CSS에서 z-index는 요소의 쌓임 순서를 결정하는 데 사용된다. 그러나 특정 상황에서는 z-index를 설정했음에도 불구하고 예상한 대로 동작하지 않는 경우가 있다. 이 문제의 원인은 Stacking Context(스태킹 컨텍스트)에 있다. 이번 글에서는 캐러셀 구현 중 z-index 적용 문제를 예시로, 스태킹 컨텍스트와 z-index가 왜 의도대로 동작하지 않는지 자세히 알아보자.
문제 상황
const DesktopInputForm = () => {
return(
<div
className='flex flex-col gap-[24px] relative duration-500'
style={{
transform: `translateY(-${currentOffset-24}px)`,
}}
>
{orderList.map((e, previewStep) => (
<div
key={e.labelForInput}
className='w-full h-full flex flex-col justify-center items-center gap-[24px] reltaive'
>
{e.input.map((inputElement, inputStep) => {
return (
<div
key={e.name[inputStep]}
style={{
zIndex:
currentStep.currentPreviewStep === previewStep && currentStep.currentInputStep === inputStep
? 30
: 0,
}}
className={`w-full h-full border-[1px] border-solid shadow-md rounded-[12px] px-[24px] py-[16px] relative bg-white`}
ref={(el) => {
inputHeightRef.current[e.name[inputStep]] = { height: el?.offsetHeight };
}}
>
