forecast(시계열)
- 배경 및 설치
- 함수의 기초
- Prophet 기초
- 실습 pinkwink웹페이지 분석
0. 배경 및 설치
- Windows환경에서는 visualCode C++ BuildTool먼저 설치해주어야함.
- 그 다음 pandas_datareader 설치.
- 그 다음 fbprophet을 설치하려는데 python 3.11.* 이랑 버전 호환이 안된다고 오류가 계속 났음.
- 구글링 결과 Prophet으로 업데이트 되어 Prophet으로 설치해야함.
공식 깃헙 문서
0. 함수의 기초
set_matplotlib_hangul 모듈 생성
%%writefile ./set_matplotlib_hangul.py
import platform
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import rc
print('Hangul OK in windows!')
rc('font', family='Malgun Gothic')
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False결과 : Overwriting ./set_matplotlib_hangul.py
import set_matplotlib_hangul결과 : Hangul OK in windows!
- Sine wave 만들기 함수
공식
y = a sin(2 pi f t + t_0) + b
np.arange(start, stop, step) : start에서 stop까지 step개의 숫자 반환
def plotSineWave(amp, freq, endTime, sampleTime, startTime, bias):
'''
plot sine wave
y = a sin(2 pi f t + t_0) + b
'''
time = np.arange(startTime, endTime, sampleTime)
result = amp * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * time + startTime) + bias
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(time, result)
plt.grid(True)
plt.xlabel('time')
plt.ylabel('sin')
plt.title('한글테스트'+str(amp) + '*sin(2*pi' + str(freq) + '*t+' + str(startTime) + ')+' + str(bias))
plt.showplotSineWave(2, 1, 10, 0.01, 0.5, 0)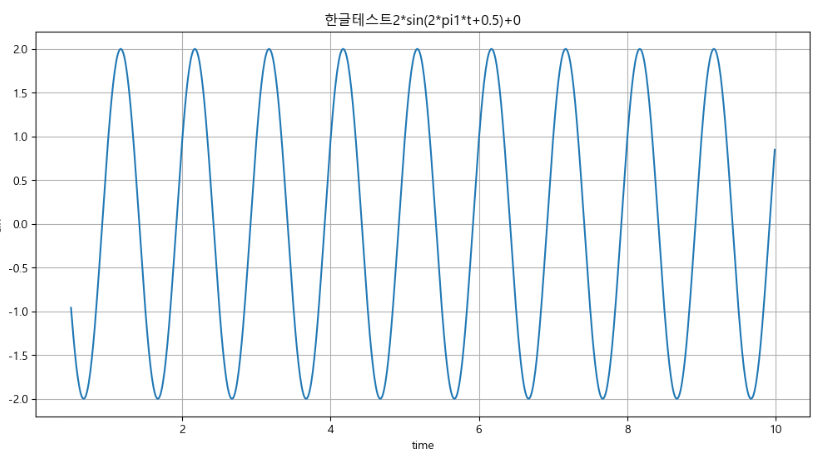
** kwargs : key word arguments의 약자. 글자는 상관없지만 ** 는 필수
''' : docstring 생성, 디폴트 값 넣어줄 수 있음
def plotSinWave(**kwargs):
'''
plot sine wave
y = a sin(2 pi f t + t_0) + b
'''
endTime=kwargs.get('endTime', 1)
sampleTime=kwargs.get('sampleTime', 0.01)
amp=kwargs.get('amp', 1)
freq=kwargs.get('freq', 1)
startTime=kwargs.get('startTime', 0)
bias=kwargs.get('bias', 1)
figsize = kwargs.get('figsize', (12, 6))
time = np.arange(startTime, endTime, sampleTime)
