Shape Errors (One of the most common errors in deep learning)
- Shape errors occur when the dimensions of tensors do not match up.
- 텐서의 차원이 맞지 않는 경우 발생.
- 예를 들어, 두 텐서를 곱하려고 할 때 차원이 맞지 않으면 오류가 발생할 수 있음.
There are two rules that are performing or two main rules that performing matrix multiplication needs :
1. The inner dimensions(차원) must match. - 행렬 곱셈에서 내부 차원이 일치해야 함.
(3, 2) @ (3, 2)에러(2, 3) @ (3, 2)작동(3, 2) @ (2, 3)작동
- The resulting matrix has the shape of the outer dimenstions - 결과 행렬의 차원은 외부 차원에 따라 결정됨.
(3, 2) @ (2, 3)->(3, 3)(2, 3) @ (3, 2)->(2, 2)
1. 내부차원 불일치 예시,
torch.matmul(torch.rand(2, 3), torch.rand(2, 5))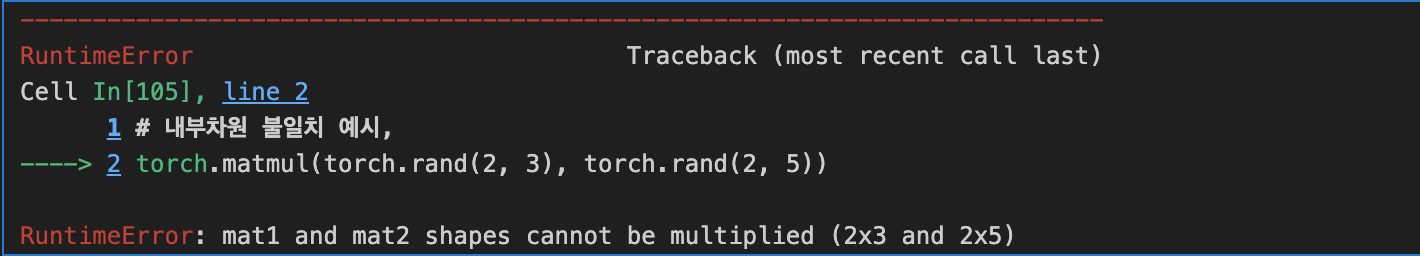
2. 외부차원에 의해 결정된 행렬 결과
torch.matmul(torch.rand(3, 6), torch.rand(6, 5))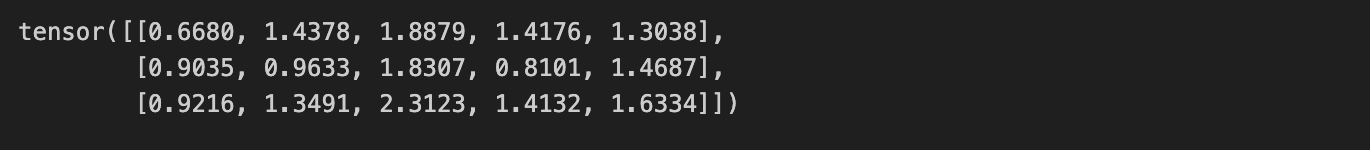
Shape for matrix multiplication
- 행렬 곱셈에서 행렬의 차원은 다음과 같이 결정됨.
- 외부 차원은 결과 행렬의 차원이 되며, 내부 차원은 행렬 곱셈에 필요한 차원이 됨.
- 예를 들어, 두 행렬
(3, 2)와(2, 3)의 곱셈은 결과 행렬의 차원이(3, 3)이 됨. - 이러한 원리를 이해하면 행렬 곱셈을 통해 원하는 결과를 얻을 수 있음.
