모듈 정의
train.py
- 모델 학습과 검증 함수 정의
import os
os.makedirs('module', exist_ok=True)%%writefile module/train.py
import torch
import time
def test_multi_classification(dataloader, model, loss_fn, device="cpu") -> tuple:
"""
다중 분류 검증/평가 함수
[parameter]
dataloader: DataLoader - 검증할 대상 데이터로더
model: 검증할 모델
loss_fn: 모델 추정값과 정답의 차이를 계산할 loss 함수.
device: str - 연산을 처리할 장치. default-"cpu", gpu-"cuda"
[return]
tuple: (loss, accuracy)
"""
model.eval()
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_steps = len(dataloader)
test_loss, test_accuracy = 0., 0.
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
# 정확도 계산
pred_label = torch.argmax(pred, axis=-1)
test_accuracy += torch.sum(pred_label == y).item()
test_loss /= num_steps
test_accuracy /= size
return test_loss, test_accuracy
def test_binary_classification(dataloader, model, loss_fn, device="cpu") -> tuple:
"""
이진 분류 검증/평가 함수
[parameter]
dataloader: DataLoader - 검증할 대상 데이터로더
model: 검증할 모델
loss_fn: 모델 추정값과 정답의 차이를 계산할 loss 함수.
device: str - 연산을 처리할 장치. default-"cpu", gpu-"cuda"
[return]
tuple: (loss, accuracy)
"""
model.eval() # 모델을 평가모드로 변환
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
num_steps = len(dataloader)
test_loss, test_accuracy = 0., 0.
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
test_loss += loss_fn(pred, y).item()
## 정확도 계산
pred_label = (pred >= 0.5).type(torch.int32)
test_accuracy += (pred_label == y).sum().item()
test_loss /= num_steps
test_accuracy /= size #전체 개수로 나눈다.
return test_loss, test_accuracy
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer, device="cpu", mode:"binary or multi"='binary'):
"""
모델을 1 epoch 학습시키는 함수
[parameter]
dataloader: DataLoader - 학습데이터셋을 제공하는 DataLoader
model - 학습대상 모델
loss_fn: 모델 추정값과 정답의 차이를 계산할 loss 함수.
optimizer - 최적화 함수
device: str - 연산을 처리할 장치. default-"cpu", gpu-"cuda"
mode: str - 분류 종류. binary 또는 multi
[return]
tuple: 학습후 계산한 Train set에 대한 train_loss, train_accuracy
"""
model.train()
size = len(dataloader.dataset)
for X, y in dataloader:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
pred = model(X)
loss = loss_fn(pred, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if mode == 'binary':
train_loss, train_accuracy = test_binary_classification(dataloader, model, loss_fn, device)
else:
train_loss, train_accuracy = test_multi_classification(dataloader, model, loss_fn, device)
return train_loss, train_accuracy
def fit(train_loader, val_loader, model, loss_fn, optimizer, epochs, save_best_model=True,
save_model_path=None, early_stopping=True, patience=10, device='cpu',
mode:"binary or multi"='binary',
lr_scheduler=None):
"""
모델을 학습시키는 함수
[parameter]
train_loader (Dataloader): Train dataloader
test_loader (Dataloader): validation dataloader
model (Module): 학습시킬 모델
loss_fn (Loss): Loss function
optimizer (Optimizer): Optimizer
epochs (int): epoch수
save_best_model (bool, optional): 학습도중 성능개선시 모델 저장 여부. Defaults to True.
save_model_path (str, optional): save_best_model=True일 때 모델저장할 파일 경로. Defaults to None.
early_stopping (bool, optional): 조기 종료 여부. Defaults to True.
patience (int, optional): 조기종료 True일 때 종료전에 성능이 개선될지 몇 epoch까지 기다릴지 epoch수. Defaults to 10.
device (str, optional): device. Defaults to 'cpu'.
mode(str, optinal): 분류 종류. "binary(default) or multi
lr_scheduler: Learning Scheduler객체 default=None ====> 한 에폭 끝날때 마다 learning rate 변경.
[return]
tuple: 에폭 별 성능 리스트. (train_loss_list, train_accuracy_list, validation_loss_list, validataion_accuracy_list)
"""
train_loss_list = []
train_accuracy_list = []
val_loss_list = []
val_accuracy_list = []
if save_best_model:
best_score_save = torch.inf
############################
# early stopping
#############################
if early_stopping:
trigger_count = 0
best_score_es = torch.inf
# 모델 device로 옮기기
model = model.to(device)
s = time.time()
for epoch in range(epochs):
train_loss, train_accuracy = train(train_loader, model, loss_fn, optimizer, device=device, mode=mode)
# 한 epoch 학습 종료 후 LR scheduler를 이용해 LR 변경.
if lr_scheduler is not None:
lr_scheduler.step()
if mode == "binary":
val_loss, val_accuracy = test_binary_classification(val_loader, model, loss_fn, device=device)
else:
val_loss, val_accuracy = test_multi_classification(val_loader, model, loss_fn, device=device)
train_loss_list.append(train_loss)
train_accuracy_list.append(train_accuracy)
val_loss_list.append(val_loss)
val_accuracy_list.append(val_accuracy)
print(f"Epoch[{epoch+1}/{epochs}] - Train loss: {train_loss:.5f} Train Accucracy: {train_accuracy:.5f} || Validation Loss: {val_loss:.5f} Validation Accuracy: {val_accuracy:.5f}")
print('='*100)
# 모델 저장
if save_best_model:
if val_loss < best_score_save:
torch.save(model, save_model_path)
print(f"<<<<<<<저장: {epoch+1} - 이전 : {best_score_save}, 현재: {val_loss}")
best_score_save = val_loss
# early stopping 처리
if early_stopping:
if val_loss < best_score_es: # 성능 개선 (O)
best_score_es = val_loss
trigger_count = 0
else: # 성능 개선 (X)
trigger_count += 1
if patience == trigger_count:
print(f">>>>>>Early stopping: Epoch - {epoch}")
break
e = time.time()
print(e-s, "초")
return train_loss_list, train_accuracy_list, val_loss_list, val_accuracy_listdata.py
- dataset 생성 함수 제공 모듈
%%writefile module/data.py
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
def load_mnist_dataset(root_path, batch_size, is_train=True):
"""
mnist dataset dataloader 제공 함수
[parameter]
root_path: str|Path - 데이터파일 저장 디렉토리
batch_size: int
is_train: bool = True - True: Train dataset, False - Test dataset
[return]
DataLoader
"""
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor()
])
dataset = datasets.MNIST(root=root_path, train=is_train, download=True, transform=transform)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=is_train) # shuffle: train이면 True, test면 False 할 것이므로 is_train을 넣음.