result = amp * np.sin(2 * np.pi * freq * time + startTime) + bias
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.plot(time, result)
plt.grid(True)
plt.xlabel('time')
plt.ylabel('sin')
plt.title(str(amp) + '*sin(2*pi' + str(freq) + '*t+' + str(startTime) + ')+' + str(bias))
plt.showendTime, startTime 등 인자 지정할 수 있음
plotSinWave()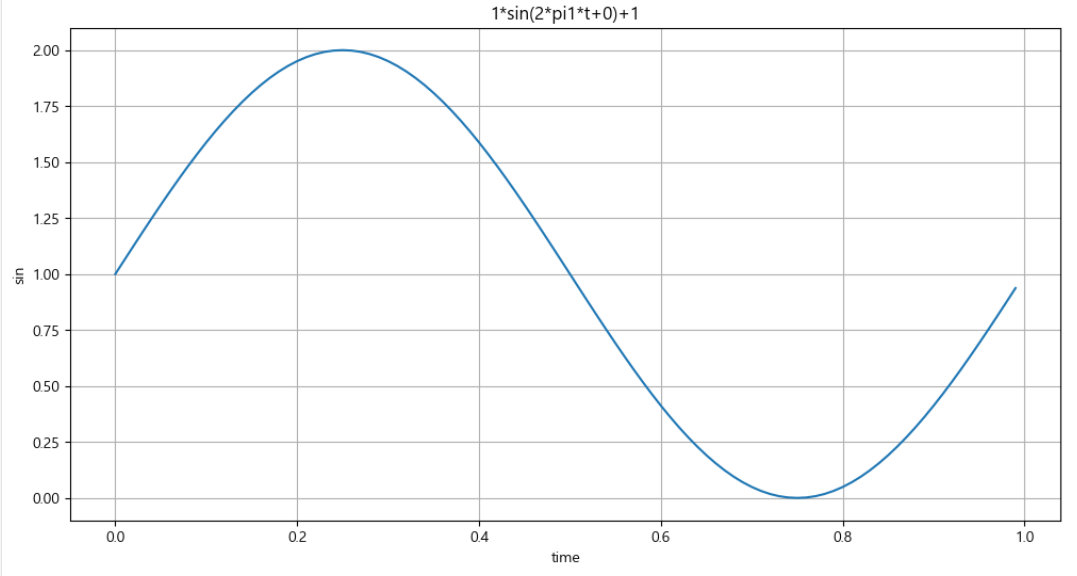
2. Fbprophet의 기초
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inlinetime = np.linspace(0, 1, 365*2)
result = np.sin(2*np.pi*12*time)
ds = pd.date_range('2018-01-01', periods=365*2, freq='D')
df = pd.DataFrame({'ds':ds, 'y':result})
df.head()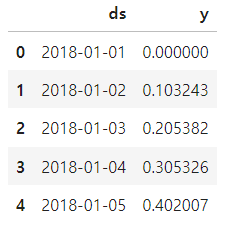
df['y'].plot(figsize=(10,6))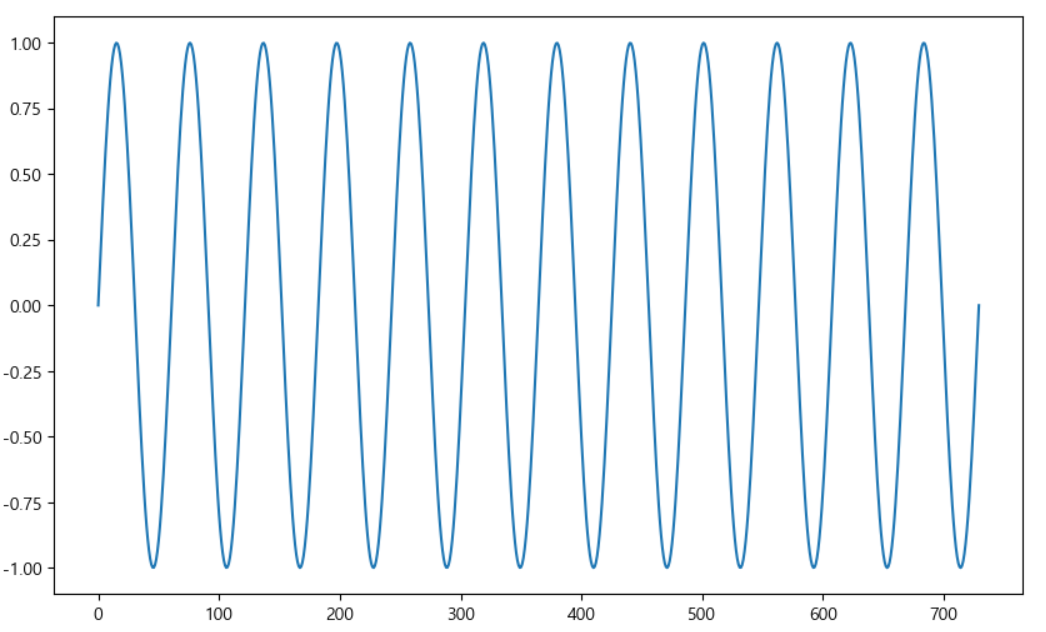
Prophet사용
학습시키기
from prophet import Prophet
m = Prophet(yearly_seasonality=True, daily_seasonality=True)
m.fit(df) # 학습시키기
예측값의 데이터 프레임 생성
future = m.make_future_dataframe(periods=30) #30일간의 데이터를 예측하라