<p className='text-gray-900 text-[18px] font-bold mb-[14px]'>{e.name[inputStep]}</p>
{inputElement}
</div>
);
})}
</div>
))}
</div>
)
}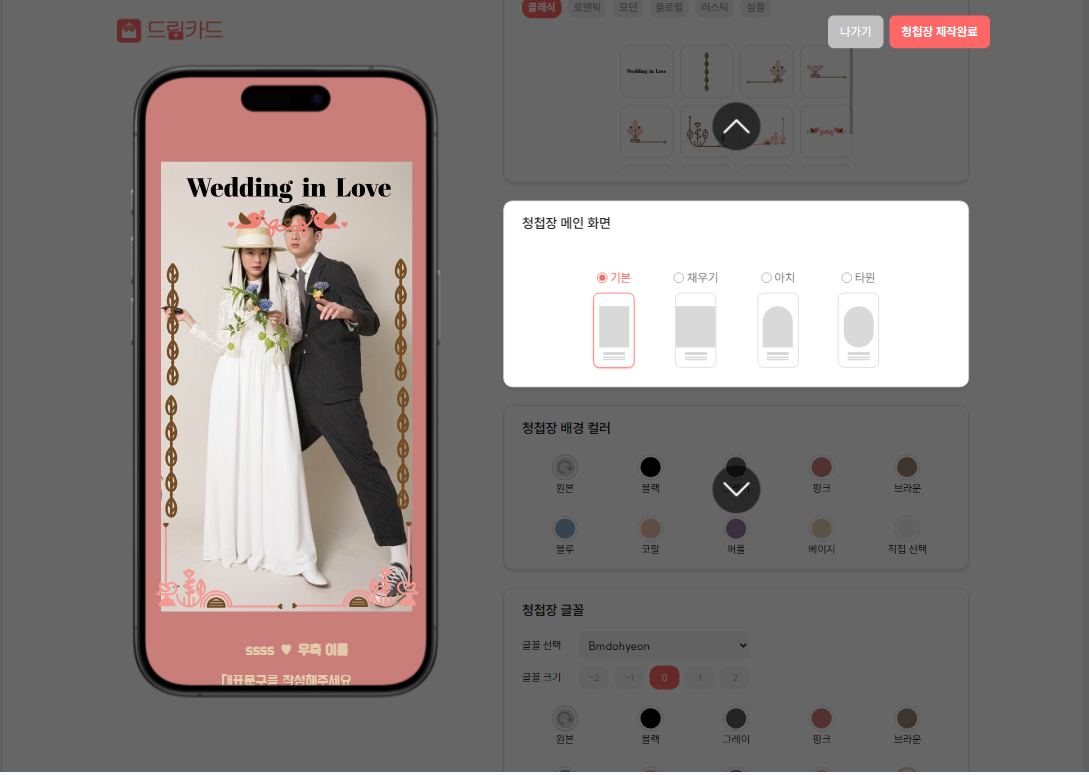
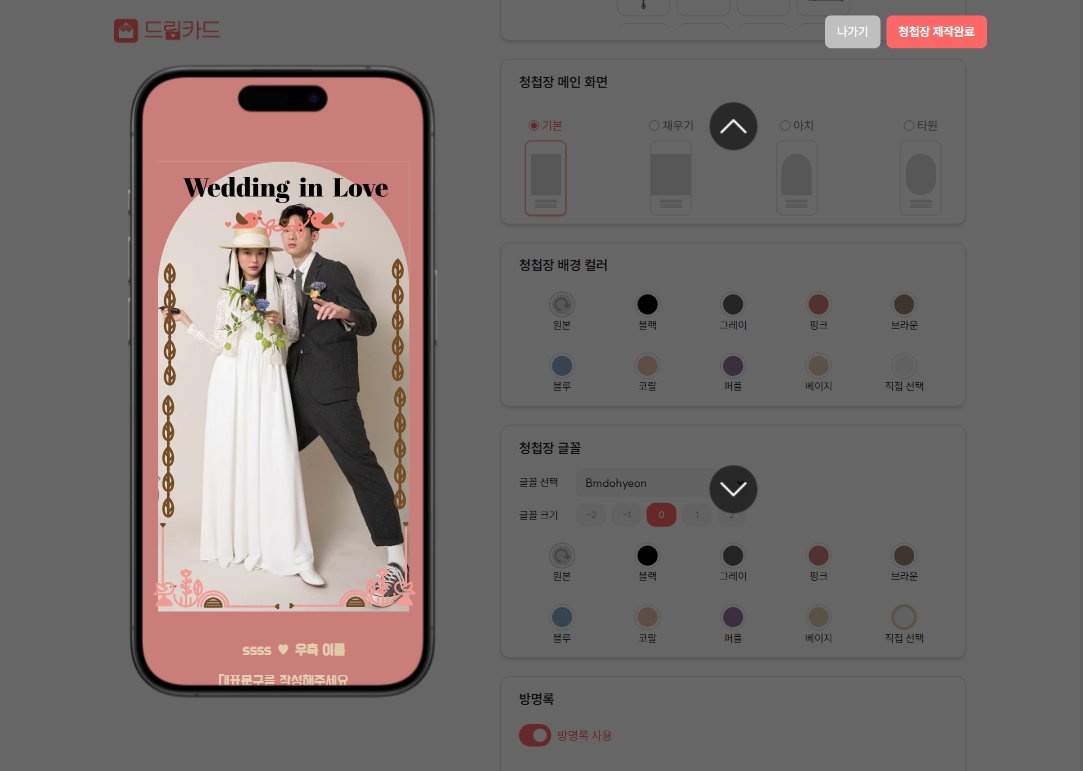
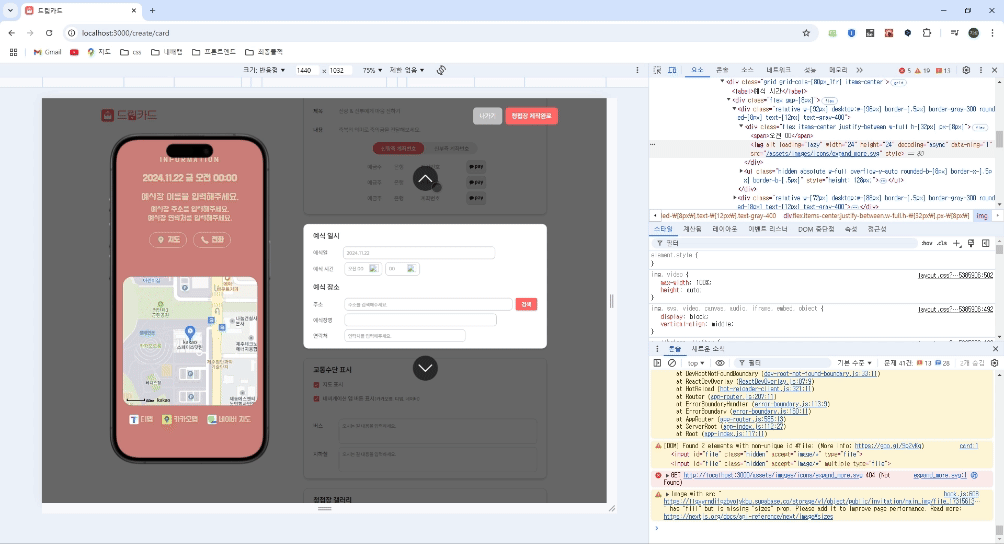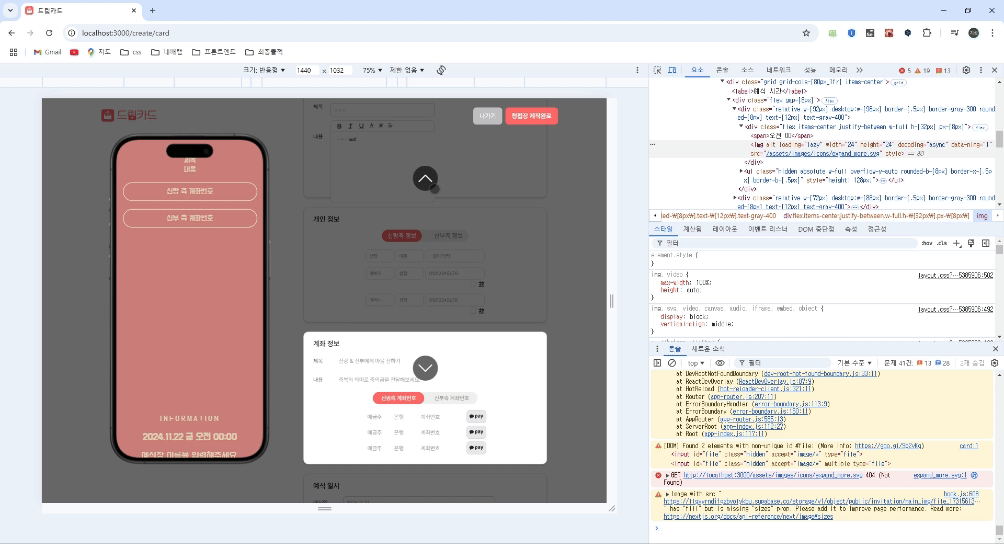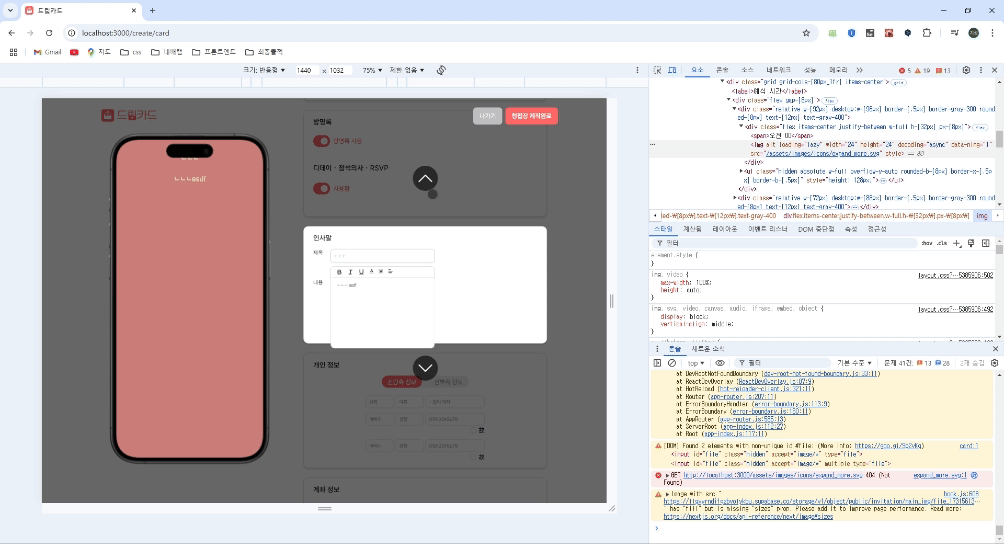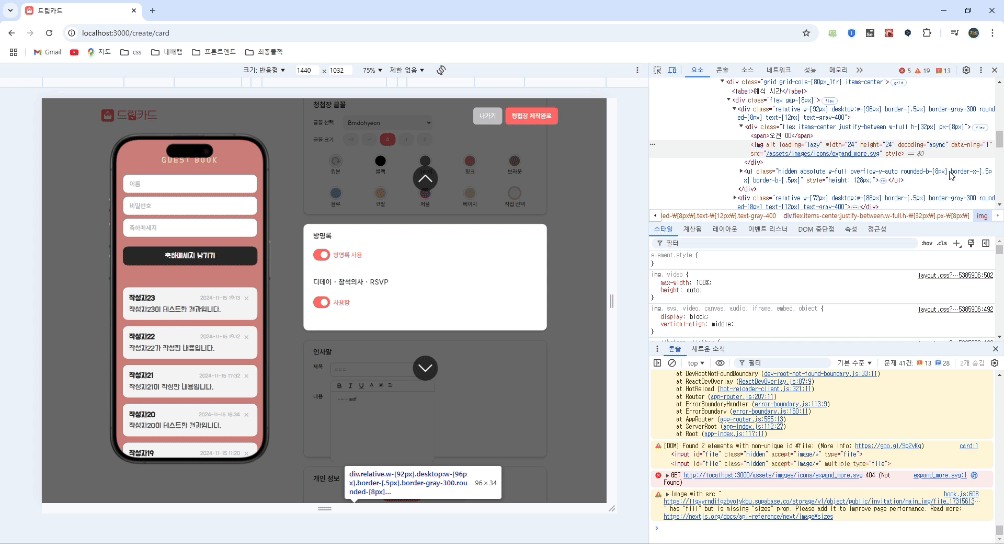
위쪽 사진은 요구사항이고 아래쪽 사진은 transform을 사용했을 때의 사진이다. 위 코드 예시에서, transform: translateY를 사용해 캐러셀을 구현했지만, z-index가 제대로 적용되지 않아 오버레이가 input 위로 나오지 않는 현상이 발생했다.