return dataloader
def load_fashion_mnist_dataset(root_path, batch_size, is_train=True):
"""
fashion mnist dataset dataloader 제공 함수
[parameter]
root_path: str|Path - 데이터파일 저장 디렉토리
batch_size: int
is_train: bool = True - True: Train dataset, False - Test dataset
[return]
DataLoader
"""
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor()
])
dataset = datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root_path, train=is_train, download=True, transform=transform)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=is_train) # shuffle: train이면 True, test면 False 할 것이므로 is_train을 넣음.
return dataloader%%writefile module/utils.py
## 학습 결과를 시각화하는 함수.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_fit_result(train_loss_list, train_accuracy_list, valid_loss_list, valid_accuracy_list):
epoch = len(train_loss_list)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(range(epoch), train_loss_list, label="train loss")
plt.plot(range(epoch), valid_loss_list, label="validation loss")
plt.title("Loss")
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("loss")
plt.grid(True, linestyle=':')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(range(epoch), train_accuracy_list, label="train accuracy")
plt.plot(range(epoch), valid_accuracy_list, label="validation accuracy")
plt.title("Accuracy")
plt.xlabel("epoch")
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.grid(True, linestyle=':')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()import
import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch.utils.data import DataLoader from torchinfo import summary from module.train import fit # fit 함수 import from module.data import load_mnist_dataset, load_fashion_mnist_dataset from module.utils import plot_fit_result print(torch.__version__)
하이퍼파라미터, 변수 정의
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" # device = "mps" if torch.backends.mps.is_available() else "cpu" print("device:", device) dataset_path = r"C:\Classes\deeplearning\datasets" epochs = 100 batch_size = 256 lr = 0.001
Data 준비
mnist 데이터 로딩
train_loader = load_mnist_dataset(dataset_path, batch_size) #trainset test_loader = load_mnist_dataset(dataset_path, batch_size, False) # testset # train_loader = load_fashion_mnist_dataset(dataset_path, batch_size) #trainset # test_loader = load_fashion_mnist_dataset(dataset_path, batch_size, False) # testset print(train_loader) print(train_loader.dataset)<torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader object at 0x0000028386E6F450>
Dataset MNIST
Number of datapoints: 60000
Root location: C:\Classes\deeplearning\datasets
Split: Train
StandardTransform
Transform: Compose(
ToTensor()
)
모델의 크기 변경에 따른 성능변화
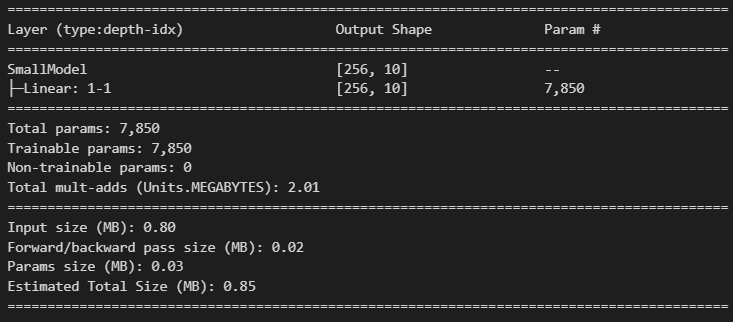
# 모델정의 class SmallModel(nn.Module):def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.lr = nn.Linear(784, 10) # 784(1*28*28) -> 10(class개수)def forward(self, X): out = nn.Flatten()(X) # N x 1 x 28 x 28 -> N x 784 out = self.lr(out) return out# 모델 생성 small_model = SmallModel() summary(small_model, (batch_size, 1, 28, 28))
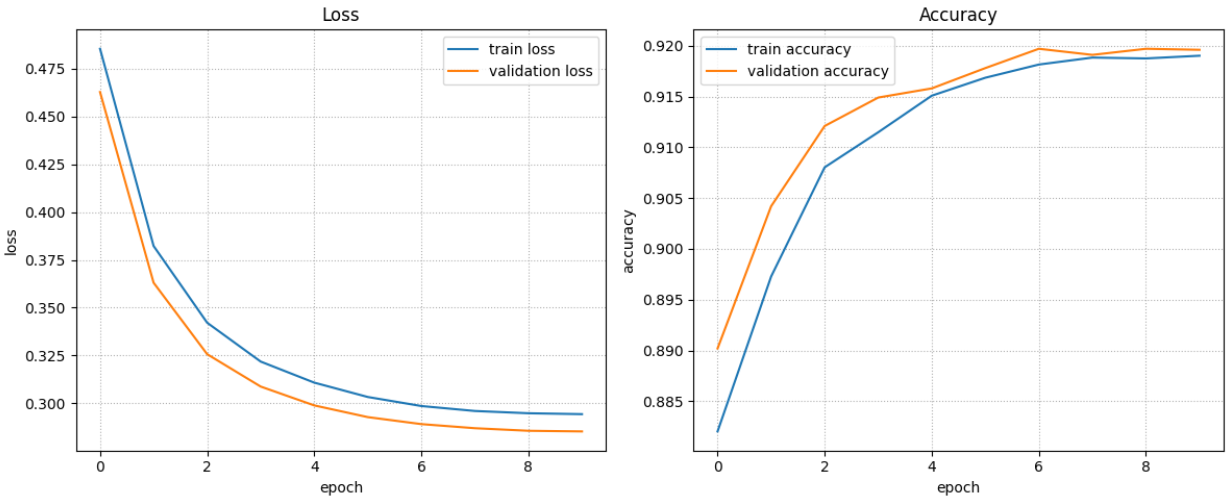