forecast = m.predict(future) #예측하기예측하기
m.plot(forecast);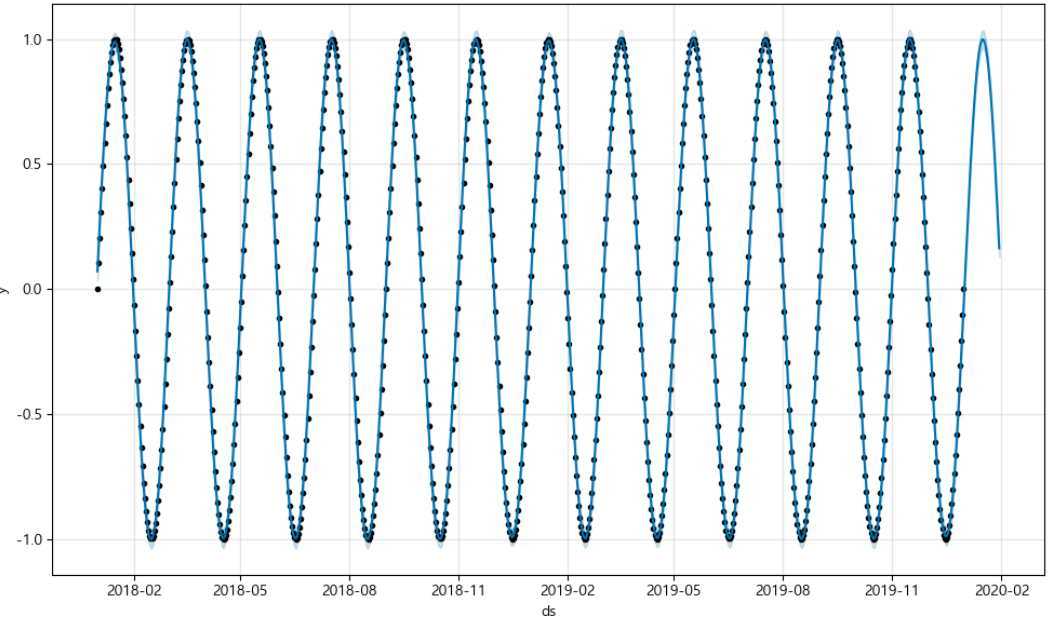
time bias 추가
time = np.linspace(0, 1, 365*2)
result = np.sin(2*np.pi*12*time) + time
ds = pd.date_range('2018-01-01', periods=365*2, freq='D')
df = pd.DataFrame({'ds':ds, 'y':result})
df['y'].plot(figsize=(10, 6))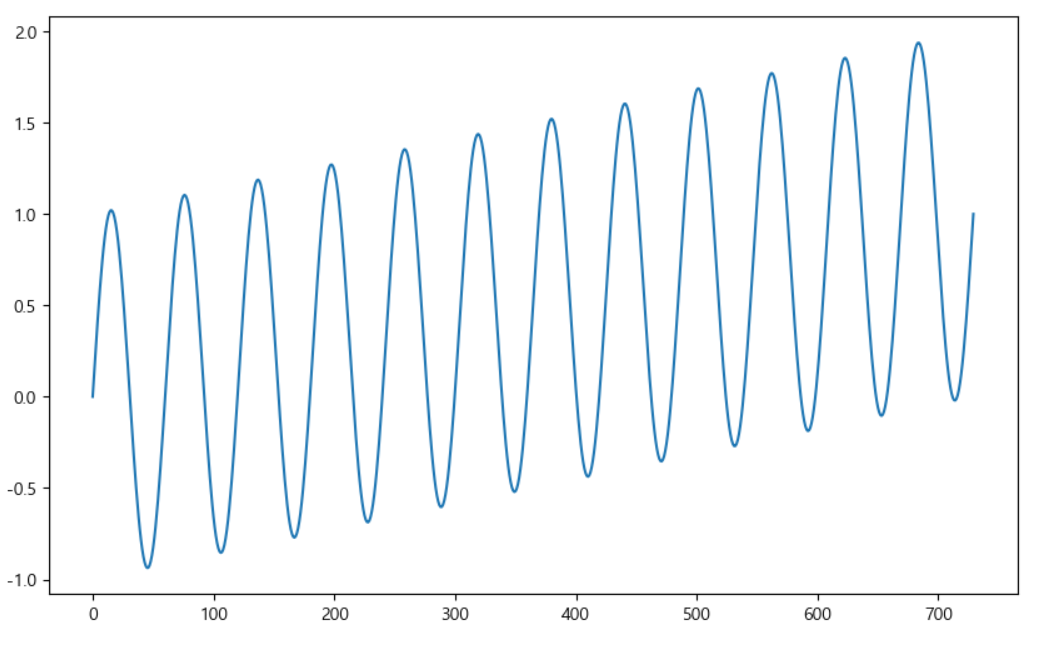
m = Prophet(yearly_seasonality=True, daily_seasonality=True)
m.fit(df) #학습
future = m.make_future_dataframe(periods=30)
forecast = m.predict(future) #예측
m.plot(forecast); #시각화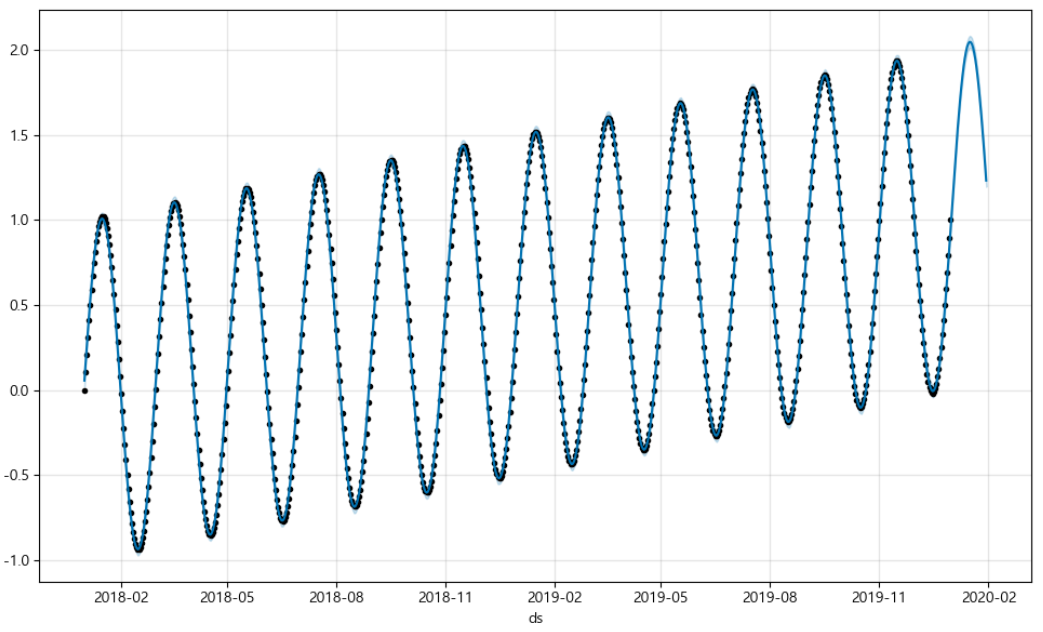
1. random.rand() : 0과 1 사이의 균일 분포를 따르는 난수를 생성한다. 인자로는 원하는 배열의 크기를 지정한다.\
eg.rand_num = np.random.rand(3, 3)\ # (개수, 열)
[[0.42656567, 0.707024 , 0.93653248],\
[0.1935818 , 0.56052649, 0.59793347],\
[0.83235891, 0.84720889, 0.17890702]]
2. random.randn() : 평균이 0이고 표준편차가 1인 정규 분포를 따르는 난수를 생성한다. 원하는 배열의 크기를 지정한다.
