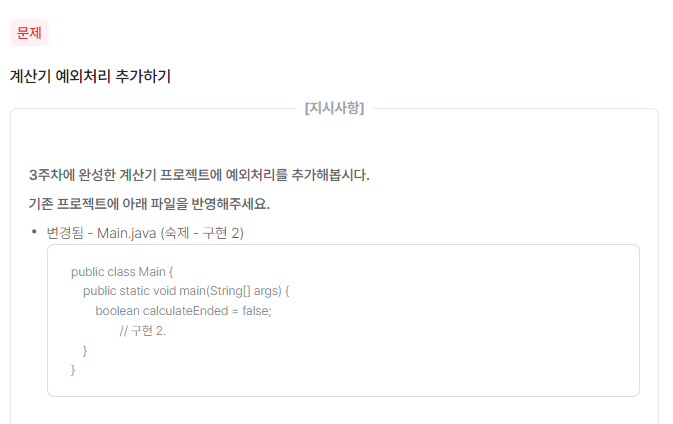
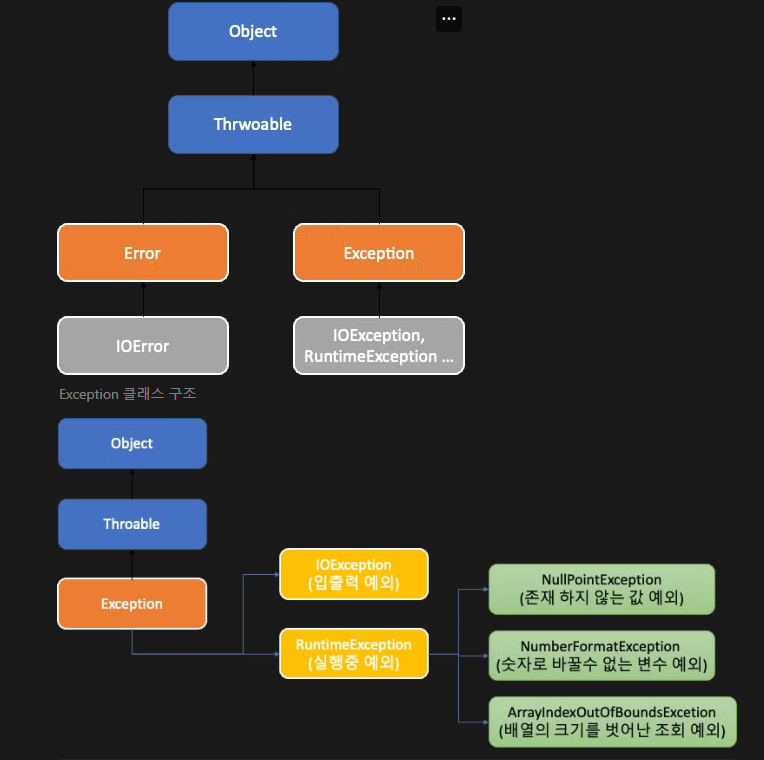
오류 및 예외
- 프로그램을 개발하는 개발자가 개발자의 의도 외에 행동을 하려고 할때 행동의 방향성을 유도할수 있음.
(예외 및 오류에대한 규정 및 정의)
오류
- 일반적으로는 회복이 불가능.
- 시스템레벨에서 발생하며 프로그램 종료의 단계까지 도달.
- 개발자가 대응이 힘듬.
예외
- 일반적으로 회복이 가능 (핸들링이 가능)
- 사전에 발생할거아
정의하고처리할 수 있기때문에 대응이 가능하다. - 개발자가 대응 및 예방이 가능.
컴파일 예외
- .java -> .class 로 컴파일할 때 발생하는 예외
- 대부분은 문법에대한 언어의 규칙을 지키지않았을때 발생.
런타임 예외
- 컴파일은 되었지만 프로그램이 수행중 발생하는 예외.