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 다중분류 Loss: pred-LogSoftmax() , y-OneHotEncoding optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(small_model.parameters(), lr=lr)# LR Scheduler 추가 lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts( optimizer, T_0=10, T_mult=2, eta_min=1e-5, verbose=True # LR 변경할 때마다 log출력 )train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list = fit( train_loader, test_loader, # 학습, 검증 데이터셋 small_model, loss_fn, optimizer, # 학습에 필요한 세개 객체(모델, loss함수, 옵티마이저) 10, # 에폭수. save_best_model=True, save_model_path="saved_models/small_model.pth", patience=5, device=device, mode="multi", lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler )Epoch[1/10] - Train loss: 0.48549 Train Accucracy: 0.88203 || Validation Loss: 0.46286 Validation Accuracy: 0.89020
<<<<<<<저장: 1 - 이전 : inf, 현재: 0.46285842210054395
Epoch[2/10] - Train loss: 0.38229 Train Accucracy: 0.89728 || Validation Loss: 0.36307 Validation Accuracy: 0.90420
<<<<<<<저장: 2 - 이전 : 0.46285842210054395, 현재: 0.3630656661465764
Epoch[3/10] - Train loss: 0.34213 Train Accucracy: 0.90803 || Validation Loss: 0.32567 Validation Accuracy: 0.91210
<<<<<<<저장: 3 - 이전 : 0.3630656661465764, 현재: 0.32566529819741846
Epoch[4/10] - Train loss: 0.32179 Train Accucracy: 0.91148 || Validation Loss: 0.30872 Validation Accuracy: 0.91490
<<<<<<<저장: 4 - 이전 : 0.32566529819741846, 현재: 0.30871520629152654
Epoch[5/10] - Train loss: 0.31078 Train Accucracy: 0.91508 || Validation Loss: 0.29885 Validation Accuracy: 0.91580
<<<<<<<저장: 5 - 이전 : 0.30871520629152654, 현재: 0.29885398177430034
Epoch[6/10] - Train loss: 0.30326 Train Accucracy: 0.91685 || Validation Loss: 0.29273 Validation Accuracy: 0.91780
<<<<<<<저장: 6 - 이전 : 0.29885398177430034, 현재: 0.29272730015218257
Epoch[7/10] - Train loss: 0.29853 Train Accucracy: 0.91815 || Validation Loss: 0.28907 Validation Accuracy: 0.91970
<<<<<<<저장: 7 - 이전 : 0.29272730015218257, 현재: 0.28906617211177943
Epoch[8/10] - Train loss: 0.29594 Train Accucracy: 0.91883 || Validation Loss: 0.28692 Validation Accuracy: 0.91910
<<<<<<<저장: 8 - 이전 : 0.28906617211177943, 현재: 0.28691873978823423
Epoch[9/10] - Train loss: 0.29475 Train Accucracy: 0.91875 || Validation Loss: 0.28558 Validation Accuracy: 0.91970
...
Epoch[10/10] - Train loss: 0.29428 Train Accucracy: 0.91902 || Validation Loss: 0.28524 Validation Accuracy: 0.91960
<<<<<<<저장: 10 - 이전 : 0.2855781141668558, 현재: 0.28524379348382356
138.6000452041626 초plot_fit_result(train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list)
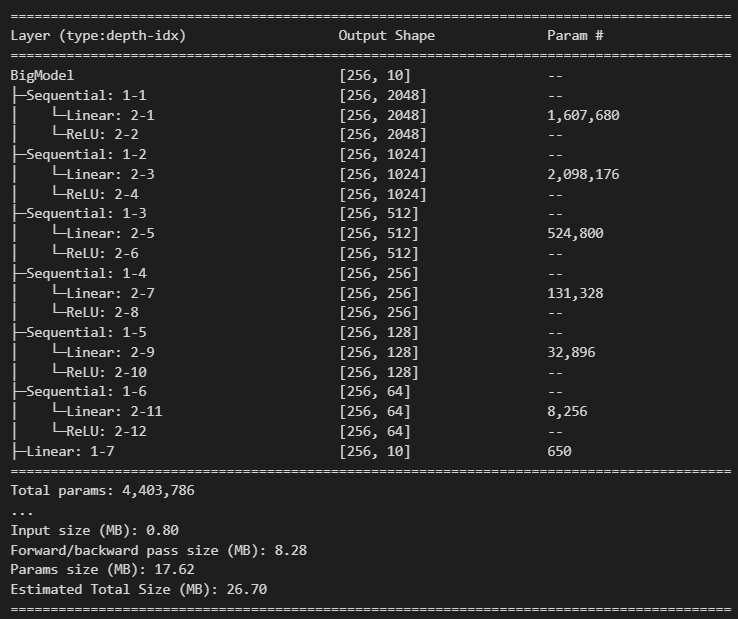