time bias, noise 추가
time = np.linspace(0, 1, 365*2)
result = np.sin(2*np.pi*12*time) + time + np.random.randn(365*2)/4 # time bias 추가, noise 추가
ds = pd.date_range('2018-01-01', periods=365*2, freq='D')
df = pd.DataFrame({'ds':ds, 'y':result})
df['y'].plot(figsize=(10, 6))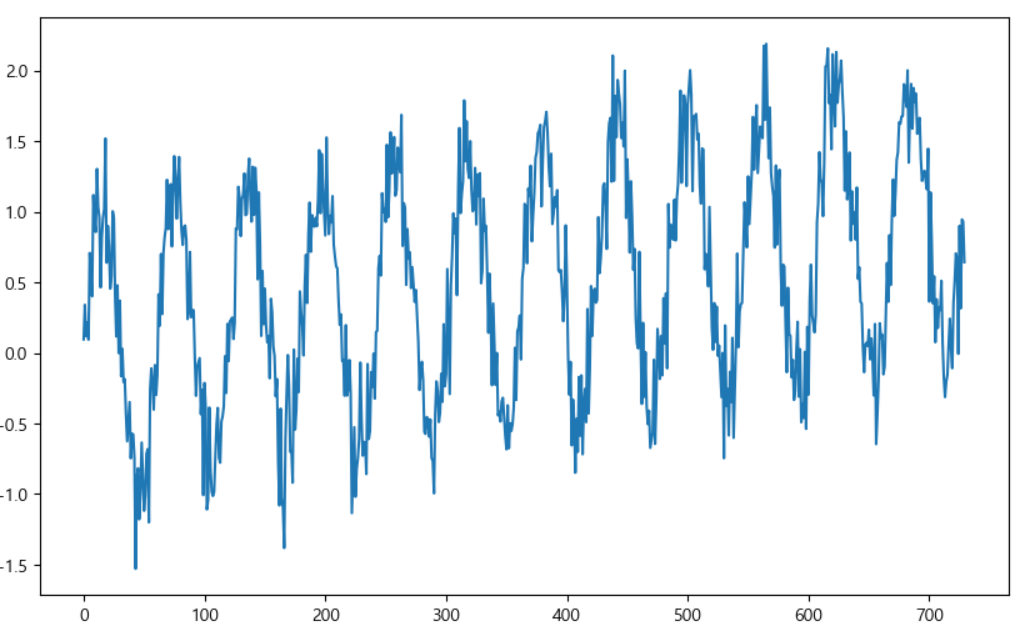
m = Prophet(yearly_seasonality=True, daily_seasonality=True)
m.fit(df) #학습
future = m.make_future_dataframe(periods=30)
forecast = m.predict(future) #예측
m.plot(forecast); #시각화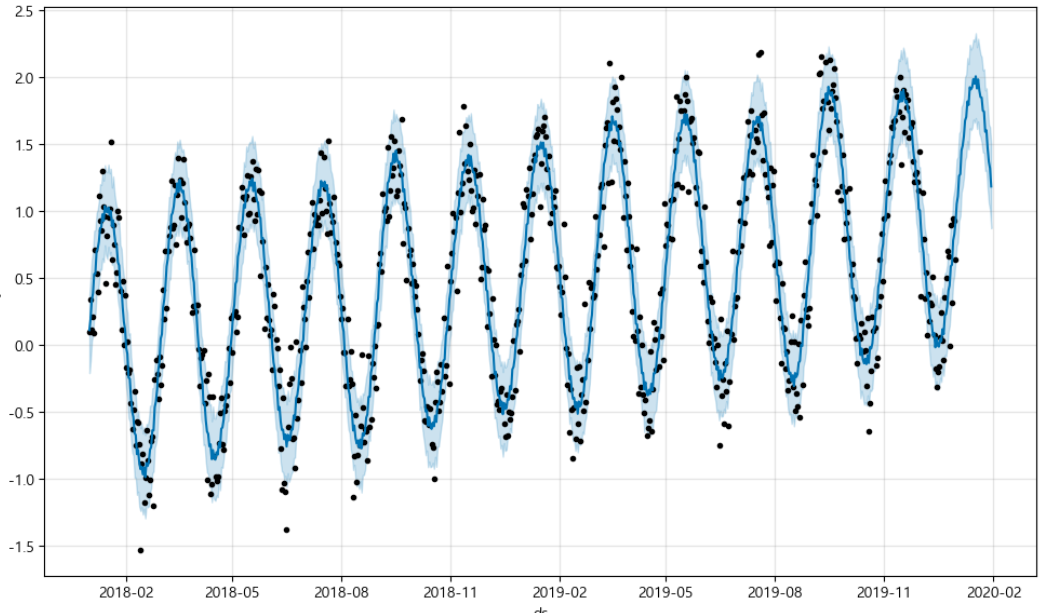
3.pinkwink hit 시계열 예측
import
import pandas as pd
import pandas_datareader as web
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from prophet import Prophet
from datetime import datetime
%matplotlib inlineencoding=
thousands=
names=(칼럼 이름을 지정한 이름으로 변경)
index_col=0
pinkwink_web = pd.read_csv(
'../data/05_PinkWink_Web_Traffic.csv',
encoding='utf-8',
thousands=',',
names=['date','hit'],
index_col=0)
pinkwink_web = pinkwink_web[pinkwink_web['hit'].notnull()]
pinkwink_web
pinkwink_web['hit'].plot(figsize=(12, 4), grid=True)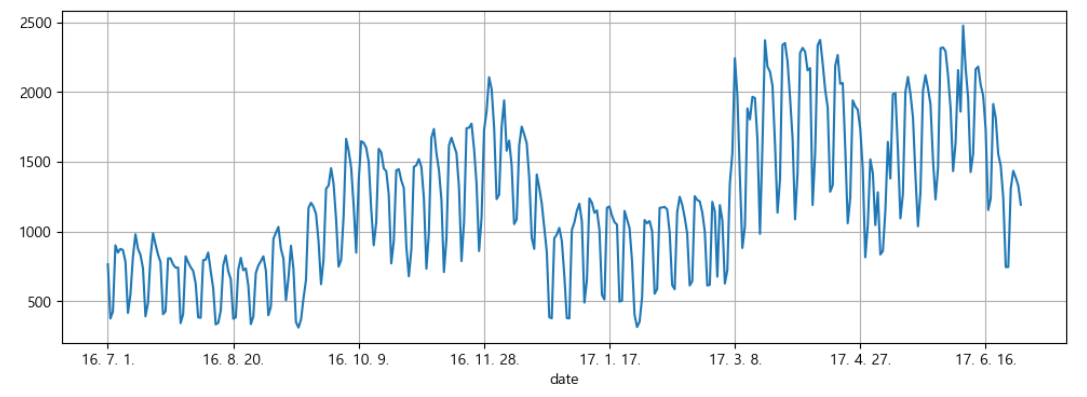
함수 요소 만들기
# trend 분석을 시각화하기 위한 x축 값 만들기
time = np.arange(0, len(pinkwink_web))
