter() : 콜백함수가 true를 반환하게 하는 요소들을 새로운 배열로 만든다.
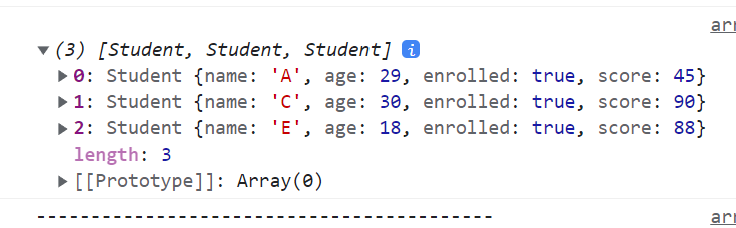
{
const result = students.filter((student) => student.enrolled === true);
console.log(result);
}
map(콜백함수)
- 배열의 각 요소를 콜백함수를 거쳐 ✨✨✨새로운 값(배열)으로 1:1 변환
//7. make an array contarining only the students' scores : map(콜백함수)
//result should be: [45, 80, 90, 66, 88]
//map() : 배열의 각 요소를 콜백함수를 거쳐 새로운 값(배열)으로 변환, 1:1로
{
const result = students.map((student) => student.score);
console.log(result);
const result2 = students.map((student) => student.score * 2);
console.log(result2);
}
some(콜백함수), every(콜백함수)
- some() : 배열의 요소 중 하나라도 콜백함수의 조건에 만족해서 true를 반환하게 된다면, true를 반환한다.
- every() : 배열의 요소 중 모두가 콜백함수의 조건에 만족해서 true를 반환하게 된다면, true를 반환한다.
//8. check if there is a student with the score lower than 50 : some(콜백함수)
//some() : 배열의 요소 중 하나라도 콜백함수의 조건에 만족해서 true를 반환하게 된다면, true를 반환한다.
//every() : 배열의 요소 중 모두가 콜백함수의 조건에 만족해서 true를 반환하게 된다면, true를 반환한다.
{
const result = students.some((student) => student.score < 50);
console.log(result);
const result1 = !students.every((student) => student.score >= 50);
console.log(result1);
}
reduce(콜백함수)
- 누적된 결과를 반환할 때 사용
배열.reduce(콜백함수, 초깃값); 콜백함수 = (누적값pre, 현잿값cur, 인덱스i, 요소) => {... return 다음acc}
//9. compute students' average score : reduce(콜백함수)
//콜백함수 : 누적된 결과를 반환한다.
//reduce() : 배열의 모든 요소의 값을 누적한다.
//배열.reduce(콜백함수, 초깃값)
//콜백함수 = (누적값pre, 현잿값cur, 인덱스i, 요소) => {... return 다음pre}
{
const result = students.reduce((pre, cur, i) => {
console.log(pre, cur, i);
// return pre;
// 리턴값이 pre로 가는데, 없으니까 undefined
}, 0);
console.log("---------------------------------");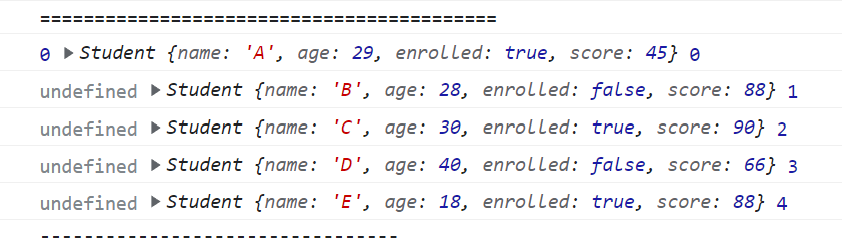
const result1 = students.reduce((pre, cur, i) => {
console.log(pre, cur, i);
return pre;
//처음에 초깃값 0으로 고정했으니 pre==0
}, 0);
console.log("---------------------------------");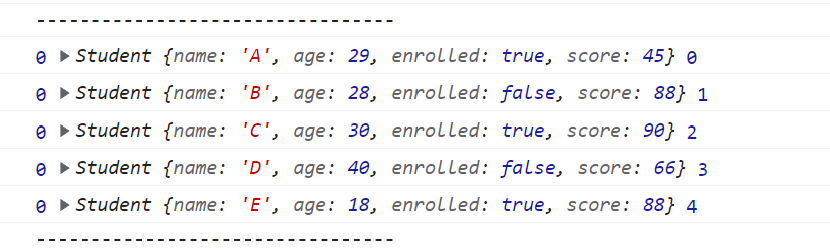
const result2 = students.reduce((pre, cur, i) => {
console.log(pre, cur, i);
return cur;
//리턴값 cur이 다음 pre로 들어간다.
}, 0);
console.log("---------------------------------");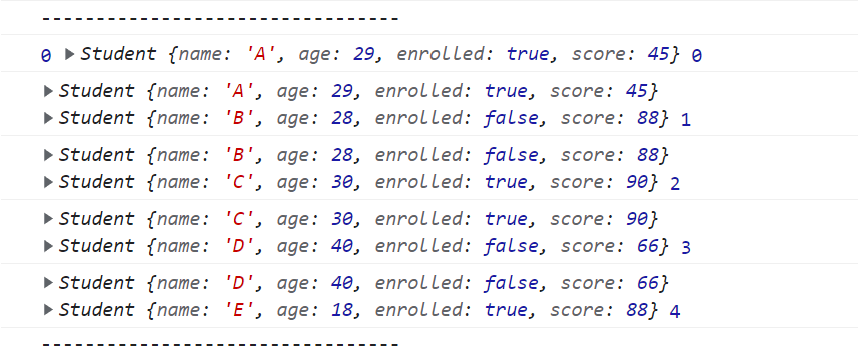
const result3 = students.reduce((pre, cur, i) => {
console.log(pre, cur.score, i);
return pre + cur.score;
//리턴값 : 0 + 45 -> 45 + 80 -> 125 + 90 -> ... 이 다음 pre로 들어간다.
}, 0);
console.log(result3);
console.log("---------------------------------");
const result4 =
students.reduce((pre, cur) => pre + cur.score, 0) / students.length;
console.log(result4);
// const result = students.map((student) => student.score);
// console.log(result);
// let all = 0;
// result.forEach((score) => all += score);
// console.log(all / result.length);
}
복합
//10. make a string containing all the scores
//result should be: '45, 80, 90, 66, 88'
{
const scores = students.map((student) => student.score).join(", ");
console.log(scores);
//여기에 점수가 50점 이상인 사람들을 골라낸다면?
const scores1 = students
.map((student) => student.score)
.filter((score) => score >= 50)
.join(", ");
console.log(scores1);
}
sort(콜백함수)
//11. do Q10 sorted in ascending order : sort(콜백함수)
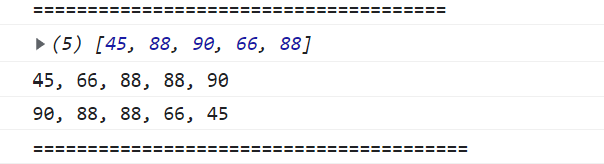
//result should be: '45, 66, 80, 88, 90'
{
const scores = students.map((student) => student.score);
console.log(scores);
const result = scores.sort((a, b) => a - b).join(", ");
//그냥 sort()하면 안된다!!! 문자기준 오름차순이기 때문에
console.log(result);
//내림차순 정렬이라면?
const result1 = scores.sort((a, b) => b - a).join(", ");
console.log(result1);
}