## 큰 모델 class BigModel(nn.Module):def __init__(self): super().__init__() # Linear -> ReLU 하나의 block 묶어서 정의. self.b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(784, 2048), nn.ReLU()) self.b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2048, 1024), nn.ReLU()) self.b3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(1024, 512), nn.ReLU()) self.b4 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512, 256), nn.ReLU()) self.b5 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(256, 128), nn.ReLU()) self.b6 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 64), nn.ReLU()) # output layer self.output = nn.Linear(64, 10)def forward(self, X): out = nn.Flatten()(X) out = self.b1(out) out = self.b2(out) out = self.b3(out) out = self.b4(out) out = self.b5(out) out = self.b6(out) out = self.output(out) return outbig_model = BigModel() summary(big_model, (batch_size, 1, 28, 28))
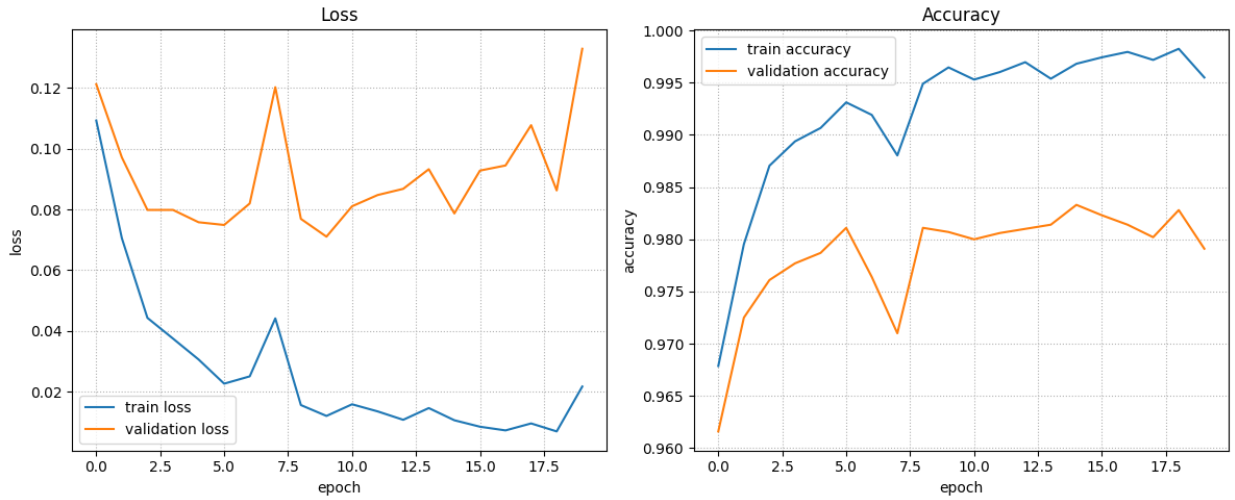
### 학습 loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(big_model.parameters(), lr=lr) train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list = fit( train_loader, test_loader, big_model, loss_fn, optimizer, epochs, save_best_model=True, save_model_path='saved_models/big_model.pth', device=device, mode="multi" )Epoch[1/100] - Train loss: 0.10929 Train Accucracy: 0.96787 || Validation Loss: 0.12124 Validation Accuracy: 0.96160
<<<<<<<저장: 1 - 이전 : inf, 현재: 0.1212444677716121
Epoch[2/100] - Train loss: 0.07055 Train Accucracy: 0.97953 || Validation Loss: 0.09715 Validation Accuracy: 0.97250
<<<<<<<저장: 2 - 이전 : 0.1212444677716121, 현재: 0.09715114108403214
Epoch[3/100] - Train loss: 0.04429 Train Accucracy: 0.98705 || Validation Loss: 0.07984 Validation Accuracy: 0.97610
<<<<<<<저장: 3 - 이전 : 0.09715114108403214, 현재: 0.07984241372032556
Epoch[4/100] - Train loss: 0.03747 Train Accucracy: 0.98938 || Validation Loss: 0.07985 Validation Accuracy: 0.97770
Epoch[5/100] - Train loss: 0.03058 Train Accucracy: 0.99067 || Validation Loss: 0.07579 Validation Accuracy: 0.97870
<<<<<<<저장: 5 - 이전 : 0.07984241372032556, 현재: 0.07578893480822443
Epoch[6/100] - Train loss: 0.02262 Train Accucracy: 0.99312 || Validation Loss: 0.07489 Validation Accuracy: 0.98110
<<<<<<<저장: 6 - 이전 : 0.07578893480822443, 현재: 0.07489473557288875
Epoch[7/100] - Train loss: 0.02502 Train Accucracy: 0.99192 || Validation Loss: 0.08198 Validation Accuracy: 0.97640
Epoch[8/100] - Train loss: 0.04412 Train Accucracy: 0.98803 || Validation Loss: 0.12028 Validation Accuracy: 0.97100
Epoch[9/100] - Train loss: 0.01557 Train Accucracy: 0.99490 || Validation Loss: 0.07690 Validation Accuracy: 0.98110
Epoch[10/100] - Train loss: 0.01198 Train Accucracy: 0.99647 || Validation Loss: 0.07104 Validation Accuracy: 0.98070
...
Epoch[20/100] - Train loss: 0.02167 Train Accucracy: 0.99550 || Validation Loss: 0.13293 Validation Accuracy: 0.97910
<<<<<<Early stopping: Epoch - 19
718.734453201294 초plot_fit_result(train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list)
Dropout 예제
- dropout 각 레이어에 적용
- dropout은 nn.Dropout 객체를 사용
- 객체 생성시 dropout_rate 설정: 0.2 ~ 0.5
- Drop시킬 노드를 가진 Layer 뒤에 추가한다.