tensor_A = torch.tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
tensor_B = torch.tensor([[7, 10],
[8, 11],
[9, 12]])
tensor_A.shape, tensor_B.shape
tensor.matmul(tensor_A, tensor_B) # torch.mm() = torch.matmul() 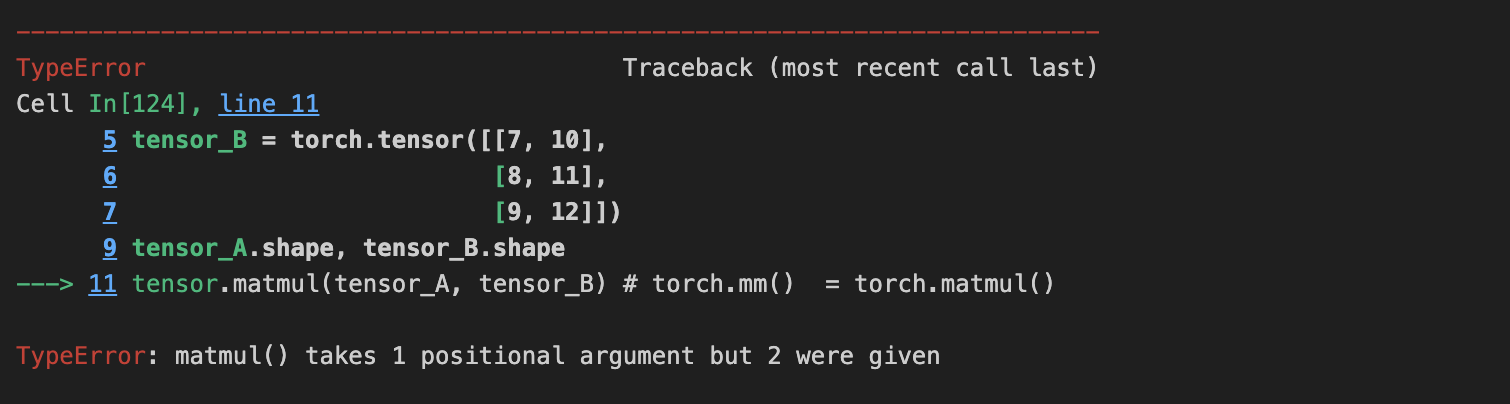
다음과 같은 에러가 난다.
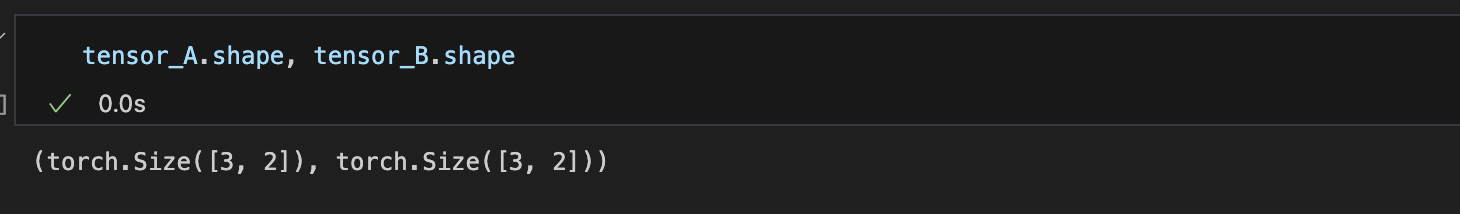
둘의 inner demention이 다르기 때문이다.
To fix our tensor shape issues, we can manipulate the shape of our tensors using a transpose.
A transpose switches the dimensions of a given tensor.
transpose로 텐서의 차원을 변경하여 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
transpose
tensor_B.T, tensor_B.T.shape
.T 즉, transpose는 차원을 변경해준다.