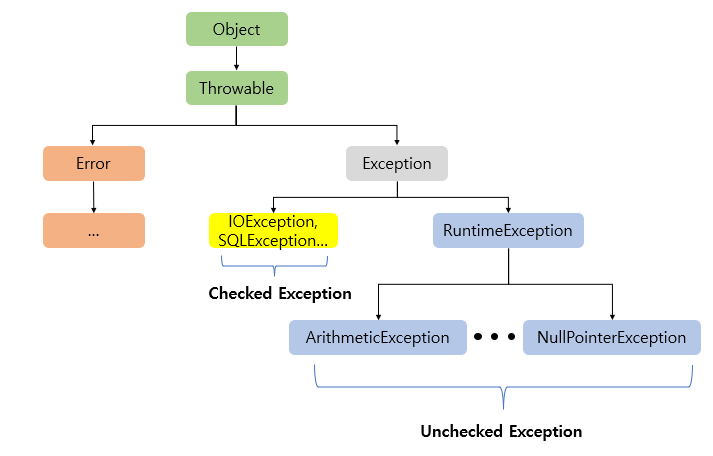
Checked Exception
- RuntimeException을 상속하지 않는 예외
- 컴파일 시점에 확인되는 예외.
- 사전에 예외가 발생할것이라 알고 처리 해줘야하는 예외
- 반드시 예외처리를 해줘야하고 컴파일러가 동작하며 예외처리를 확인하며 발생하기에 확인된 예외라 부름
- 예외처리방식에서 하위에서 올라온 예외를 상위 클래스들이 모두 알고있어야하는
의존관계발생
Unchecked Exception
- RuntimeException을 상속한 예외
- 컴파일러가 예외를 확인하지 않는다.
- 개발자가 필요하다면 생략이 가능하며 누락될 가능성이 존재.
- 예측할수 없는 예외
try-catch-finally 문
class OurBadException extends Exception {
public OurBadException() {
super("위험한 행동을 하면 예외처리를 꼭 해야합니다!");
}
}- Exception Class 를 상속받아 예외 클래스를 작성할 수 있다.
- Exception Class 를 상속받기 때문에 체크예외로 구성.
class OurClass {
private final Boolean just = true;
// 신규 문법 throws!
public void thisMethodIsDangerous() throws OurBadException {
if (just) {
// 신규 문법 throw!
throw new OurBadException();
}
}
}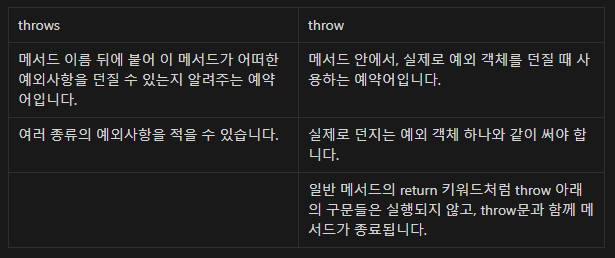
throws키워드를 통해 해당 예외가 발생할수 있다 명시.throw키워드를 통해 예외객체를 생성시켜 예외발생.- 예외를 직접 처리하지 않고 던지기 때문에 호출한 곳에서 처리를 해줘야함.
public class StudyException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OurClass ourClass = new OurClass();
try {
// 1. 위험한 메소드의 실행을 "시도" 해 봅니다.
// "시도" 해보는 코드가 들어가는 블럭입니다.
ourClass.thisMethodIsDangerous();
} catch (OurBadException e) {
// 2. 예외가 발생하면, "잡아서" handling 합니다.
// 예외가 발생하는경우 "handling" 하는 코드가 들어가는 블럭입니다.
// 즉 try 블럭 내의 구문을 실행하다가 예외가 발생하면
// 예외가 발생한 줄에서 바로 코드 실행을 멈추고
// 여기 있는 catch 블럭 내의 코드가 실행됩니다.
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
// 3. 예외의 발생 여부와 상관없이, 실행시켜야 하는 코드가 들어갑니다.