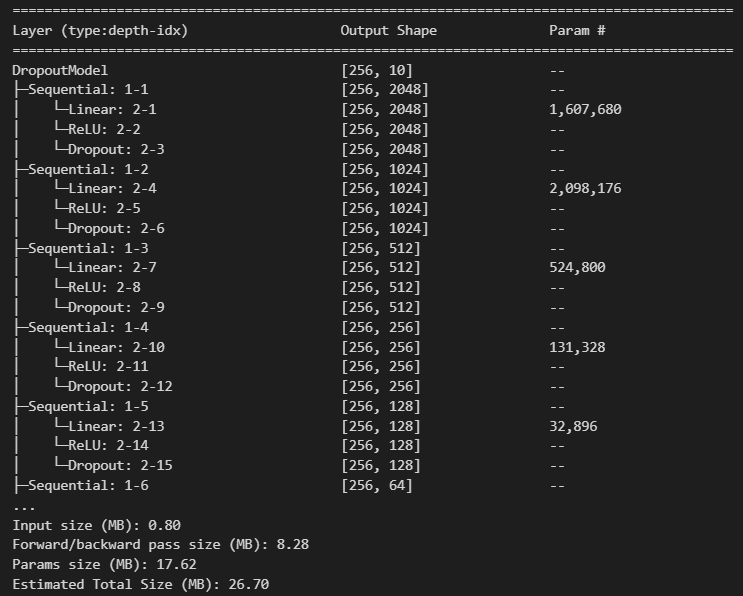
class DropoutModel(nn.Module): """ BigModel의 Layer들에 Dropout 추가. linear block: Linear -> ReLU -> Dropout Dropout Layer는 model.train() 일때 작동. model.eval() 일때는 작동하지 않는다. """def __init__(self, dropout_rate=0.5): super().__init__() # Linear -> ReLU 하나의 block 묶어서 정의. self.b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(784, 2048), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2048, 1024), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(1024, 512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b4 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b5 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(256, 128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b6 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) # output layer self.output = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(64, 10), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate))def forward(self, X): out = nn.Flatten()(X) out = self.b1(out) out = self.b2(out) out = self.b3(out) out = self.b4(out) out = self.b5(out) out = self.b6(out) out = self.output(out) return out# 모델 생성 do_model = DropoutModel() # loss loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(do_model.parameters(), lr=lr)summary(do_model, (batch_size, 1, 28, 28))
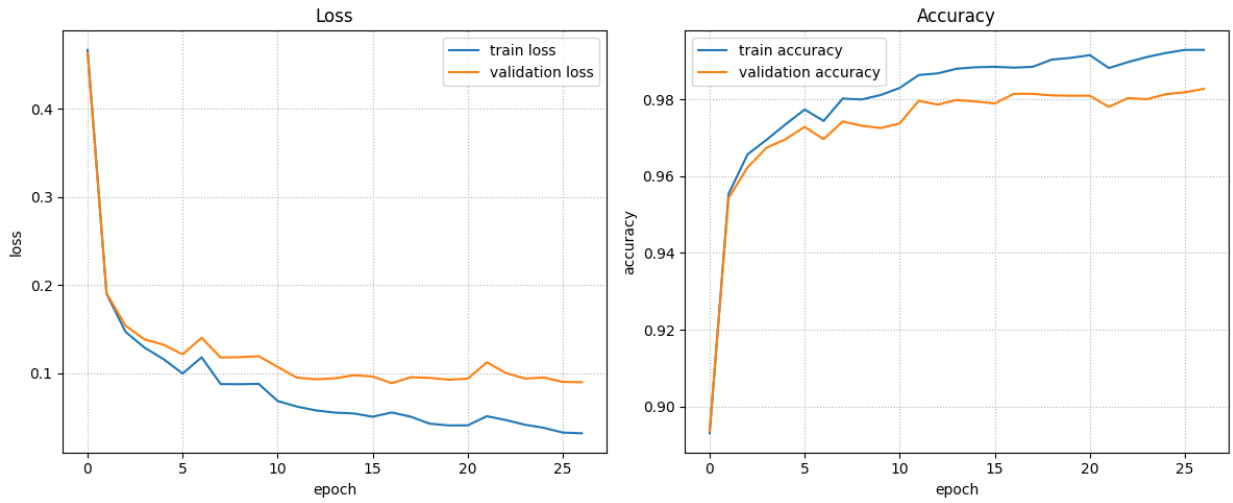
train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list = fit( train_loader, test_loader, do_model, loss_fn, optimizer, epochs, save_best_model=True, save_model_path='saved_models/do_model.pth', device=device, mode="multi" )Epoch[1/100] - Train loss: 0.46657 Train Accucracy: 0.89308 || Validation Loss: 0.46282 Validation Accuracy: 0.89380
<<<<<<<저장: 1 - 이전 : inf, 현재: 0.46282288432121277
Epoch[2/100] - Train loss: 0.18992 Train Accucracy: 0.95540 || Validation Loss: 0.19055 Validation Accuracy: 0.95430
<<<<<<<저장: 2 - 이전 : 0.46282288432121277, 현재: 0.19054761359002442
Epoch[3/100] - Train loss: 0.14683 Train Accucracy: 0.96567 || Validation Loss: 0.15387 Validation Accuracy: 0.96230
<<<<<<<저장: 3 - 이전 : 0.19054761359002442, 현재: 0.153874615393579
Epoch[4/100] - Train loss: 0.12892 Train Accucracy: 0.96947 || Validation Loss: 0.13829 Validation Accuracy: 0.96740
<<<<<<<저장: 4 - 이전 : 0.153874615393579, 현재: 0.13828999311081133
Epoch[5/100] - Train loss: 0.11586 Train Accucracy: 0.97348 || Validation Loss: 0.13228 Validation Accuracy: 0.96960
<<<<<<<저장: 5 - 이전 : 0.13828999311081133, 현재: 0.13227536028716713
Epoch[6/100] - Train loss: 0.09963 Train Accucracy: 0.97732 || Validation Loss: 0.12134 Validation Accuracy: 0.97280
<<<<<<<저장: 6 - 이전 : 0.13227536028716713, 현재: 0.12134245320921763
Epoch[7/100] - Train loss: 0.11799 Train Accucracy: 0.97435 || Validation Loss: 0.14014 Validation Accuracy: 0.96960
Epoch[8/100] - Train loss: 0.08767 Train Accucracy: 0.98017 || Validation Loss: 0.11776 Validation Accuracy: 0.97420
<<<<<<<저장: 8 - 이전 : 0.12134245320921763, 현재: 0.11776183005131316
Epoch[9/100] - Train loss: 0.08751 Train Accucracy: 0.97993 || Validation Loss: 0.11820 Validation Accuracy: 0.97310
...
