NEXT : [[04 동적 템플릿]]
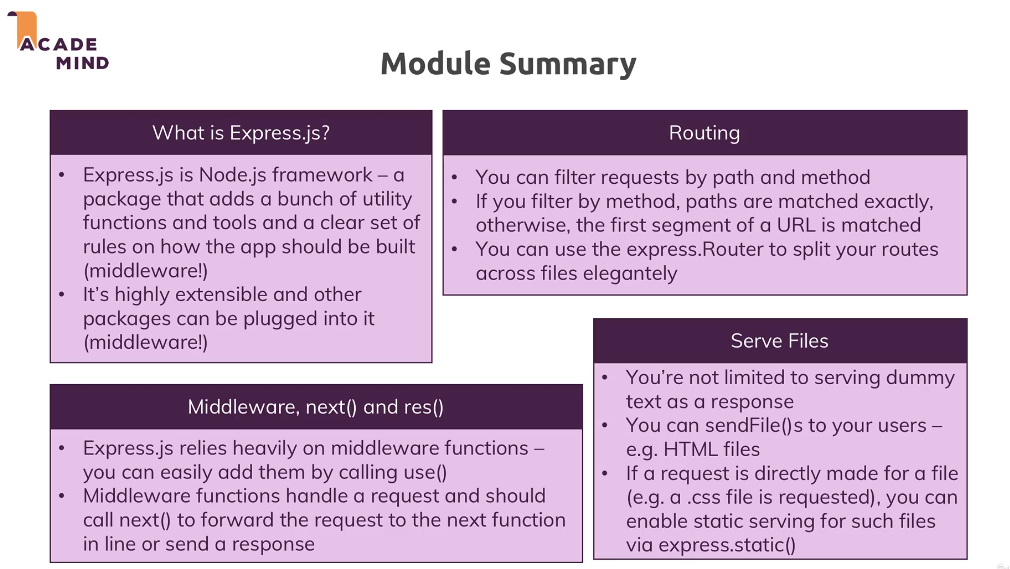
Express.js 란?
Express.js는 Node.js를 기반으로 한 웹 애플리케이션 프레임워크이다. 간단하고 유연한 구조를 가지고 있어 개발자들에게 많은 인기를 얻고 있습니다. Express.js를 사용하면 라우팅, 미들웨어, HTTP 요청 및 응답 처리 등을 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
Express.js는 다양한 기능을 제공하며, 다른 모듈과의 연동도 용이하다. 또한 RESTful API를 쉽게 구축할 수 있는데, 이는 웹 애플리케이션의 성능과 확장성을 향상시키는데 도움이 된다.
- 서버 로직을 간단하게 해주는 제 3자 패키지 프레임워크
- 미드웨어로서 작용하여 메서드의 기능을 절차적으로 추가하고 간단히 정의할 수 있음
대안
- Vanilla Node.js
- Adonis.js
- Koa
- Sails.js
- ...
설치
npm install --save express사용
// express.js package 사용하기
const express = require('express'); // method 객체
const app = express(); // requestHandler로서 사용됨
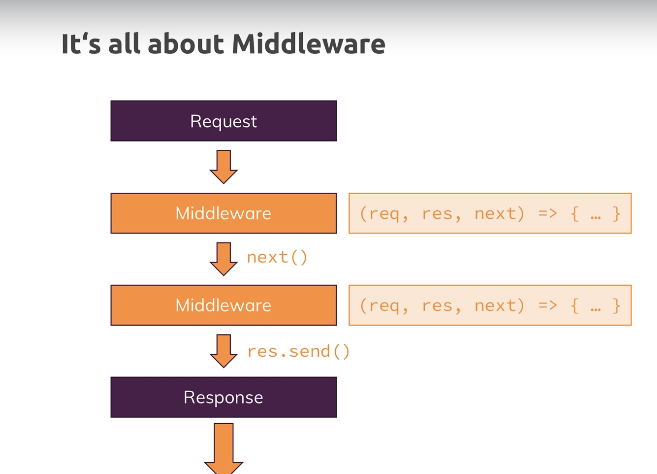
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log("In the middleware!");
next();
}); // midware 메서드 정의
app.use((req, res, next) => {
console.log("In another middleware!");
res.send("<h1>Hello World!</h1>"); // send
next();
});
app.listen(8080);express.js에서 지원하는 send 메서드를 사용하면 자동으로 html 태그등의 기본구성을 만들어줌
- body-parser 가 기본적으로 포함되어 있음
const http = require('http'); // Global Module of Node Js
// express.js package 사용하기
const express = require('express'); // method 객체
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express(); // requestHandler로서 사용됨
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded());
// file, json, form의 내용들을 미리 파싱해줌
app.use("/", (req, res, next) => {
console.log("This always runs!");
next();
})
app.add("/add-product", (req, res, next) => {
res.send(`
<h1>The Add Product Page</h1>
<form action="/product" method="POST"><input type="text" name="title"><button type="submit">Add Product</button></form>
`);
});
app.get("/product", (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.body);
// 자동으로 파싱하지 않으므로 bodyParser를 거쳐야함
res.redirect("/");
});
app.use("/", (req, res, next) => {
console.log("In another middleware!");
res.send("<h1>Hello World!</h1>"); // send
}); // midware 메서드 정의
app.listen(8080);- middleware로 추가한 모든 모듈을 거쳐 그 결과를 출력함
- use에 url을 추가하여 특정 주소에 대한 처리를 정의할 수 있음
- get, post 등의 함수는 use에 특정 메소트의 필터링을 추가한 함수임 url 또한 정확히 일치할 때 미들웨어가 실행됨
Router
app.js
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const adminRoutes = require("./routes/admin");
const shopRoutes = require("./routes/shop");
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: false}));
app.use("/admin", adminRoutes); // url base url을 추가할 수 있음
app.use("/shop", shopRoutes);
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.status(404).send("<h1>Page not found!</h1>")
}); // 예상치 못한 요청시 404 페이지 호출
app.listen(8080);admin.js
const express = require("express");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const router = express.Router();
router.get("/add-product", (req, res, next) => {
res.send(`
<h1>The Add Product Page</h1>
<form action="/admin/product" method="POST"><input type="text" name="title"><button type="submit">Add Product</button></form>
`);
});
router.post("/product", (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.body);
// 자동으로 파싱하지 않으므로 bodyParser를 거쳐야함
res.redirect("/");
});
module.exports = router;const express = require("express");
const path = require("path")
const router = express.Router();
router.get("/add-product", (req, res, next) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "../", "views", "add-product.html"))
// 다음과 같이 path 모듈과 html 폴더를 사용해 html 문서를 전송할 수 있음
});
router.post("/add-product", (req, res, next) => {
console.log(req.body);
// 자동으로 파싱하지 않으므로 bodyParser를 거쳐야함
res.redirect("/");
});
module.exports = router;Path
main 모듈의 위치 알기
const path = require("path");
module.exports = path.dirname(require.main.filename);join 함수를 통해 os와 독립적으로 사용가능
router.get("/add-product", (req, res, next) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(rootPath, "views", "add-product.html"))
});js나 css와 같은 정적 리소스들은 다음과 같이 추가해줘야함
app.use(express.static(path.join(rootPath, "public")));