JSON
- JavaScript Object Notation
- simplest data interchange format
- lightweight text-based structure
- easy to read
- key-value pairs(
{key:value})
- used for serialization(직렬화) and transmission of data between the network the network connection
- independent programming language and platform
Object to JSON
JSON.stringify(obj)
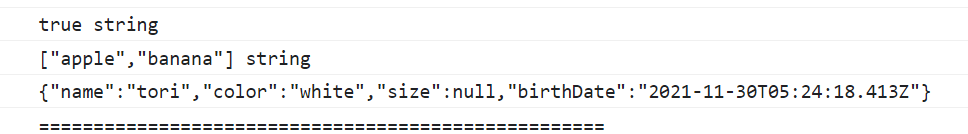
let json = JSON.stringify(true);
console.log(json, typeof json);
json = JSON.stringify(["apple", "banana"]);
console.log(json, typeof json);
const rabbit = {
name: "tori",
color: "white",
size: null,
birthDate: new Date(),
jump: () => {
console.log(`${this.name} can jump!`);
},
};
json = JSON.stringify(rabbit);
console.log(json);
JSON.stringify(obj, replacer배열|함수)
- 내가 원하는 정보만
- 처음엔 최상위 객체가 전달된다.
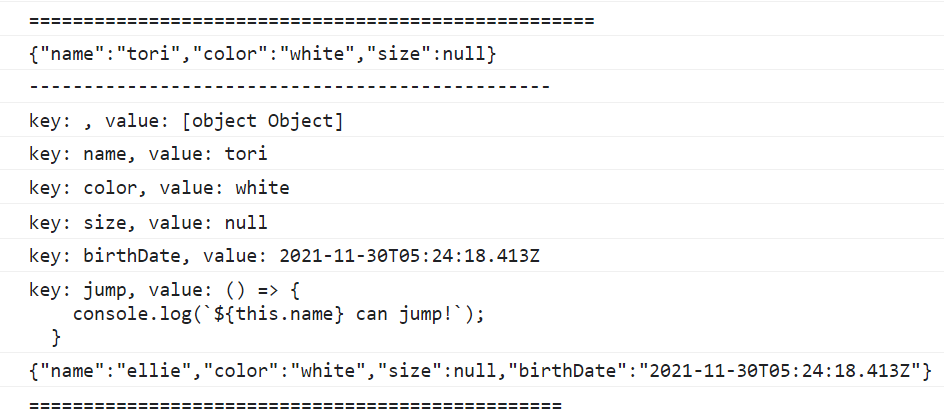
json = JSON.stringify(rabbit, ["name", "color", "size"]);
console.log(json);
console.log("------------------------------------------------");
json = JSON.stringify(rabbit, (key, value) => {
console.log(`key: ${key}, value: ${value}`);
return key === "name" ? "ellie" : value;
});
console.log(json);
JSON to Object
JSON.parse(json문자열, reviver배열|함수))
json = JSON.stringify(rabbit);
console.log(json);
console.log("-------------------------------------------------");

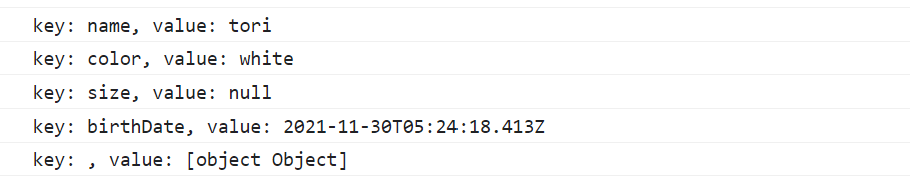
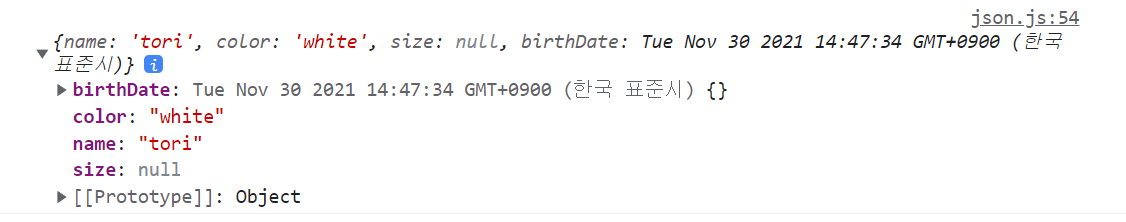
const obj = JSON.parse(json, (key, value) => {
console.log(`key: ${key}, value: ${value}`);
return key === "birthDate" ? new Date() : value;
});
console.log(obj);
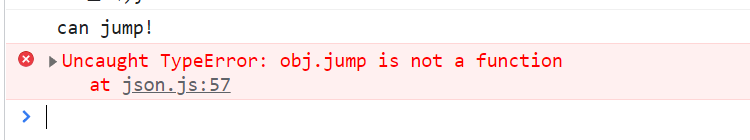
📢📢주의!!!
rabbit.jump();
obj.jump();
console.log("------------------------------------------------");
console.log(rabbit.birthDate.getDate());
console.log(obj.birthDate);
console.log(obj.birthDate.getDate());








