프로세스와 쓰레드
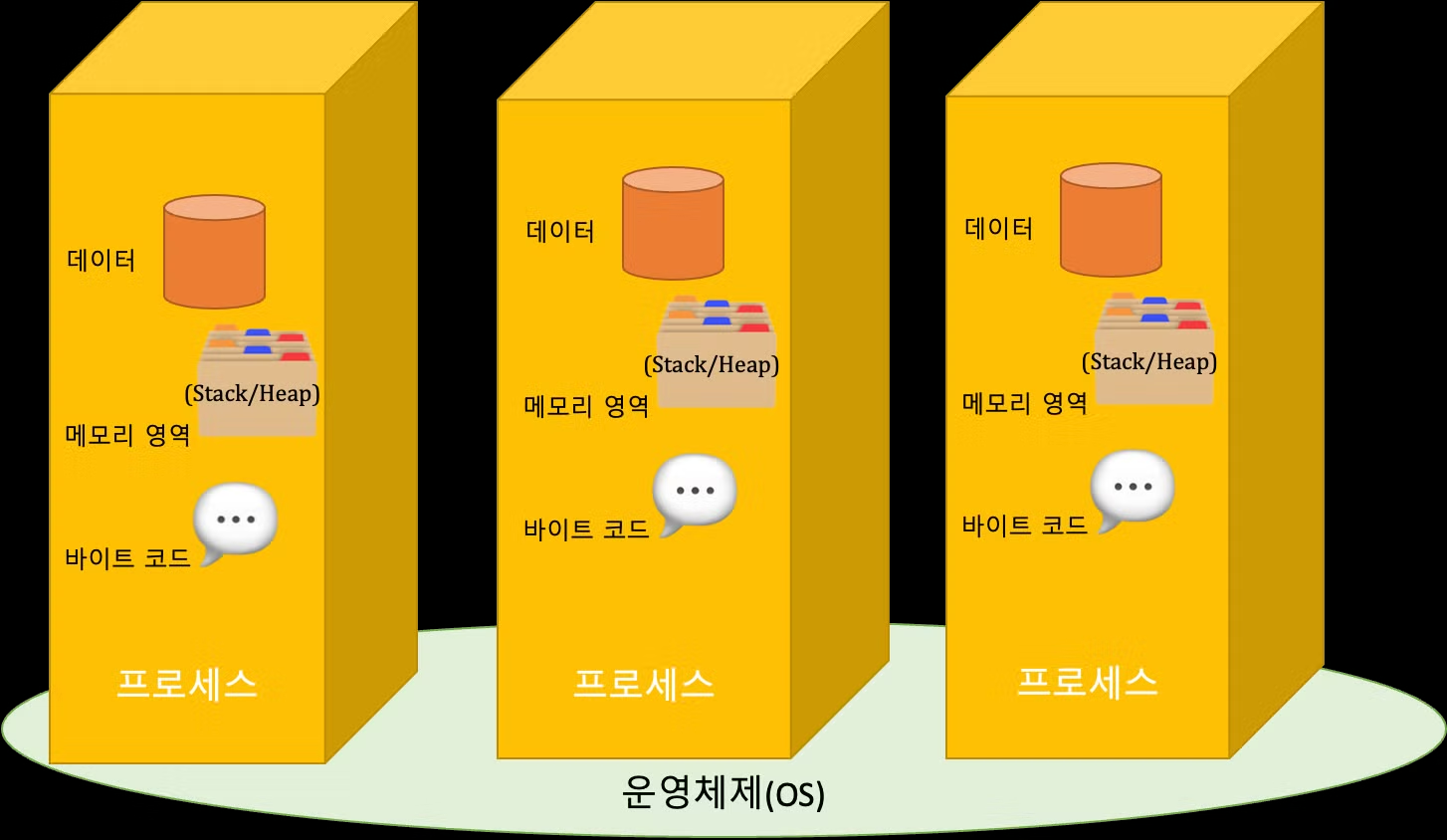
프로세스
- OS로부터 자원을 할당받는 작업의 단위.