Epoch[27/100] - Train loss: 0.03187 Train Accucracy: 0.99283 || Validation Loss: 0.08978 Validation Accuracy: 0.98270
<<<<<<Early stopping: Epoch - 26
1932.0103719234467 초plot_fit_result(train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list)
Batch Normalization
- Dense => BN => Activation => Dropout
class BatchNormModel(nn.Module): """ DropoutModel의 Layer들에 Batch Normalization Layer 추가. linear block: Linear -> BatchNorm -> ReLU -> Dropout BatchNorm Layer는 model.train() 때 계산된 평균, 표준편차를 이용해서 model.eval() 일때는 scaling을 한다. """def __init__(self, dropout_rate=0.5): super().__init__() # Linear -> ReLU 하나의 block 묶어서 정의. self.b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(784, 2048), nn.BatchNorm1d(2048), ## 입력 Feature 수(출력 features) nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b2 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(2048, 1024), nn.BatchNorm1d(1024), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b3 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(1024, 512), nn.BatchNorm1d(512), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b4 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(512, 256), nn.BatchNorm1d(256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b5 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(256, 128), nn.BatchNorm1d(128), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) self.b6 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(128, 64), nn.BatchNorm1d(64), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate)) # output layer # 마지막 Layer에는 BatchNorm을 정의할 필요 없다. (이 출력을 다음 입력으로 사용안하므로.) self.output = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(64, 10), nn.Dropout(p=dropout_rate))def forward(self, X): out = nn.Flatten()(X) out = self.b1(out) out = self.b2(out) out = self.b3(out) out = self.b4(out) out = self.b5(out) out = self.b6(out) out = self.output(out) return outbn_model = BatchNormModel() loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(bn_model.parameters(), lr=lr)summary(bn_model, (batch_size, 1, 28, 28))
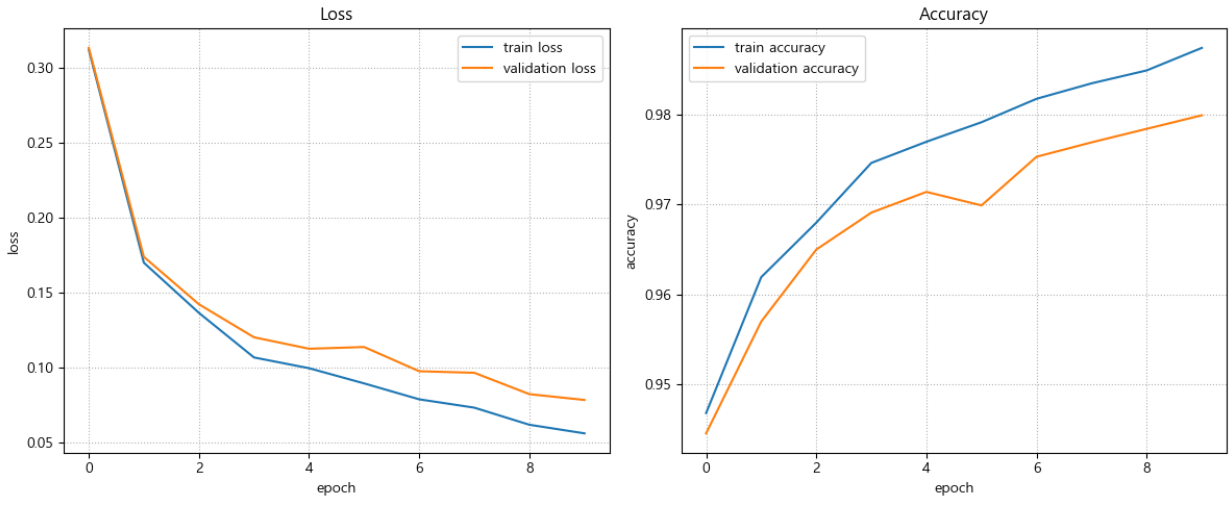
train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list = fit( train_loader, test_loader, bn_model, loss_fn, optimizer, 10, # epochs save_best_model=True, save_model_path='saved_models/bn_model.pth', device=device, mode="multi" )Epoch[1/10] - Train loss: 0.35100 Train Accucracy: 0.94113 || Validation Loss: 0.34233 Validation Accuracy: 0.94300
<<<<<<<저장: 1 - 이전 : inf, 현재: 0.3423349268734455
Epoch[2/10] - Train loss: 0.17738 Train Accucracy: 0.96037 || Validation Loss: 0.18025 Validation Accuracy: 0.96010
<<<<<<<저장: 2 - 이전 : 0.3423349268734455, 현재: 0.18024875978007912
Epoch[3/10] - Train loss: 0.14680 Train Accucracy: 0.96460 || Validation Loss: 0.15000 Validation Accuracy: 0.96320
<<<<<<<저장: 3 - 이전 : 0.18024875978007912, 현재: 0.15000107015948744
Epoch[4/10] - Train loss: 0.11840 Train Accucracy: 0.97177 || Validation Loss: 0.13113 Validation Accuracy: 0.96620
<<<<<<<저장: 4 - 이전 : 0.15000107015948744, 현재: 0.1311329869320616
Epoch[5/10] - Train loss: 0.10032 Train Accucracy: 0.97675 || Validation Loss: 0.11260 Validation Accuracy: 0.97300
<<<<<<<저장: 5 - 이전 : 0.1311329869320616, 현재: 0.1125988107174635
Epoch[6/10] - Train loss: 0.09455 Train Accucracy: 0.97868 || Validation Loss: 0.11072 Validation Accuracy: 0.97260
<<<<<<<저장: 6 - 이전 : 0.1125988107174635, 현재: 0.11072200031485409plot_fit_result(train_loss_list, train_acc_list, valid_loss_list, valid_acc_list)
Learning rate decay
Optimizer와 Learning rate scheduler의 속성, 메소드 확인
- 파이토치는
torch.optim모듈에서 다양한 Learning rate 알고리즘을 제공한다.
