
프로그래머스 155651번
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/155651
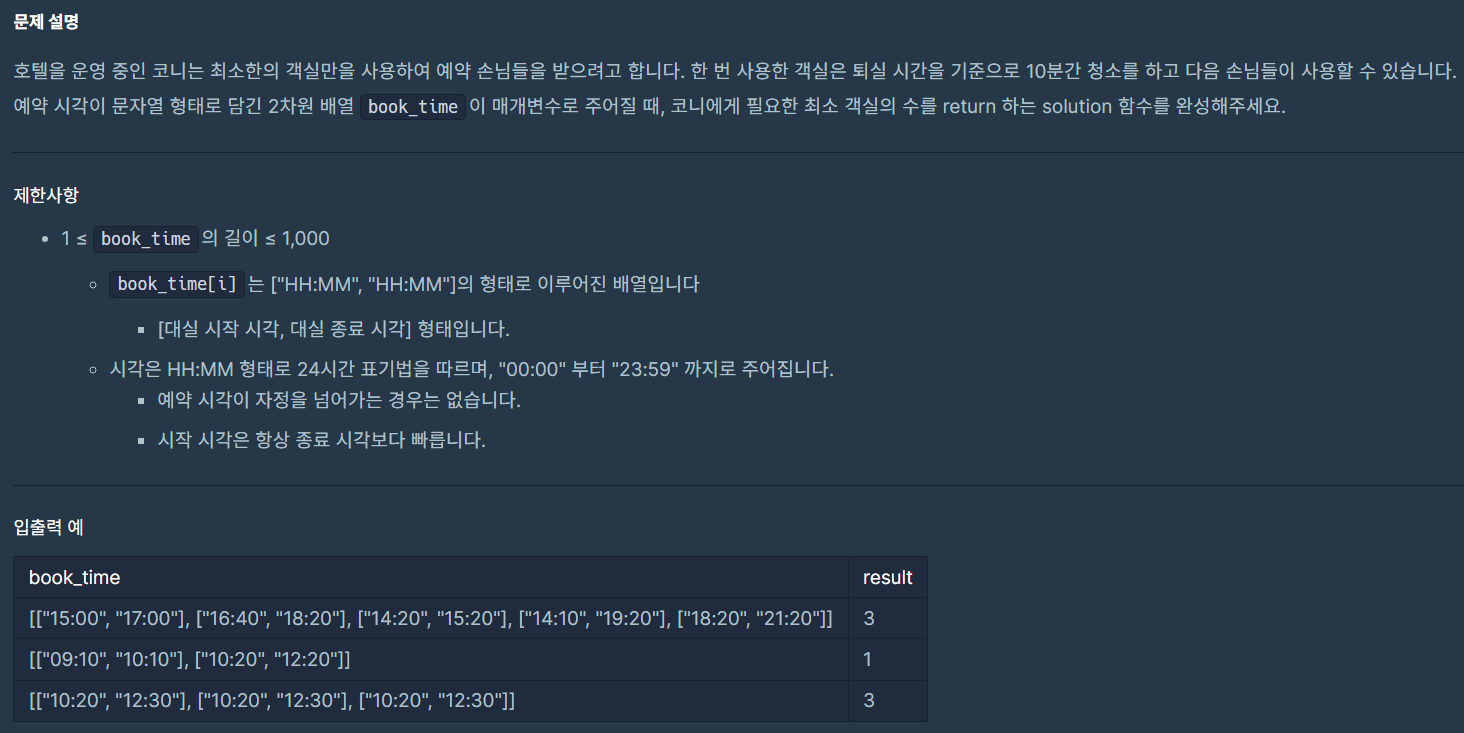
문제
생각하기
- 정렬을 핵심으로 두고 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
동작
결과
코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public static Time[] times;
public static class Time implements Comparable<Time> {
int start;
int end;
public Time(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Time o) {
return end - o.end;
}
} // End of Time class
public int solution(String[][] book_time) {
int n = book_time.length;
times = new Time[n];
// PriorityQueue의 특성을 잘 활용하자.
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
String start = book_time[i][0];
String end = book_time[i][1];
times[i] = new Time(calcTime(start, 0), calcTime(end, 1));
}
// 시작시간 순으로 정렬
Arrays.sort(times, new Comparator<Time>() {
@Override
public int compare(Time o1, Time o2) {
if(o1.start == o2.start) {
return o1.end - o2.end;
}
return o1.start - o2.start;
}
});
PriorityQueue<Integer> pque = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 방이 최소 몇개가 필요한지 계산하기
int ans = 0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
Time current = times[i];
while(!pque.isEmpty() && pque.peek() <= current.start) {
pque.poll();
}
pque.offer(current.end);
ans = Math.max(ans, pque.size());
}
return ans;
} // End of solution()
public int calcTime(String time, int option) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(time, ":");
int total = 0;
// 모든 시간을 분단위로 전환
total += Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) * 60;
total += Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(option == 1) {
total += 10;
}
return total;
} // End of calcTime()
} // End of Solution class