- 실행중인 프로그램, N개의 프로세스가 작업중일땐 멀티프로세스

구조
- 프로세스 할당시 Code, Data, Memory(Stack,Heap) 할당.
- Code : Java Main 메소드같은 코드
- Data : 프로그램 실행중 저장될수있는 저장공간.
- 전역변수, 정적변수, 배열들 초기화된 데이터저장공간
- Memory :
- Stack : 지역변수, 매개변수 리턴 변수 저장(1회용 공간)
- Heap : 프로그램이 동적으로 필요한 변수저정(참조 영역)
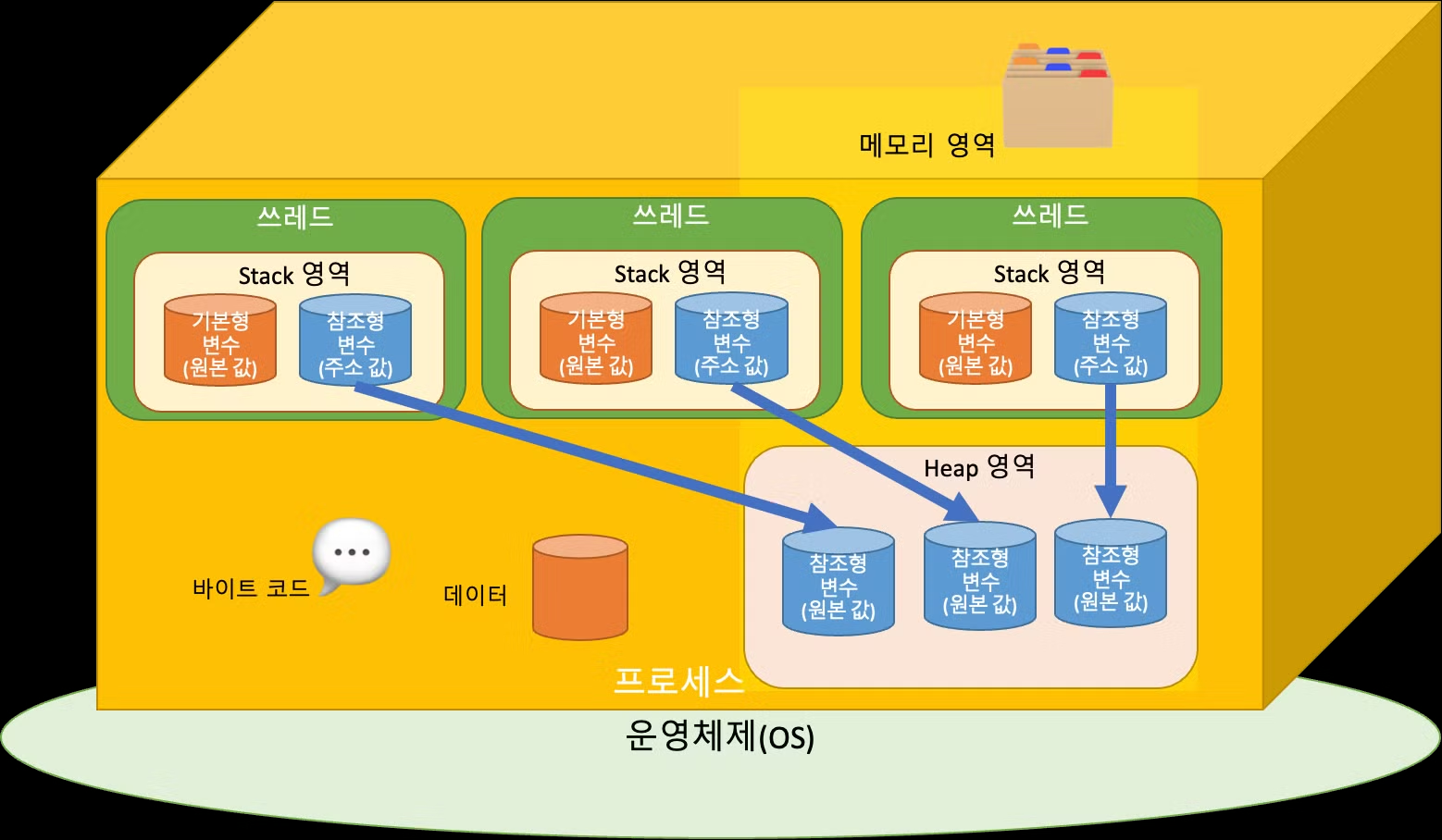
쓰레드
- 프로세스 내에서 동작하는 실행의 단위
- 작업중인 프로그램에서 실행요청이 들어온 순간 쓰레드생성(필요할때)
- 쓰레드는 실행을 위해 프로세스의 Heap 영역을 공유.