// 무조건 실행되는 코드가 들어가는 블럭입니다.
System.out.println("우리는 방금 예외를 handling 했습니다!");
}
}
}try - catch - finally구문을 통해 예외를 핸들링 가능하다.- try : 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 실행구문 블록.
- catch : 예외가 발생했을때 어덯게 핸들링 할건지 에 대한 블록.
- 하나의 try에 다중 catch가 가능하다.
- finally : 예외의 발생 유무와 관계없이 실행되는 구문 생략이 가능하다. / 보통 파일이나 메모리를 닫아야할때.
예외 Class 구조
Chained Exception
- 예외가 다른 예외를 유발한 경우.
- N개 이상의 예외를 1개의 분류로써 지정해 한번에 다루기위해.
- A->B 일때 A는 B의 원인임. 원인을 찾기가 편하다.
- checked exception을 unchecked exception으로 포장하여 사용.
// 연결된 예외
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 예외 생성
NumberFormatException ex = new NumberFormatException("가짜 예외이유");
// 원인 예외 설정(지정한 예외를 원인 예외로 등록)
ex.initCause(new NullPointerException("진짜 예외이유"));
// 예외를 직접 던집니다.
throw ex;
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
// 예외 로그 출력
ex.printStackTrace();
// 예외 원인 조회 후 출력
ex.getCause().printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 출력
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException: 진짜 예외이유initCause(): 지정예외를 원인예외로 등록하는 메소드.getCause(): 원인예외를 반환하는 메소드.
// checked exception 을 감싸서 unchecked exception 안에 넣습니다.
throw new RuntimeException(new Exception("이것이 진짜 예외 이유 입니다."));- 체크예외를 언체크예외로 포장함으로써 try-catch 생략이 가능.
예외처리기법
1. 예외 복구
public String getDataFromAnotherServer(String dataPath) {
try {
return anotherServerClient.getData(dataPath).toString();
} catch (GetDataException e) {
return defaultData;
}
}- 가장 기본적인 방식의 예외처리 방법.
- 최소한의 대응(프로그램이 종료되지않는정도) 만 가능하기에 자주 사용되지않음.
2. 예외 회피

public void someMethod() throws Exception { ... }
public void someIrresponsibleMethod() throws Exception {
this.someMethod();
}- 호출된곳에서 예외를 처리하는것이 아닌 예외발생시 호출한곳에서 예외를 처리하도록 지정.
3. 예외 전환
public void someMethod() throws IOException { ... }
public void someResponsibleMethod() throws MoreSpecificException {
try {
this.someMethod();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new MoreSpecificException(e.getMessage());
}
}- 회피와 방법은 비슷하지만, 조금 더 상세하게 예외를 구체적인 예외로 포장.
- 예외처리에 신경을 쓰거나, RuntimeException처럼 일괄적으로 처리하기 편한 예외로 바꿔서 던지고 싶은 경우 사용
- 일반적인 예외처리 기법.
추가사항
- catch에는 로깅,복구등의 로직 추가하기.
- 예외 stack을 남겨 추적, 유지보수성 높이기
- Logging Framework 사용하기.
참조 :
https://devlog-wjdrbs96.tistory.com/351
https://inpa.tistory.com/entry/JAVA-%E2%98%95-Exception-Handling-%EC%98%88%EC%99%B8%EB%A5%BC-%EC%B2%98%EB%A6%AC%ED%95%98%EB%8A%94-3%EA%B0%80%EC%A7%80-%EA%B8%B0%EB%B2%95
제네릭
제네릭 알아보기
- 타입언어에서 중복되거나 필요 없는 코드를 줄여주는것.
- 타입 안정성을 해치지 않는 것.
public class Generic {
public Object plusReturnFunction(Object a,Object b) { ... }
}- 가능은 하나 결국 해당변수를 피연산자로 사용하기위핸 타입을 캐스팅해줘야함. (필요한 부수적인 코드발생)
// 1.
public class Generic<T> {
// 2.
private T t;
// 3.
public T get() {
return this.t;
}
public void set(T t) {
this.t = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 4.
