스파르타 Java 단기 심화 과정
코드카타
프로그래머스 77484 로또의 최고 순위와 최저 순위
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/77484
— 문제 설명
로또 6/45(이하 '로또'로 표기)는 1부터 45까지의 숫자 중 6개를 찍어서 맞히는 대표적인 복권입니다. 아래는 로또의 순위를 정하는 방식입니다. 1
| 순위 | 당첨 내용 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 6개 번호가 모두 일치 |
| 2 | 5개 번호가 일치 |
| 3 | 4개 번호가 일치 |
| 4 | 3개 번호가 일치 |
| 5 | 2개 번호가 일치 |
| 6(낙첨) | 그 외 |
로또를 구매한 민우는 당첨 번호 발표일을 학수고대하고 있었습니다. 하지만, 민우의 동생이 로또에 낙서를 하여, 일부 번호를 알아볼 수 없게 되었습니다. 당첨 번호 발표 후, 민우는 자신이 구매했던 로또로 당첨이 가능했던 최고 순위와 최저 순위를 알아보고 싶어 졌습니다.
알아볼 수 없는 번호를 0으로 표기하기로 하고, 민우가 구매한 로또 번호 6개가 44, 1, 0, 0, 31 25라고 가정해보겠습니다. 당첨 번호 6개가 31, 10, 45, 1, 6, 19라면, 당첨 가능한 최고 순위와 최저 순위의 한 예는 아래와 같습니다.
| 당첨 번호 | 31 | 10 | 45 | 1 | 6 | 19 | 결과 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 최고 순위 번호 | 31 | 0→10 | 44 | 1 | 0→6 | 25 | 4개 번호 일치, 3등 |
| 최저 순위 번호 | 31 | 0→11 | 44 | 1 | 0→7 | 25 | 2개 번호 일치, 5등 |
- 순서와 상관없이, 구매한 로또에 당첨 번호와 일치하는 번호가 있으면 맞힌 걸로 인정됩니다.
- 알아볼 수 없는 두 개의 번호를 각각 10, 6이라고 가정하면 3등에 당첨될 수 있습니다.
- 3등을 만드는 다른 방법들도 존재합니다. 하지만, 2등 이상으로 만드는 것은 불가능합니다.
- 알아볼 수 없는 두 개의 번호를 각각 11, 7이라고 가정하면 5등에 당첨될 수 있습니다.
- 5등을 만드는 다른 방법들도 존재합니다. 하지만, 6등(낙첨)으로 만드는 것은 불가능합니다.
민우가 구매한 로또 번호를 담은 배열 lottos, 당첨 번호를 담은 배열 win_nums가 매개변수로 주어집니다. 이때, 당첨 가능한 최고 순위와 최저 순위를 차례대로 배열에 담아서 return 하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.
— 제한 조건
- lottos는 길이 6인 정수 배열입니다.
- lottos의 모든 원소는 0 이상 45 이하인 정수입니다.
- 0은 알아볼 수 없는 숫자를 의미합니다.
- 0을 제외한 다른 숫자들은 lottos에 2개 이상 담겨있지 않습니다.
- lottos의 원소들은 정렬되어 있지 않을 수도 있습니다.
- win_nums은 길이 6인 정수 배열입니다.
- win_nums의 모든 원소는 1 이상 45 이하인 정수입니다.
- win_nums에는 같은 숫자가 2개 이상 담겨있지 않습니다.
- win_nums의 원소들은 정렬되어 있지 않을 수도 있습니다.
— 입출력 예
| lottos | win_nums | result |
|---|---|---|
| [44, 1, 0, 0, 31, 25] | [31, 10, 45, 1, 6, 19] | [3, 5] |
| [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] | [38, 19, 20, 40, 15, 25] | [1, 6] |
| [45, 4, 35, 20, 3, 9] | [20, 9, 3, 45, 4, 35] | [1, 1] |
입출력 예 #1
문제 예시와 같습니다.