- Stakc 영역은 개인적으로 할당 (지역변수 및 매개변수는 작업종료후 사라지기 때문에)
JAVA
- Java 의 쓰레드는 JVM위에서 실행되며
Main쓰레드에서 부터 실행됌.
멀티쓰레드 & 싱글쓰레드
싱글쓰레드
- Java의 경우 main() 메소드 하나만으로 돌아가는 프로그램.
- 메인쓰레드가 종료되면 JVM도 같이종료.
멀티쓰레드
- 1개의 프로세스에서 여러개의 쓰레드가 실행되는것.
- 프로세스의 자원을 공유하여 작업한다 (Stack 제외)
- 작업순서를 보장하지 못하기에 시간,동작을 예측불가능.
(OS스케쥴러가 작업을 제어)
장점
- 여러개의 작업흐름을 병렬적으로 처리하기에 작업효율이 높다.
- 메모리영역을 공유하기에 자원효율성이 높다.
- 비동기방식을 통해 CPU의 작업시간을 향상시킨다.
단점
- 동기화문제 발생 : 자원을 공유하기에 자원을 사용하기위한 충돌, 대기가 발생.
- 교착상태 발생 : 2개 이상의 쓰레드가 서로 자원을 원하며 작업이 멈추었을때
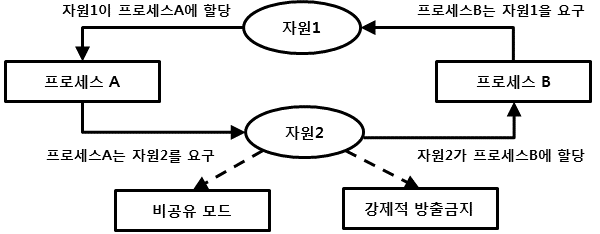
- 상호배제 : 1개의 자원을 1개의 프로세스 만이 사용가능.
- 비섬점 : 다른 프로세스가 사용하는 자원을 뺏을수 없음.
- 점유대기 : 프로세스가 1개의 자원을 지닌채 다른 프로세스의 자원을 대기
- 환형대기 : 모든 프로세스가 자신의 앞순번 프로세스의 자원을 기다림.
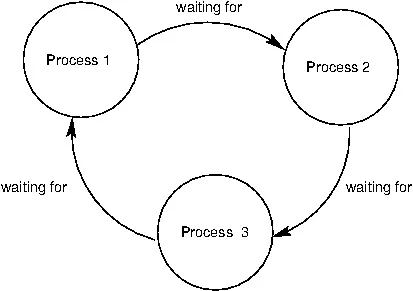
쓰레드 생성
- Thread Class 상속.
public class TestThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
// 쓰레드 수행작업
}
}
...
TestThread thread = new TestThread(); // 쓰레드 생성
thread.start() // 쓰레드 실행- Runnable Interface 구현.
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 쓰레드 수행작업
}
}
...
Runnable run = new TestRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(run); // 쓰레드 생성
thread.start(); // 쓰레드 실행- 클래스는 다중상속을 지원하지 않기때문에 인터페이스에 비해 확장성이 매우 떨어짐.
- 인터페이스로 구현하고 다른 클래스를 상속받을수 있기에 확장성에서 유리.
