🔑클래스 복사
▪ 다른 변수와 마찬가지로 다른 클래스에서 클래스를 복사할 수 있습니다.
▪ 할당 연산자 '='를 사용하여 클래스를 복사할 수 있습니다.
"=" 이 클래스 간 복사가 되도록 오버로딩이 됨
클래스 A를 B로 복사하고 싶으면
B = A or B(A)와 같이 작성
🔑얕은 복사, 깊은 복사
얕은 복사
• A를 얕게 복사하는 과정에서 B는 A의 필드 값을 모두 복사합니다. 필드 값이 메모리 주소일 경우 메모리 주소가 복사됩니다.
• B의 필드 중 하나가 가리키는 메모리 주소를 수정하면 A의 필드가 가리키는 메모리 주소도 수정됩니다
깊은 복사
• 모든 필드를 복사하고 필드가 가리키는 동적으로 할당된 메모리의 복사본을 만듭니다.
• A와 B는 서로 의존하지 않고 더 느리고 더 용량을 소모하는 복사를 한다.

복사 생성자
• 복사 생성자는 새 개체를 기존 개체의 복사본으로 만들기 위한 특수 생성자입니다.
• 컴파일러는 각 클래스에 대한 복사 생성자(암묵 복사 생성자)를 자동으로 만듭니다.
• 필요에 따라 프로그래머는 사용자 정의 복사 생성자로 알려진 복사 생성자를 생성해야 합니다.
ex1) 복사 생성자 정의
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Unit {
public:
Unit() {
cout << "기본 생성자" << endl;
str = NULL;
}
Unit(const char* agStr)
{
cout << "매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자" << endl;
int strLength = strlen(agStr);
str = new char[strLength + 1];
strcpy(str, agStr);
}
void set(const char* agStr) {
strcpy(str, agStr);
}
void show() {
cout << str << "\n";
}
Unit(Unit& agUnit) {
cout << "복사 생성자" << endl;
}
private:
char* str;
};
int main() {
Unit A("Test1");
Unit B(A);
cout << "----------------------------\n";
A.set("Test2");
cout << "A's str = : ";
A.show();
cout << "B's str = : ";
B.show();
}결과:
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
복사 생성자
"----------"
A's str = : Test2
B's str = :
ex2) 얕은 복사
단순히 포인터를 공유하기 때문에 A의 str값이 바뀌면 B도 함께 바뀐다
Unit(Unit& agUnit) {
cout << "복사 생성자" << endl;
str = agUnit.str;
}결과:
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
복사 생성자
---------------------
A's str = : Test2
B's str = : Test2
ex3) 깊은 복사
str의 값을 복사해 오는 것이기 때문에 A의 str이 바뀌어도 영향을 받지 않는다.
Unit(Unit& agUnit) {
cout << "복사 생성자" << endl;
str = new char[strlen(agUnit.str) + 1];
strcpy(str, agUnit.str);
}결과:
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
복사 생성자
------------------------
A's str = : Test2
B's str = : Test1
🔑복사 함수 만들기
위 예제를 copyFrom과 copyTo 함수로 구현해 보았다
얕은 복사
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Unit {
public:
Unit() {
cout << "기본 생성자" << endl;
str = NULL;
}
Unit(const char* agStr)
{
cout << "매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자" << endl;
int strLength = strlen(agStr);
str = new char[strLength + 1];
strcpy(str, agStr);
}
void set(const char* agStr) {
strcpy(str, agStr);
}
void show() {
cout << str << "\n";
}
Unit(Unit& agUnit) {
cout << "복사 생성자" << endl;
str = new char[strlen(agUnit.str) + 1];
strcpy(str, agUnit.str);
}
void copyFrom(Unit& agUnit) {
str = agUnit.str;
}
void copyTo(Unit& agUnit) {
agUnit. str = str;
}
private:
char* str;
};
int main() {
Unit A("Unit A"), B("Unit B"), C("Unit C");
A.show(); B.show(); C.show();
cout << endl;
A.copyFrom(B);
C.copyTo(B);
A.show(); B.show(); C.show();
cout << endl;
B.set("Unit B");
A.show(); B.show(); C.show();
cout << endl;
A.set("Unit A");
A.show(); B.show(); C.show();
cout << endl;
}결과:
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
Unit A
Unit B
Unit C
Unit B
Unit C
Unit C
Unit B
Unit B
Unit B
Unit A
Unit B
Unit B
기본 생성자가 각각 호출되고
얕은 복사로 A가 B에게서 얕은복사(A=B), C에게서 B로 얕은 복사(B=C)가 되었다.