traffic = pinkwink_web['hit'].values
fx = np.linspace(0, time[-1], 1000)에러 계산할 함수(편차계산)
def error(f, x, y):
return np.sqrt(np.mean((f(x) - y)**2))x=time, y=traffic 함수 만들기
fp1 = np.polyfit(time, traffic, 1)
f1 = np.poly1d(fp1)
f2p = np.polyfit(time, traffic, 2)
f2 = np.poly1d(f2p)
f3p = np.polyfit(time, traffic, 3)
f3 = np.poly1d(f3p)
f15p = np.polyfit(time, traffic, 15)
f15 = np.poly1d(f15p)에러 계산하기
print(error(f1, time, traffic))
print(error(f2, time, traffic))
print(error(f3, time, traffic))
print(error(f15, time, traffic))430.85973081109626
430.6284101894695
429.53280466762925
330.47773079342267
그래프 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.scatter(time, traffic, s=10)
plt.plot(fx, f1(fx), lw=4, label='f1')
plt.plot(fx, f2(fx), lw=4, label='f2')
plt.plot(fx, f3(fx), lw=4, label='f3')
plt.plot(fx, f15(fx), lw=4, label='f15')
plt.grid(True, linestyle='-', color='0.75')
plt.legend(loc=2)
plt.show()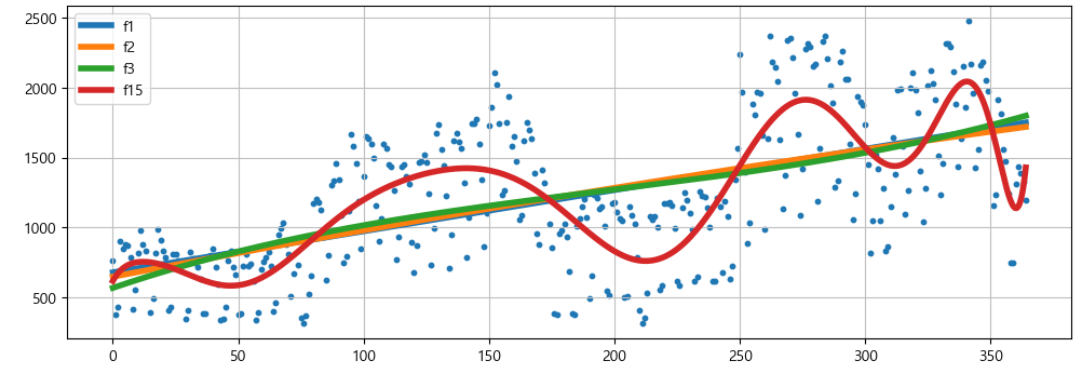
데이터프레임 만들기
df = pd.DataFrame({'ds':pinkwink_web.index, 'y':pinkwink_web['hit']})
df.reset_index(inplace=True)
df['ds'] = pd.to_datetime(df['ds'], format='%y. %m. %d.')