- 람다식 (익명객체 비슷)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task = () -> {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
sum += i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 최종 합 : " + sum);
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task);
thread1.setName("thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(task);
thread2.setName("thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}- run()메소드 작업부부분을 {} 안에 작성해서 사용.
- setname()을 통해 쓰레드 이름 부여 가능.
Daemon Thread
- 낮은 우선순위를 가지는 보조 쓰레드. 대표적으로 GC가 있음.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable demon = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
System.out.println("demon");
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(demon);
thread.setDaemon(true); // true로 설정시 데몬스레드로 실행됨
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("task");
}
}
}
task 작업 종료시 데몬쓰레드 강제종료- 우선순위가 낮기에 다른 쓰레드가 모두 종료시 강제종료당함.
사용자 Thread
- 높은 우선순위를 가지는 주작업 쓰레드, 데몬쓰레드가 아닌 쓰레드
- 대표적인 예로는 Main쓰레드. 작업이 끝날시 모든 데몬쓰레드를 강제종료시킨다.
Thread 우선순위
- 쓰레드가 가지는 작업의 중요성에 따라 우선순위를 부여할수있음. 더많은 작업리소스가 할당된다.
- OS가 아닌 JVM이 설정한 우선순위.
Thread thread1 = new Thread(task1);
thread1.setPriority(8);
int threadPriority = thread1.getPriority();
System.out.println("threadPriority = " + threadPriority);- 우선순위가 높기에
상대적으로 확률이 높을뿐 절대적으로 먼저 호출 및 종료가되는것은 아님.
Thread Group
- 서로 관련되어있는 쓰레드들을 그룹화하여 관리
- 쓰레드들은 무조건 하나의 그룹에 포함되어짐.
- 부모쓰레드의 그룹과 우선순위를 상속받으며, 암묵적으로 main 쓰레드그룹에 속함.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task = () -> {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Interrupted");
};
// ThreadGroup 클래스로 객체를 만듭니다.
ThreadGroup group1 = new ThreadGroup("Group1");
// Thread 객체 생성시 첫번째 매개변수로 넣어줍니다.
// Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name)
Thread thread1 = new Thread(group1, task, "Thread 1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(group1, task, "Thread 2");
