Memory area functions
void memset(void *b, int c, size_t len)
- Writes len bytes of value c (converted to an unsigned char) to the string b.
void bzero(void *s, size_t n)
- Writes n zeroed bytes to the string s.
void memcpy(void *dst, const void *src, size_t n)
void memccpy(void *dst, const void *src, int c, size_t n)
void memmove(void *dst, const void *src, size_t len)
- Above functions copies len bytes from memory area src to memory area dst.
- memcpy and memccpy have undefined behaviors when dst and src are overlapped.
- memmove is safer function for overlapped dst and src.
(dst 와 src 가 어떻게 overlap 되었느냐에 따라 copy하는 방향이 달라짐)Why converting pointer to unsigned char *?
- Because we are handling with bytes and we do not know about given pointer types, whether int type or char type.
- Thus, we need to convert void type pointer to unsigned char type (char type is ok) to handle each bytes.
Bonus
Linked List Data Structure
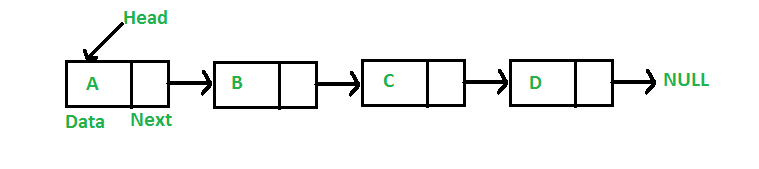
- Elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations.
- Elements are linked using pointers (*next)