# The matrix multiplication operation works when tensor_B is transposed.
print(f"Original shapes: tensor_A: {tensor_A.shape}, tensor_B: {tensor_B.shape}")
print(f"New shapes : tensor_A: {tensor_A.shape}, tensor_B.T: {tensor_B.T.shape}")
print(f"Mutiplying : {tensor_A.shape} @ {tensor_B.T.shape} <- inner dimensions must match")
output = torch.mm(tensor_A, tensor_B.T)
print(output)
print(f"\nOutput shape : {output.shape}")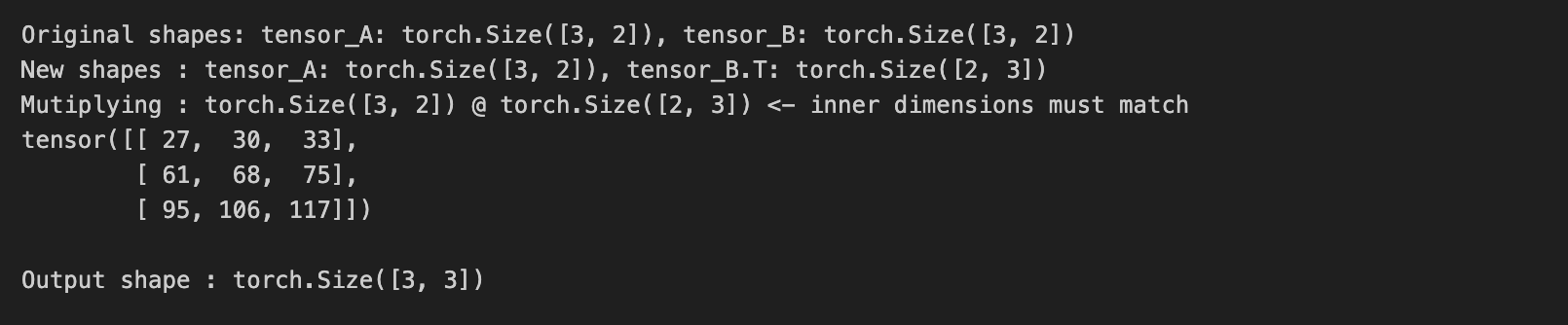
- matrixmultiplication에서 실제 calculation이 되는 과정을 시각화하여 볼 수 있다.
텐서 집계: 최소값, 최대값, 평균, 합계 등 계산하기 (Tensor Aggregation)
텐서 집계는 텐서 데이터에서 특정 값을 요약하거나 분석하기 위해 중요한 작업이다. 예를 들어, 텐서의 최소값, 최대값, 평균, 합계 등을 구하는 과정이 포함. 이 작업은 대규모 데이터를 처리하고 요약하는 데 유용하며, 딥 러닝 모델에서도 자주 사용된다.
텐서 집계(Aggregation)는 텐서의 여러 값을 하나의 값으로 요약하는 작업이다. 예를 들어:
- 최소값(min): 텐서에서 가장 작은 값.
- 최대값(max): 텐서에서 가장 큰 값.
- 평균(mean): 텐서 값의 평균.
- 합계(sum): 텐서 값의 총합.
torch.arange()를 사용하여 텐서를 생성할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 0에서 100까지 10씩 증가하는 텐서를 생성해보자.
# Create a tensor
x = torch.arange(0, 100, 10)
x, x.dtype
min
# Find the minimum value in a tensor
torch.min(x), x.min()
max
# Find the maximum value in a tensor
torch.max(x), x.max()
mean
- Note : 기본값이 int64이므로 Long type 에러가 발생. float32로 변환하여 계산
# Find the mean value in a tensor
torch.mean(x.type(torch.float32)), x.type(torch.float32).mean() 
sum
# Find the sum of all values in a tensor
torch.sum(x), x.sum()
Find the positional min and max
# Create a tensor
x = torch.arange(1, 100, 10)
x, x.dtype
argmin()
- Find the position in tensor that has the minimum value with
argmin()-> returns index position of target tensor where the minimum value argmin()를 사용하여 최소값을 갖는 텐서의 위치를 찾은 다음 인덱스 위치를 반환
x.argmin() # 인덱스 위치
# 0번째 인덱스 위치의 값
x[0] 
argmax()
- Find the position in tensor that has the maximum value with
argmax()-> returns index position of target tensor where the maximum value argmax()를 사용하여 최대값을 갖는 텐서의 위치를 찾은 다음 인덱스 위치를 반환
x.argmax() # 최대값의 인덱스 위치
# 9번째 인덱스 위치의 값
x[9]

짱이다!!!