여기서 B의 값을 바꾸면 얕은 복사가 된 C의 값도 바뀐다.
다음 A의 값을 바꾼다면 기존의 B가 가리키던 곳은 C가 가리키던 곳으로 되어있으므로 B,C의 값에 변화는 없다.
깊은 복사
void copyFrom(Unit& agUnit) {
str = new char[strlen(agUnit.str) + 1];
strcpy(str, agUnit.str);
}
void copyTo(Unit& agUnit) {
agUnit.str=new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(agUnit.str, str);
}결과:
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
매개변수를 가진 기본 생성자
Unit A
Unit B
Unit C
Unit B
Unit C
Unit C
Unit B
Unit B
Unit C
Unit A
Unit B
Unit C
새로운 메모리를 할당하여 값을 복사해오기 때문에 복사를 받은 값의 변화에 따른 영향이 없다.
🔑Friend 함수
• 클래스 외부에서 정의된 일반 함수는 개인 데이터와 보호된 데이터에 액세스할 수 없습니다.
• 특정 클래스의 "친구"인 friend 함수는 해당 클래스의 비공개 및 보호된 데이터에 액세스할 수 있으며, 일반적으로 데이터가 공용인 것처럼 액세스할 수 없습니다.
• 클래스 정의에 friend 함수의 프로토타입이 나타나더라도 멤버 함수가 아닙니다.
• 함수는 여러 클래스의 친구로 정의할 수 있습니다.
구문
friend return_type function(arguments);
friend int max(int a, int b);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Unit {
int x, y;
public:
Unit(int i, int j) { x = i; y = j; }
friend bool isSame(Unit a);
};
bool isSame(Unit a)
{
if (a.x == a.y) return true;
else return false;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Unit a(1, 2), b(3, 3);
cout << "a(1,2) : " << isSame(a) << "\n";
cout << "b(3,3) : " << isSame(b) << "\n";
}
isSame함수는 Unit class의 멤버변수와 함수를 사용할 수 있다는 의미로 클래스 안에 선언되나
클래스의 멤버는 아니다.
friend 함수 퀴즈

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Square {
int height, width;
public:
Square(int x, int y) {
height = x;
width = y;
}
friend int addSquare(Square A, Square B);
};
int addSquare(Square A, Square B) {
int add = A.height * A.width + B.height * B.width;
cout << "Sum of Areas : " << add << endl;
return add;
}
int main()
{
Square A(5, 3), B(4, 4);
addSquare(A, B);
return 0;
}여러 클래스에 쓰인 friend 함수
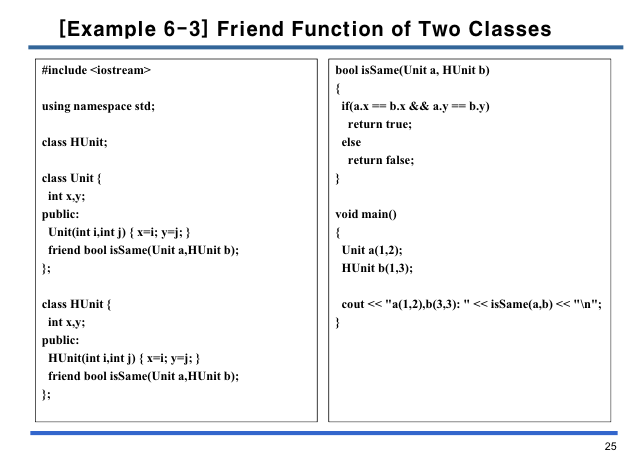
매개변수로 받는 클래스가 2개 이상인 friend 함수는 클래스들에 모두 프로토타입을 적어주며 사용할 수 있다.