// Thread에 ThreadGroup 이 할당된것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
System.out.println("Group of thread1 : " + thread1.getThreadGroup().getName());
System.out.println("Group of thread2 : " + thread2.getThreadGroup().getName());
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
try {
// 현재 쓰레드를 지정된 시간동안 멈추게 합니다.
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// interrupt()는 일시정지 상태인 쓰레드를 실행대기 상태로 만듭니다.
group1.interrupt();
}
}- 관련이 된 쓰레드끼리의 작업흐름을 조정하기가 편하다.
쓰레드의 상태와 제어
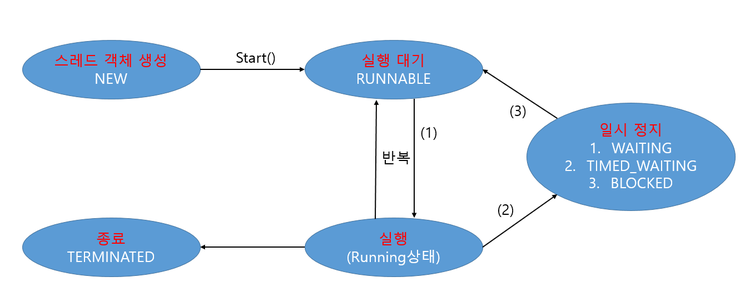
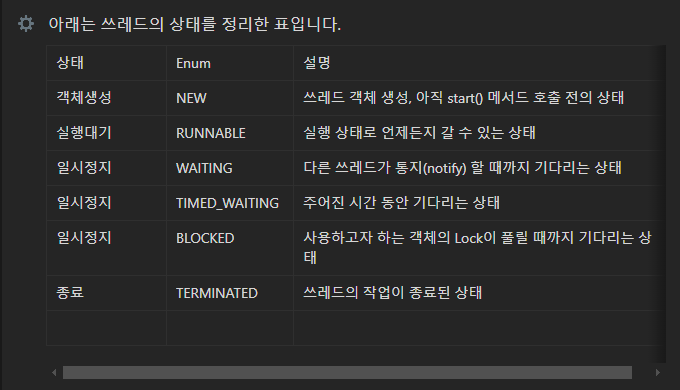
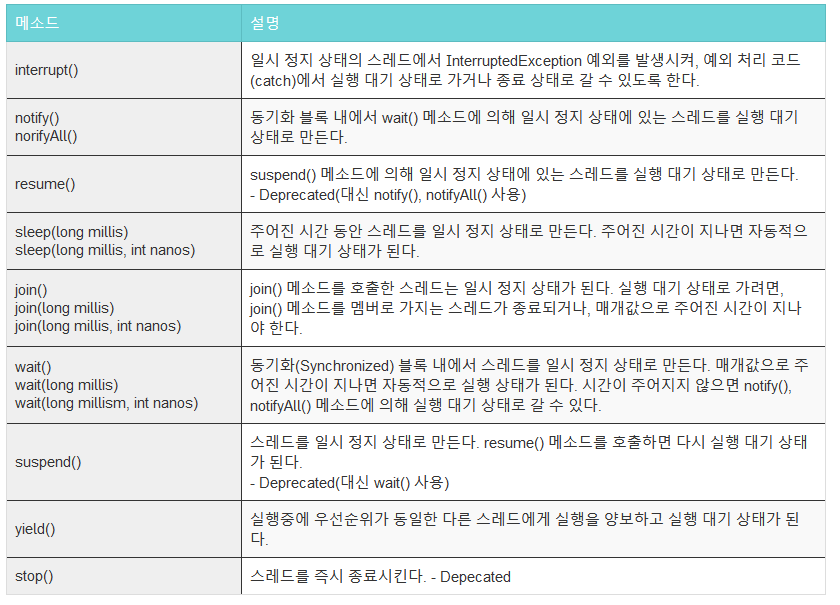
- sleep() : 현재 쓰레드를 지정된시간동안 멈춤.
(자기자신한정 : static 메서드기에 객체를 지정하고 멈추지않음)- interrupt()발생가능성(바로 실행대기상태로 전환)이 있기에 예외처리필요.
try {
Thread.sleep(2000); // 2초
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}- interrupt() : 일시정지상태 쓰레드를 실행대기 상태로 전환
실행중에도 실행대기상태로 돌아간다.- sleep() 도중 interrupt()를 만나면 예외가발생.
- isInterrupted() 메소드를 통해 상태를 확인하여 조절가능.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable task = () -> {
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
System.out.println("task : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
};
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "Thread");
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("thread.isInterrupted() = " + thread.isInterrupted());
}
}- join() : 정해진 시간동안 지정한 쓰레드의 작업을 기다림.
Thread thread = new Thread(task, "thread");
thread.start();
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}- interrupt()를 만나면 기다리는 것을 멈추기 때문에 예외발생.
- 여러쓰레드의 순서성을 보장하기 위해선 .start()후 jion메소드를 바로사용해야한다.
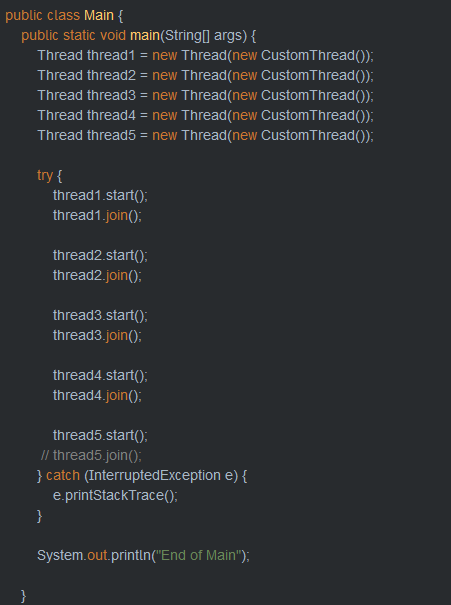 참조 : https://defacto-standard.tistory.com/1191
참조 : https://defacto-standard.tistory.com/1191
-
yield() : 남은 자원을 다른 쓰레드에게 양보하고 자신은 실행대기상태로 빠짐.