del df['date']
df.head()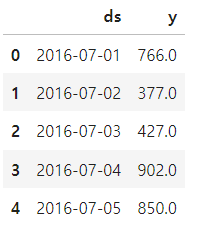
학습시키기
m = Prophet(yearly_seasonality=True, daily_seasonality=True)
m.fit(df);60일에 해당하는 데이터 프레임 생성
future = m.make_future_dataframe(periods=60)
future.tail()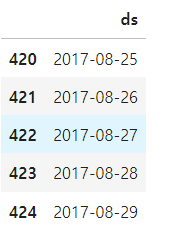
예측 결과는 상한/하한의 범위를 포함해서 얻어진다.
forecast = m.predict(future)
forecast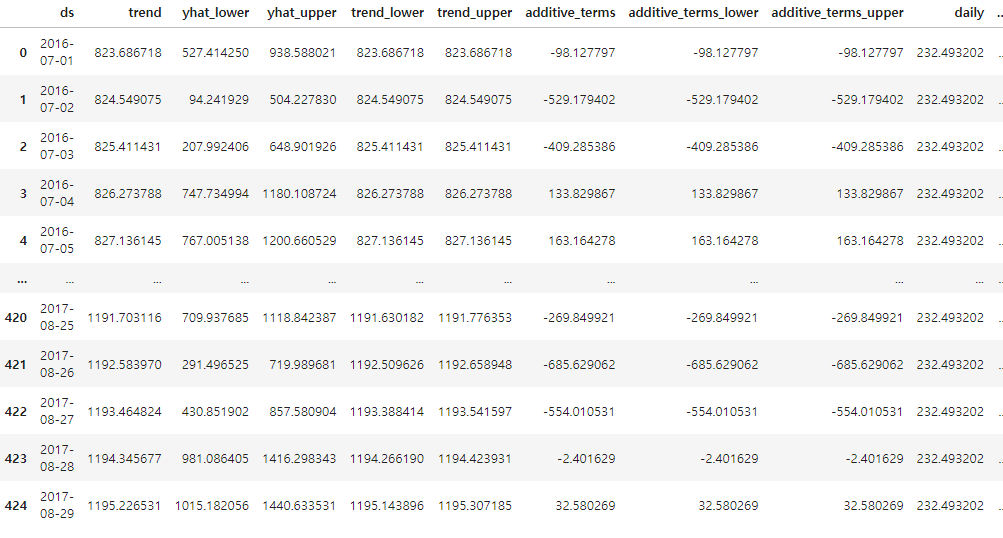