원인: Stacking Context
transform, filter, opacity 등 특정 CSS 속성은 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트(Stacking Context)를 생성한다. 스태킹 컨텍스트는 HTML 문서에서 요소가 어떻게 쌓이는지 정의하는 독립된 레이어다. 이 컨텍스트 안에서는 자식 요소의 z-index가 부모 컨텍스트의 다른 요소와 독립적으로 동작한다.
쉽게 말하면 z-index가 적용이 되는 그룹이 생성된다 생각했을 때 이 그룹이 여러 개 생성 되면 서로 다른 그룹끼리는 z-index가 적용되지 않는다. 각 스태킹 컨텍스트는 형제 요소와는 완전히 독립적인 요소이고 stacking이 처리될 경우 스태킹 컨텍스트가 생성된 요소의 하위 요소만 그룹으로 취급되는 것이다.
Stacking Context의 주요 특징
- 새로운 컨텍스트 생성 조건:
- 부모 요소에 다음 속성이 포함되면 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트가 생성된다:
position: relative,absolute,fixed와 함께 사용되는z-index값.transform속성 (translate,scale등 포함).filter,opacity,perspective등 CSS 속성.will-change속성.
- 부모 요소에 다음 속성이 포함되면 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트가 생성된다:
- 독립성:
- 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트는 상위 스태킹 컨텍스트와 별도로 동작한다.
- 자식 요소의
z-index는 같은 스태킹 컨텍스트 내에서만 영향을 미친다.
- z-index 무효화:
- 상위 컨텍스트의
z-index가 자식 컨텍스트에 영향을 주지 않는다. - 이로 인해 부모에 의해 생성된 새로운 컨텍스트 내의
z-index가 오버레이보다 아래에 배치될 수 있다.
- 상위 컨텍스트의
이러한 특징 때문에 transform을 사용하였을 때 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트가 생성되어 상위 스태킹 컨텍스트와 별개로 독립적으로 동작하게 되어 z-index가 아무리 높아도 오버레이 위로 올라가지 않는 현상이 발생하게 되었다.
해결 방안
transform 대신 position으로 움직이기
const DesktopInputForm = () => {
return(
<div
className='flex flex-col gap-[24px] relative duration-500'
style={{
top: -currentOffset - 24,
}}
>
{orderList.map((e, previewStep) => (
<div
key={e.labelForInput}
className='w-full h-full flex flex-col justify-center items-center gap-[24px] reltaive'
>
{e.input.map((inputElement, inputStep) => {
return (
<div
key={e.name[inputStep]}
style={{
zIndex:
currentStep.currentPreviewStep === previewStep && currentStep.currentInputStep === inputStep
? 30
: 0,
}}
className={`w-full h-full border-[1px] border-solid shadow-md rounded-[12px] px-[24px] py-[16px] relative bg-white`}
ref={(el) => {
inputHeightRef.current[e.name[inputStep]] = { height: el?.offsetHeight };
}}
>
<p className='text-gray-900 text-[18px] font-bold mb-[14px]'>{e.name[inputStep]}</p>
{inputElement}
</div>
);
})}
</div>
))}
</div>
)
}transform을 사용하지 않고 position으로만 위치를 조정하여 캐러셀을 구현하면 새로운 스태킹 컨텍스트가 생성되지 않기 때문에 간단하게 수정할 수 있었다. 자연스럽게 위치가 조정되는 것을 보여주기 위해서 duration 속성을 추가하여 위치 변경을 자연스럽게 수정할 수 있었다.