-
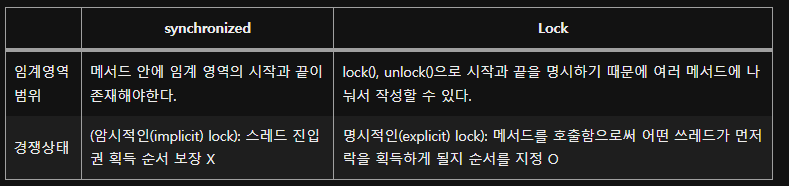
synchronized : 멀티쓰레드의 자원동기화를 위한 진입방지 키워드
- 쓰레드가 작업을 유지하는 동안 다른쓰레드의 진입을막음.
- 임계영역에 Lock 을 가진 쓰레드만이 진입이 가능해진다.
- 메서드 전체의 영역지정
public synchronized void asyncSum() { ...침범을 막아야하는 코드... } - 특정영역에 대한 지정
synchronized(해당 객체의 참조변수(this 등..)) { ...침범을 막아야하는 코드... }
-
wait() : 임계구역내에서 작업을 수행중 더이상 진행을 할 상황이 아닌경우 wait를 호출하여 스레드가 Lock을 반남하고 기다리게함.
- waiting pool에서 통지를 기다림.
-
notify() : 객체의 waiting pool에서 임의의(랜덤) 쓰레드에게 통지를 통해 작업을 재수행 다시 Lock을 얻는다.
-
제대로된 처리를 하지않은면 병목현상이 발생할 가능성이 높다.
(원하는 쓰레드, 아이템을 원하는 쓰레드 등을 지정할수 없음.)
ReentrantLock
- Synchronized의 단점을 보완하기 위해 만든 Lock 인터페이스 개체
- Synchronized와 다르게 명시적으로 lock&unlock 이 가능
- 원하는 범위만큼 Lock이 가능하다.
- 특정조건에서 lock을 풀고 나중에 다시 lock을 걸어 재진입이 가능.
- lock을 잡는 순서를 보장할 수 있음
ReentrantReadWriteLock
- 읽기 lock 과 쓰기 lock을 따로 제공.
- 읽기는 공유적이고, 쓰기는 베타적.
- 읽기 lock을 중복으로 얻을수 있어 여러 쓰레드가 진입이 가능.
- 읽기 lock을 소유하고있는 상태에서 쓰기는 불가능.
StampedLock
- ReentrantReadWriteLock 에서 낙관적인 Lock 기능 추가
- 데이터를 변경하기 전에는 Lock을 사용하지않음.
- 쓰기와 읽기가 충돌할때만 쓰기를 우선적으로하고 읽기 재진입.
Condition
- wait() & notify()의 문제점인 waiting pool 내 쓰레드를 구분하지 못한다는 것을 해결한 것
- 특정조건으로 특정쓰레드를 분리하여 만족할때만 깨움.
- ReentrantLock 클래스와 함께 사용
public class Main {
public static final int MAX_TASK = 5;
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// lock으로 condition 생성
private Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private ArrayList<String> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
// 작업 메서드
public void addMethod(String task) {
lock.lock(); // 임계영역 시작
try {
while(tasks.size() >= MAX_TASK) {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name+" is waiting.");
try {
condition1.await(); // wait(); condition1 쓰레드를 기다리게 합니다.
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
}
tasks.add(task);
condition2.signal(); // notify(); 기다리고 있는 condition2를 깨워줍니다.
System.out.println("Tasks:" + tasks.toString());
} finally {
lock.unlock(); // 임계영역 끝
}
}
}