Generic<String> stringGeneric = new Generic<>();
// 5.
stringGeneric.set("Hello World");
String tValueTurnOutWithString = stringGeneric.get();
System.out.println(tValueTurnOutWithString);
}
}제네릭의 제한
- static 멤버로 사용할수 없다.
static T get() { ... } // 에러
static void set(T t) { ... } // 에러- 타입변수는 기본적으로 인스턴스 변수로 보기때문에 static사용불가.
- 제네릭 배열 사용 불가.
제네릭 문법
- 다수의 타입변수를 사용가능.
- 다형성관계가 유지 및 적용된다.
- 와일드카드 구문을 통해 제네릭의 제한을
구체적으로 적용가능.
public class ParkingLot<T extends Car> { ... }
ParkingLot<BMW> bmwParkingLot = new ParkingLot();
ParkingLot<Iphone> iphoneParkingLot = new ParkingLog(); // error!
- 제네릭클래스가 아니더라도 메소드로 사용할수있다.
// 또는 ..
static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) { ... }- 제네릭메소드의 제네릭 타입변수는 해당 선언 메소드에만 적용되기에 메소드 단위의 인스턴스 메서드는 static을 사용할 수 있다.
- 같은 타입변수
<T>로 클래스와 메소드를 동일하게 적용했다 하더라도 별개의 타입변수로 취급한다.
Wrapper 객체
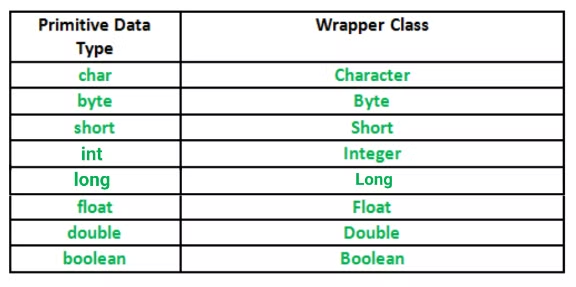
- 원시타입의 자료를 추상화하기위해 사용
- 원시타입 자료를 객체로써 사용하거나, 객체로써의 기능을 필요할때 사용
- 기본값을 객체화하는 것을 박싱, 객체를 다시 기본값으로 만드는 것을 언박싱.
Integer num = new Integer(17); // Boxing
int n = num.intValue(); // UnBoxing
Character ch = 'X'; // AutoBoxing
char c = ch; // AutoUnBoxing숙제
답안 :
package week04;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Parser {
private static final String OPERATION_REG = "[+\\-*/]";
private static final String NUMBER_REG = "^[0-9]*$";
private final Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
public Parser parseFirstNum(String firstInput) throws BadInputException {
if (firstInput.matches(NUMBER_REG)) {
this.calculator.setFirstNumber(Integer.parseInt(firstInput));
} else {
throw new BadInputException("정수값");
}
return this;
}
public Parser parseSecondNum(String secondInput) throws BadInputException {
if (secondInput.matches(NUMBER_REG)) {
this.calculator.setSecondNumber(Integer.parseInt(secondInput));
} else {
throw new BadInputException("정수값");
}
return this;
}
public Parser parseOperator(String operationInput) throws BadInputException {
if (operationInput.matches(OPERATION_REG)) {
switch (operationInput) {
case "+" -> this.calculator.setOperation(new AddOperation());
case "-" -> this.calculator.setOperation(new SubstractOperation());
case "*" -> this.calculator.setOperation(new MultiplyOperation());
case "/" -> this.calculator.setOperation(new DivideOperation());
}
} else {
throw new BadInputException("연산자");
}
return this;
}
public double executeCalculator() {
return calculator.calculate();
}
}package week04;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean calculateEnded = false;
CalculatorApp calculator = new CalculatorApp();
while (!calculateEnded) {
try {
calculator.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}