.png)
🌼 Type Inference(타입 추론)
TypeScript에서는 타입 표기가 없는 경우, 작성된 코드를 읽고 분석하여 타입을 유추하여 지정할 수 있는데 이것을 타입 추론이라고 말한다.
let a = 10;
a = "apple"; // Type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'.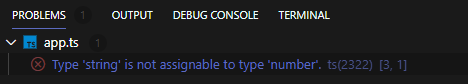
- a의 type을 명시하지 않았지만 ts는 타입 추론을 통해 변수 a의 type을 number로 하였기 때문에 string 값을 재할당하려고 할 때 error가 발생한다.
🌼 Type Declaration (타입 명시)
변수를 선언할 때, 변수 값의 type을 명시함으로써 변수 값의 데이터 type을 지정하는 것을 말한다.
// ts 타입 명시 syntax → 변수선언 변수명: 변수타입 = 변수값;
let x: string = "나는 영원한 문자열";
// 함수의 argument, return 값에도 타입을 명시할 수 있다.
// object로 간단하게 명시할 수도 있지만 내부 key의 type까지도 상세히 명시할 수 있다.
let studentID: number = 123;
let studentName: string = "Jack";
function getStudentDetails(studentID: number): {
studentID: number;
studentName: string;
} {
return null; // object 대신 null 값으로 임의 지정
}
// 함수의 return 값이 없을 경우에는 :void를 명시한다.
//(함수의 return 값을 명시할 때만 사용 가능)
function getStudentDetails(studentID: number):void {
return null;
}🌼 Interface
함수의 return 값으로 자료형 데이터를 사용해야 할 경우, 보다 깔끔하게 type을 명시하기 위해서 사용한다.
- interface로 선언된 type은 ts의 type으로 대신 사용할 수 있다.
- interface를 type으로 가지는 값은 interface의 구조를 그 값으로 가지도록 강제된다.
- interface의 이름은 대문자로 시작해야 한다.
🌻 Optional Property?
interface의 구조 중 필수로 가져야하는 항목이 아닐 경우, ?를 사용하여 선택적 프로퍼티로 정의할 수 있다.
- interface의 경우 js로 compile시, 해당 내용은 제외하고 compile된다.
- 선택적 프로퍼티 항목이 있을 경우, 제일 뒤쪽에 명시해준다.
interface Student {
studentID: number,
studentName: string,
age?: number
};
function getStudentDetails(studentID: number): Student {
return {
studentID: 123,
studentName: "Jack"
}
};- method도 interface 내부에 정의할 수 있다.
interface Method {
//addComment(comment: string): string;
//표현 방식의 차이만 있을 뿐 아래와 동일하다.
addComment?: (comment: string) => string;
}🌻 Read Only 속성?
Read Only 프로퍼티는 읽기 전용 프로퍼티로 객체 생성시 할당된 프로퍼티의 값을 바꿀 수 없다.
interface Student {
readonly studentID: number,
studentName: string,
age?: number
};
function saveStudentsDetails(student: Student): void {
student.studentID = 12222;
// Cannot assing to 'studentID' because it is a read-only property.
}출처: YOUTUBE-땅콩코딩