### optimizer 정의 optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(bn_model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # (파라미터, lr)####### LearningRate Scheduler에 의해 변화되는 learning rate의 흐름을 시각화. def plot_lr(title, lr_list): plt.figure(figsize=(15, 7)) plt.plot(range(len(lr_list)), lr_list) plt.title(title) xticks = [x for x in range(len(lr_list)) if x % 10 == 0] # 눈금 표시 -> 5 배수 자리에만 눈금. plt.xticks(xticks, rotation=45) plt.xlabel("Epochs or Steps") plt.ylabel("LR") plt.grid(True, linestyle=":") plt.show()StepLR
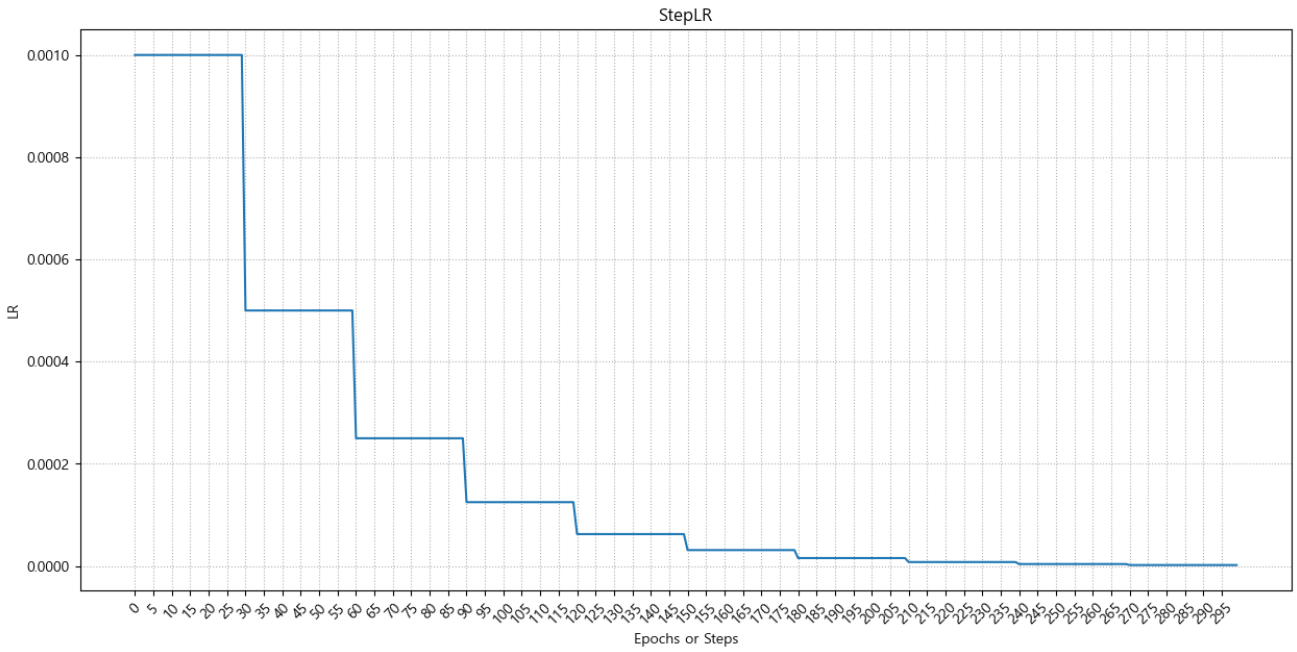
### StepLR - 계단 형태로 LR를 변화시킨다. 특정 epoch(step) 마다 특정 비율로 LR를 변경. # 모델, loss_fn, optimizer optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(bn_model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # LearningRate Scheduler를 생성. step_lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR( optimizer, # 스케줄링할 Learning Rate를 가지고 있는 Optimizer step_size=30, # 몇 step/epoch 마다 LR을 변경할 것인지 지정. (lr_scheduler.step() 한번 호출 -> 1step) gamma=0.5, # 변경 비율. new_lr = 현재_lr * gamma ) print("현재 Learning 확인:", optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'], step_lr_scheduler.get_last_lr())현재 Learning 확인: 0.001 [0.001]
epochs = 300 step_size = 10 # 1 에폭당 파라미터업데이트(step) 횟수 lr_list = [] # 에폭별 learning rate 들을 저장할 리스트. for epoch in range(epochs): # 1 epoch 학습 for _ in range(step_size): # for x, y in train_loader: 대체코드 # 1 step 학습: 모델 추론 -> loss 계산 -> gradient 계산. optimizer.step() # 1스텝: 파라미터 업데이트 optimizer.zero_grad() # step_lr_scheduler.step() # step_size(30) 단위: step lr_list.append(step_lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]) # 현재 epoch의 lr를 저장.==> 확인을 위한 코드. step_lr_scheduler.step() # step_size(30) 단위: epoch ==> 30 epoch당 한번씩 lr를 변경.for i, lr in enumerate(lr_list, start=1): print(i, lr, sep="-")1-0.001
2-0.001
3-0.001
4-0.001
5-0.001
6-0.001
7-0.001
8-0.001
9-0.001
10-0.001
11-0.001
12-0.001
13-0.001
14-0.001
15-0.001
16-0.001
17-0.001
18-0.001
19-0.001
20-0.001
21-0.001
22-0.001
23-0.001
24-0.001
25-0.001
...
