
📄 Description
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [, , ] indicates that there is a flight from city to city with cost .
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:
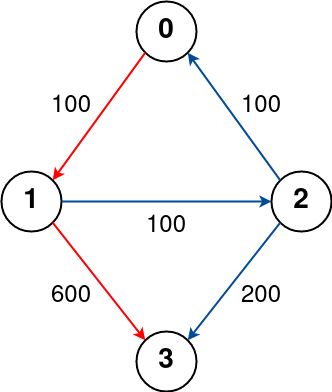
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700.
Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.Example 2:
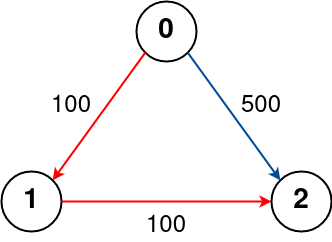
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.Example 3:
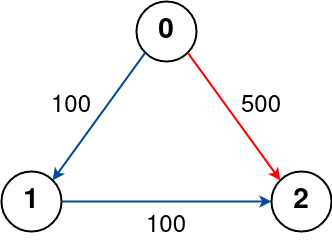
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 3- 0 <= , < n
- !=
- 1 <= <=
- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
- 0 <= src, dst, k < n
- src != dst
💡 How to solve this problem?
다익스트라 알고리즘의 응용 문제다.
엄밀히 말하면, 이 문제는 다익스트라 문제라고는 할 수 없다.
(처음 시도로는 Time Limit Exceeded였다...)
Main idea of Dijkstra's is to check single vertex and never return to it again
- 다익스트라: 항상 노드 주변의 최단 경로만을 택하는 대표적인 Greedy 알고리즘 중 하나.
하지만 이 문제에서는 최단 경로 에 더불어 K 경유지 이내 라는 조건이 있다.
다익스트라에서는 노드 주변의 ❗최단 경로❗ 만을 택하지만, 이 문제에서는 노드 주변의 경유지의 개수 또한 고려해야한다.
즉, 이전에 방문한 노드더라도, 현재 노드에 도달하기까지 거친 경유지의 개수가 더 적다면, 그 노드를 다시 방문해야 한다.
- We should avoid some cases: The current visit for the node has fewer available stops than the previous visit (totalCost < current visit and avaibleStops > current visit).
- i used a dictionary to track the number of movies it took to reach a node, and then i only visit the node again if the current path took fewer moves to reach the node than any previous path.
💻 My Solution
class Solution:
def findCheapestPrice(self, n: int, flights: List[List[int]], src: int, dst: int, k: int) -> int:
# graph for flights
graph=defaultdict(list)
for s,d,p in flights:
graph[s].append((p,d))
# (price, node, stop)
Q=[(0,src,k+1)]
seen=dict()
while Q:
price,node,stop=heapq.heappop(Q)
if node==dst and stop>=0:
return price
if node not in seen or stop>=seen[node]:
seen[node]=stop
for p, n in graph[node]:
heapq.heappush(Q,(price+p,n,stop-1))
return -1References
- https://leetcode.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/submissions/
- https://leetcode.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/discuss/115541/JavaC%2B%2BPython-Priority-Queue-Solution-(TLE-now)
- 파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰(95가지 알고리즘 문제 풀이로 완성하는 코딩 테스트), 박상길 지음
