Objectives
int get_next_line(int fd, char **line)
- Calling the function in a loop will read the text available on a file descriptor one line at a time until EOF.
- Return 1 when a line has been read, 0 when EOF has been reached, -1 when an error happened.
- Able to manage multiple file descriptors.
What to know
Static variable
- Remains while the program is running.
- Is allocated memory in data segment
Difference between global and static variable is that static variable cannot be accessed from other files.
Why using static variable
- We need to call get_next_line until EOF, so we need a static variable to hold a line read with the amount of BUFFER_SIZE until the program ends.
File descriptor
- An abstract indicator used to access a file in Unix and related computer operating systems.
- Open returns file descriptor that are not allocated.
- 0 is for standard input, 1 is for standard output, 2 is for standard error.
Implementation
- get_next_line will read a file with the amount of BUFFER_SIZE and determine if the string is a line or not.
- If the string read is not a line, a function will read a file with same amount again.
static char *saved[OPEN_MAX]
- OPEN_MAX defined in <limits.h>, is the maximum number of files that one process can have open at any one time.
- Used double pointer to manage strings from n files.
- Will hold lines read until the program ends.
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE + 1]
- Temporary array that will hold a string read with the amount of BUFFER_SIZE.
- Will be joined with saved string.
Steps
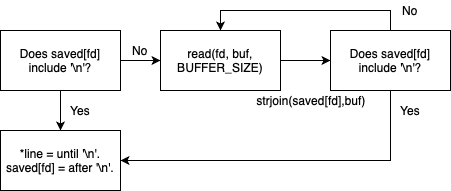
- Check if static variable saved[fd] includes new line.
-> If yes, copy a string in saved[fd] until a new line to a given variable line.
-> Then, saved[fd] will be overwritten into saved[fd] after a new line. - Read a file with the amount of BUFFER_SIZE.
-> Join existing saved[fd] with buf.
-> Return to step 1.
What to be careful
Memory leaks
- Malloc will be used in ft_strjoin and ft_strdup.
- saved[fd] will be overwritten with new memory allocation.
-> Previous saved[fd] should be freed.
BUFFER_SIZE
- Since char buf[BUFFER_SIZE] is allocated in stack memory, if a function reads more than available stack size, it will cause stack overflow.
-> Set as global or static variable that will be allocated in data segment.
-> Allocate in heap memory using malloc.
-> Manually increase stack memory size.

If you’re looking for a place where multiplayer gaming thrives, Two Player Games is the perfect site to visit. With its wide range of games, easy accessibility, and constant updates, it’s a go-to destination for anyone who enjoys gaming with a friend. So grab a partner, pick a game, and start playing today!