
📌 SSP Scenarios (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways)
1. What is SSP?
SSP (Shared Socioeconomic Pathways) are scenarios that describe possible future global socio-economic developments and their impact on climate change.
Unlike RCP (Representative Concentration Pathways), which focuses only on greenhouse gas concentrations, SSP considers factors such as population growth, economic development, technological progress, and policy changes.
📌 SSP helps model how different societal choices influence climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
📌 IPCC introduced SSP in the Sixth Assessment Report (AR6, 2021) to replace RCP-based projections.
2. Key Concept of SSP
✔ SSP scenarios define different pathways for global socio-economic development.
✔ They assess the feasibility of climate change mitigation and adaptation under different conditions.
✔ SSP is combined with RCP to create more comprehensive climate change projections (SSP-RCP scenarios).
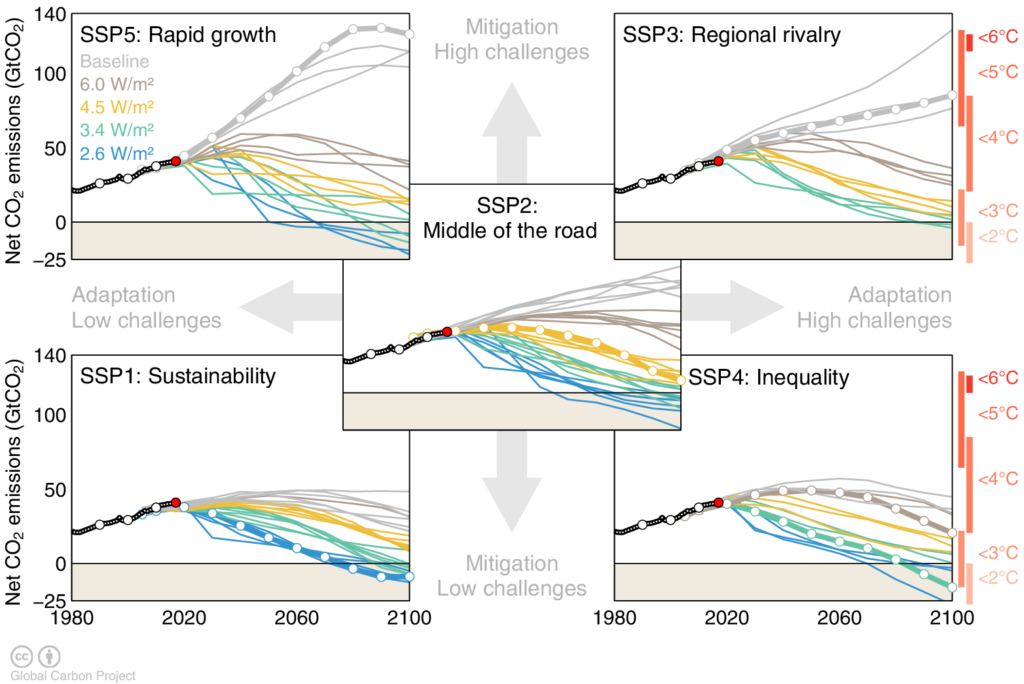
3. Types of SSP Scenarios and Their Characteristics
IPCC proposed five SSP scenarios, each describing a different socio-economic pathway.
| SSP Scenario | Description | Climate Change Mitigation Feasibility |
|---|---|---|
| SSP1 (Sustainability, Green Road) | Strong climate policies, global cooperation, reduced inequality, renewable energy transition | ✅ Very High |
| SSP2 (Middle of the Road) | Current trends continue with moderate economic growth and environmental policies | ⚖️ Medium |
| SSP3 (Regional Rivalry, Fragmentation) | High nationalism, weak international cooperation, slow economic growth | ❌ Low |
| SSP4 (Inequality, Divided World) | Widening gap between rich and poor, limited climate action | ❌ Very Low |
| SSP5 (Fossil-fueled Development, Conventional Growth) | Economic growth prioritization, reliance on fossil fuels, high emissions | 🚨 Worst |
✅ SSP1 is the most sustainable pathway, making carbon neutrality achievable.
🚨 SSP3 and SSP5 lead to severe climate change and high emissions.
4. Detailed Analysis of Each SSP Scenario
📌 SSP1: Sustainability (Green Road)
- Global cooperation ensures economic growth with strong environmental policies.
- Transition to renewable energy, reduced inequality, and improved education.
- Best scenario for climate change mitigation and adaptation.
📌 SSP2: Middle of the Road
- Continuation of current social and economic trends.
- Moderate climate policies, leading to some emissions reduction but insufficient for full carbon neutrality.
📌 SSP3: Regional Rivalry (Fragmentation)
- High nationalism and weak international cooperation hinder global climate action.
- Unequal economic development, making climate mitigation difficult.
- High reliance on domestic fossil fuel production.
📌 SSP4: Inequality (Divided World)
- A world of economic disparity: wealthy nations adopt advanced climate technologies, but developing countries struggle with high emissions.
- Limited progress in global climate adaptation due to socio-economic inequality.
📌 SSP5: Fossil-fueled Development (Worst-case Scenario)
- Economic growth is prioritized over environmental protection.
- Heavy use of coal, oil, and gas, leading to uncontrolled emissions.
- Worst scenario for climate change, similar to RCP 8.5.
5. Relationship Between SSP and RCP
📌 SSP focuses on socio-economic trends, while RCP models greenhouse gas concentration levels.
📌 They are combined to create SSP-RCP scenarios for more realistic climate projections.
📌 Example SSP-RCP combinations:
- SSP1-2.6 → Sustainable development with strong climate action → Best case for carbon neutrality
- SSP3-7.0 → Nationalistic fragmentation with high emissions → High risk of climate disasters
- SSP5-8.5 → Fossil-fuel-driven economic growth → Worst-case climate scenario
6. Future Climate Projections Based on SSP-RCP Scenarios
| SSP-RCP Scenario | Description | Projected Temperature Rise (by 2100) |
|---|---|---|
| SSP1-1.9 | Full carbon neutrality achieved, most optimistic scenario | 🌡️ Below 1.5°C |
| SSP1-2.6 | Sustainable development with emissions reduction | 🌡️ Below 2°C |
| SSP2-4.5 | Moderate policies, limited climate action | 🌡️ 2.5~3°C |
| SSP3-7.0 | Nationalistic and fragmented world, weak climate response | 🌡️ 3.5~4°C |
| SSP5-8.5 | Fossil-fuel-driven economic growth, no emissions control | 🌡️ 4.5~5.5°C |
✅ SSP1-2.6 represents the best pathway for sustainable climate action.
❌ The world is currently trending toward SSP3-7.0 or SSP5-8.5, leading to catastrophic climate risks.
7. Conclusion: Why SSP Matters
✅ SSP provides a more comprehensive approach than RCP by considering social and economic factors.
✅ SSP1 (Sustainability) is the best-case scenario for effective climate mitigation.
✅ Current trends suggest the world is moving toward SSP3 (Regional Rivalry) and SSP5 (Fossil-fueled Development).
✅ Strong international cooperation and sustainable policies are essential to shift toward SSP1.
🔥 The global community must move from SSP5-8.5 toward SSP1-2.6 to ensure a livable future. 🌍💚