그래프 시각화
m.plot(forecast);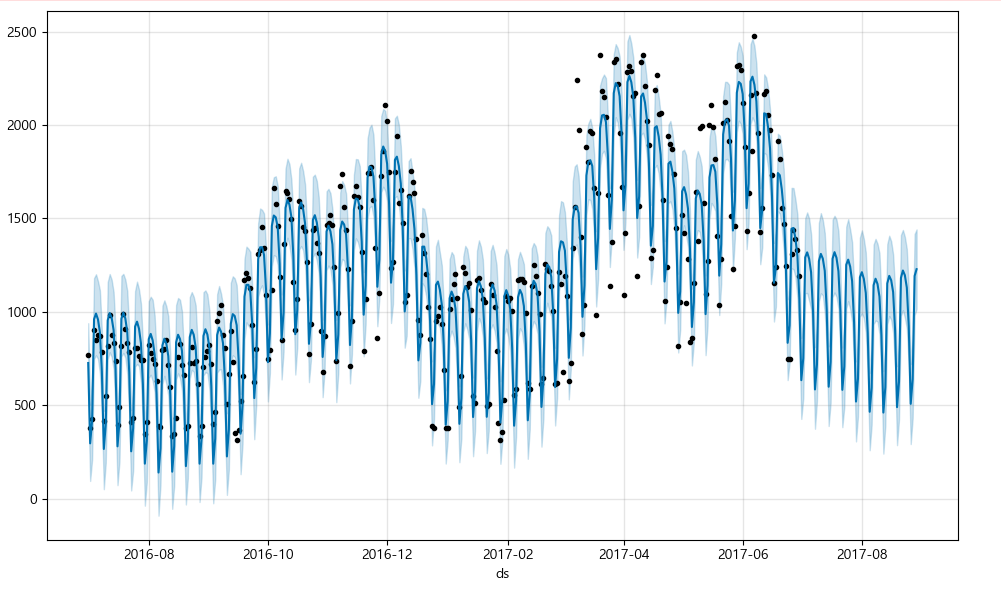
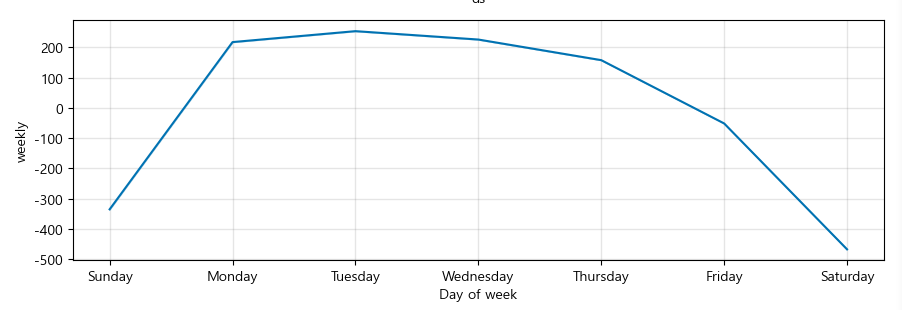
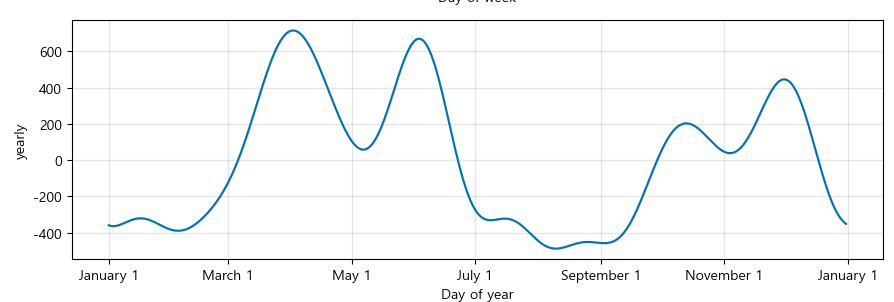
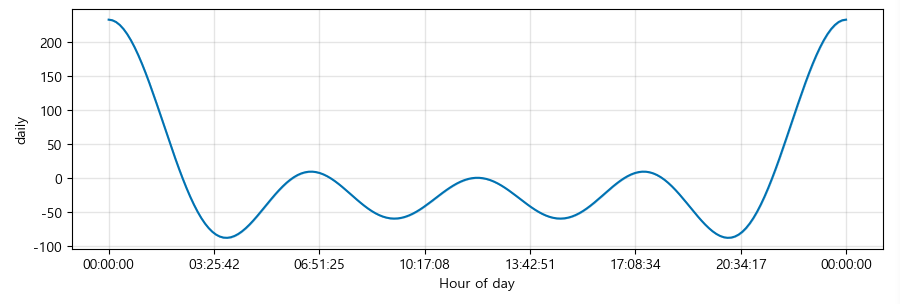
trend, weekly, yearly seasonality 확인 가능
m.plot_components(forecast);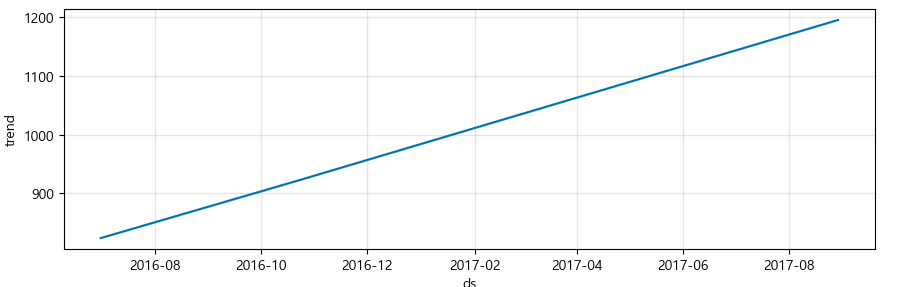
자료 출처 : 제로베이스 데이터 취업 스쿨