📌 RCP Scenarios (Representative Concentration Pathways)
1. What is RCP?
RCP (Representative Concentration Pathways) refers to future climate change scenarios based on different levels of greenhouse gas emissions.
Developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) for its Fifth Assessment Report (AR5, 2014), RCP scenarios project the possible changes in global temperature, sea levels, and climate patterns by 2100.
📌 Key Concept of RCP
- RCPs define different pathways for greenhouse gas concentrations based on emissions and policy actions.
- The number in "RCP X.X" represents the additional radiative forcing (W/m²) by 2100, compared to pre-industrial levels.
- Example: RCP 2.6 means an increase of 2.6 W/m² in radiative forcing
- Radiative forcing: The amount of extra heat trapped in Earth's atmosphere due to greenhouse gases
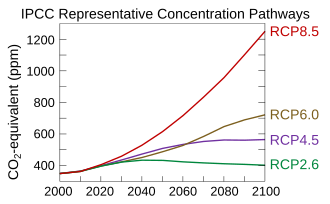
2. Types of RCP Scenarios and Their Characteristics
IPCC proposed four RCP scenarios, each reflecting a different level of greenhouse gas emissions and global warming projections.
| RCP Scenario | Description | Projected Global Temperature Rise (by 2100) | Feasibility of Carbon Neutrality |
|---|---|---|---|
| RCP 2.6 | Strong mitigation efforts, carbon neutrality achieved | 🌡️ 1.5~2.0°C increase | ✅ Achievable |
| RCP 4.5 | Moderate emissions reduction policies | 🌡️ 2.0~3.0°C increase | ❌ Difficult |
| RCP 6.0 | Partial mitigation, limited policies | 🌡️ 3.0~4.0°C increase | ❌ Unlikely |
| RCP 8.5 | Worst-case scenario, continued high emissions | 🌡️ 4.0~5.5°C increase | ❌ Impossible |
✅ The world is currently following the RCP 8.5 trajectory.
🚨 RCP 2.6 is the only pathway that aligns with global carbon neutrality goals.
3. Explanation of Each RCP Scenario
📌 RCP 2.6 (Best-Case Scenario, Carbon Neutrality)
- Requires strong global climate policies and emissions reduction.
- Achieves carbon neutrality by 2050 with heavy investment in renewable energy and carbon capture technology (CCS).
- Limits global temperature rise to 1.5~2.0°C, meeting the Paris Agreement target.
📌 RCP 4.5 (Moderate Emission Reduction)
- Some climate policies implemented, but not enough to reach carbon neutrality.
- Fossil fuel use continues, but renewable energy adoption increases.
- Expected temperature rise: 2.0~3.0°C.
📌 RCP 6.0 (Limited Emission Reduction)
- Greenhouse gas emissions continue rising until mid-century before gradually declining.
- Minimal policy action, business-as-usual approach.
- Expected temperature rise: 3.0~4.0°C.
📌 RCP 8.5 (Worst-Case Scenario)
- No significant emissions reduction policies; fossil fuel use continues to grow.
- Global temperature rises by 4.0~5.5°C, leading to catastrophic consequences:
- 🔥 Extreme heatwaves, wildfires, and droughts
- 🌊 Sea level rise causing climate refugees
- 🌀 Stronger hurricanes, heavy rainfall, and floods
- Currently, the world is closest to this scenario.
4. Limitations of RCP and the Shift to SSP Scenarios
- RCP only focuses on greenhouse gas concentrations and does not fully account for social and economic factors.
- The latest IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6, 2021) introduced SSP (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways), which integrates social and economic variables into climate modeling.
5. Future Climate Projections Based on RCP Scenarios
📌 Comparison: RCP 2.6 vs. RCP 8.5 (By 2100)
| Climate Factor | RCP 2.6 (Best-Case) | RCP 8.5 (Worst-Case) |
|---|---|---|
| Global Temperature | 🌡️ +1.5~2.0°C | 🔥 +4.0~5.5°C |
| Sea Level Rise | 📈 0.5m increase | 🌊 1~2m increase |
| Heatwaves & Droughts | ⚠️ Less frequent | 🚨 Severe increase |
| Arctic Ice (Summer) | 🧊 Partially remains | ❄️ Completely disappears |
| Climate Refugees | 🏠 Manageable | 🏃 Mass displacement |
✅ Following RCP 2.6 is essential to avoid catastrophic climate change.
❌ The world is currently on an RCP 8.5 path, requiring urgent climate action.
6. Conclusion: The Importance of RCP Scenarios
✅ RCP is a crucial tool for predicting future climate risks and shaping climate policies.
✅ Without stronger climate action, the world will continue toward RCP 8.5.
✅ To achieve carbon neutrality, we must follow RCP 2.6 by drastically reducing emissions.
✅ Delays in climate action will increase the severity of natural disasters and economic costs.
🔥 Urgent climate action is needed to shift from RCP 8.5 to RCP 2.6 and prevent irreversible climate damage! 🌍💚