297-1.953125e-06
298-1.953125e-06
299-1.953125e-06
300-1.953125e-06plot_lr("StepLR", lr_list)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(bn_model.parameters(), lr=0.001) ca_lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR( optimizer, T_max=10, # 주기 step수 를 지정. "최대_lr -> 최소_lr" 와 "최소_lr -> 최대_lr": 주기 step수(epoch, step) 지정.) eta_min = 0.00001 # 최소 lr, 최대 lr: 초기 lr값(0.001) 0.001 ~ 0.00001 )lr_list2 = [] for epoch in range(epoch): for _ in range(step_size): # .... 학습 optimizer.step() optimizer.zero_grad() lr_list2.append(ca_lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]) ### lr 업데이트 ca_lr_scheduler.step()lr_list2[0.001,
0.0009757729755661011,
0.000905463412215599,
0.0007959536998847742,
0.000657963412215599,
0.000505,
0.0003520365877844011,
0.00021404630011522585,
0.00010453658778440107,
3.4227024433899005e-05,
1e-05,
3.4227024433899005e-05,
0.00010453658778440146,
0.00021404630011522671,
0.00035203658778440265,
0.0005050000000000023,
0.000657963412215602,
0.0007959536998847778,
0.0009054634122156032,
0.0009757729755661056,
0.0010000000000000046,
0.0009757729755661055,
0.0009054634122156035,
0.0007959536998847779,
0.0006579634122156021,
...
0.0003520365877844316,
0.0005050000000000368,
0.0006579634122156489,
0.000795953699884836,
0.0009054634122156702]plot_lr("CosineAnnealingLR", lr_list2)
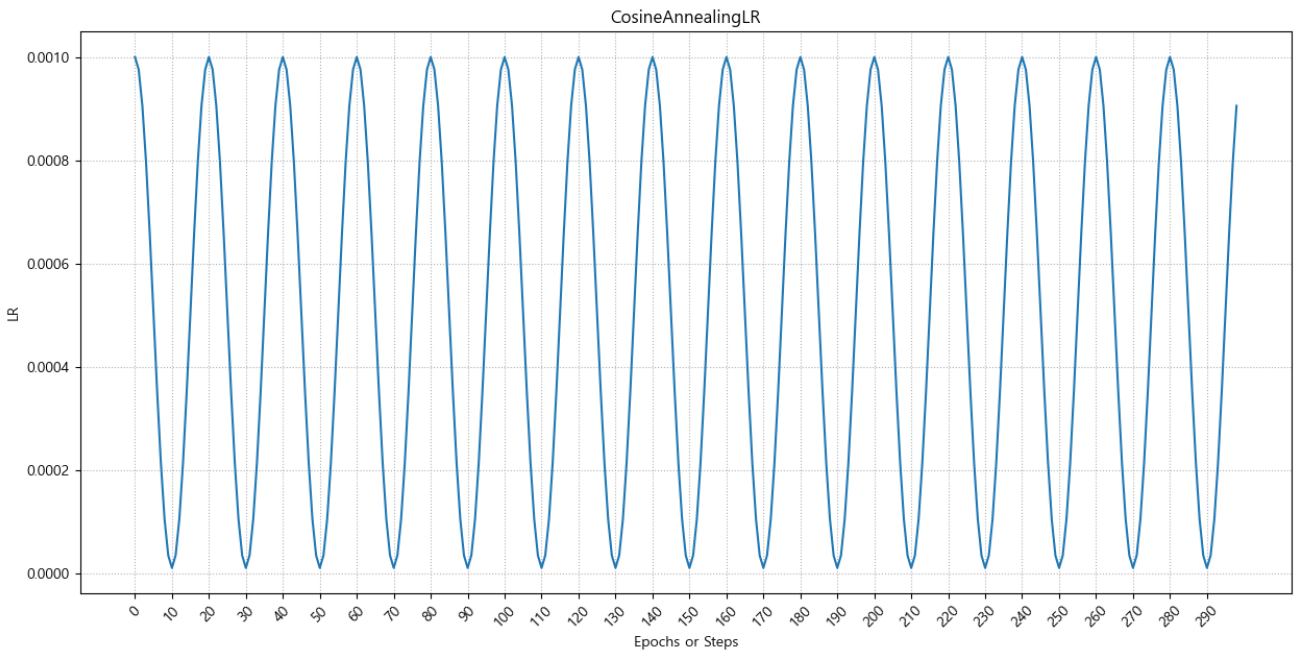
CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts
cosine annealing의 스케쥴링에 cosine 주기의 에폭을 점점 늘리거나 줄일 수 있다. (보통 늘린다.)
#### 변화 주기의 비율을 변경하는 것을 WarmStart optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(bn_model.parameters(), lr=0.001) caws_lr_scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingWarmRestarts( optimizer, T_0=10, # CosineAnnealingLR의 T_max값의 역할. -> 시작 주기. T_mult=2, # 주기를 어떤 비율로 변경할지. 새로운주기 = 현재_주기 * T_mult eta_min=1e-5 # 0.00001 # 최소 lr. 초기 LR <-> 최소 LR )lr_list3 = [] for epoch in range(epochs): for _ in range(step_size): # 학습 .... optimizer.step() optimizer.zero_grad() lr_list3.append(caws_lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]) caws_lr_scheduler.step()lr_list3[0.001,
0.0009757729755661011,
0.000905463412215599,
0.0007959536998847742,
0.000657963412215599,
0.000505,
0.0003520365877844011,
0.00021404630011522585,
0.00010453658778440107,
3.4227024433899005e-05,
0.001,
0.0009939057285945933,
0.0009757729755661011,
0.0009460482294732421,
0.000905463412215599,
0.000855017856687341,
0.0007959536998847742,
0.0007297252973710757,
0.000657963412215599,
0.0005824350601949143,
0.000505,
0.0004275649398050859,
0.0003520365877844011,
0.0002802747026289244,
0.00021404630011522585,
...
3.131453381255663e-05,
2.8584657955444653e-05,
2.6038449281671366e-05,
2.3676889403150105e-05,
2.150088874616817e-05]plot_lr("CosineAnnealingWarmStart", lr_list3)