입출력 예 #2
알아볼 수 없는 번호들이 아래와 같았다면, 1등과 6등에 당첨될 수 있습니다.
| 당첨 번호 | 38 | 19 | 20 | 40 | 15 | 25 | 결과 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 최고 순위 번호 | 0→38 | 0→19 | 0→20 | 0→40 | 0→15 | 0→25 | 6개 번호 일치, 1등 |
| 최저 순위 번호 | 0→21 | 0→22 | 0→23 | 0→24 | 0→26 | 0→27 | 0개 번호 일치, 6등 |
입출력 예 #3
민우가 구매한 로또의 번호와 당첨 번호가 모두 일치하므로, 최고 순위와 최저 순위는 모두 1등입니다.
※ 실제로 사용되는 로또 순위의 결정 방식과는 약간 다르지만, 이 문제에서는 지문에 명시된 대로 로또 순위를 결정하도록 합니다.
— 문제 풀이
class Solution {
public int[] solution(int[] lottos, int[] win_nums) {
int winCnt = 0; // 맞는 숫자 카운트
int zCnt = 0; // 알아볼 수 없는 수 카운트
for(int i=0;i<6;i++){
if(lottos[i]==0){
zCnt++;
continue;
}
for(int j=0;j<6;j++){
if(lottos[i]==win_nums[j]){
winCnt++;
break;
}
}
}
int[] answer = new int[2];
answer[0] = checkLotto(winCnt+zCnt);
answer[1] = checkLotto(winCnt);
return answer;
}
public int checkLotto(int num){
switch(num){
case 6:
return 1;
case 5:
return 2;
case 4:
return 3;
case 3:
return 4;
case 2:
return 5;
default:
return 6;
}
}
}프로그래머스 133499 옹알이(2)
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/133499
— 문제 설명
머쓱이는 태어난 지 11개월 된 조카를 돌보고 있습니다. 조카는 아직 "aya", "ye", "woo", "ma" 네 가지 발음과 네 가지 발음을 조합해서 만들 수 있는 발음밖에 하지 못하고 연속해서 같은 발음을 하는 것을 어려워합니다. 문자열 배열 babbling이 매개변수로 주어질 때, 머쓱이의 조카가 발음할 수 있는 단어의 개수를 return하도록 solution 함수를 완성해주세요.
— 제한 조건
- 1 ≤
babbling의 길이 ≤ 100 - 1 ≤
babbling[i]의 길이 ≤ 30 - 문자열은 알파벳 소문자로만 이루어져 있습니다.
— 입출력 예
| babbling | result |
|---|---|
| ["aya", "yee", "u", "maa"] | 1 |
| ["ayaye", "uuu", "yeye", "yemawoo", "ayaayaa"] | 2 |
입출력 예 #1
- ["aya", "yee", "u", "maa"]에서 발음할 수 있는 것은 "aya"뿐입니다. 따라서 1을 return합니다.
입출력 예 #2
- ["ayaye", "uuu", "yeye", "yemawoo", "ayaayaa"]에서 발음할 수 있는 것은 "aya" + "ye" = "ayaye", "ye" + "ma" + "woo" = "yemawoo"로 2개입니다. "yeye"는 같은 발음이 연속되므로 발음할 수 없습니다. 따라서 2를 return합니다.
※ 네 가지를 붙여 만들 수 있는 발음 이외에는 어떤 발음도 할 수 없는 것으로 규정합니다. 예를 들어 "woowo"는 "woo"는 발음할 수 있지만 "wo"를 발음할 수 없기 때문에 할 수 없는 발음입니다.
— 문제 풀이
class Solution {
public int solution(String[] babbling) {
String[] pronun = {"aya", "ye", "woo", "ma"};
String[] wrong = {"ayaaya", "yeye", "woowoo", "mama"};
int answer = 0;
for(int i=0;i<babbling.length;i++){
boolean flag = false;
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
if(babbling[i].contains(wrong[j])) flag = true;
}
if(flag)continue;
for(int j=0;j<4;j++){
babbling[i] = babbling[i].replaceAll(pronun[j]," ");
}
babbling[i] = babbling[i].replaceAll(" ", "");
if(babbling[i].length()==0) answer++;
}
return answer;
}
}대규모 스트림 처리
데이터 일관성 유지 방안 - 분산 트랜잭션
- 여러 개의 독립된 시스템이나 DB에서 동시에 일어나는 트랜잭션을 일관되게 관리하는 방법
- 단일 트랜잭션이 여러 시스템에 걸쳐 발생할 때, 모든 시스템이 해당 트랜잭션을 성공적으로 완료하거나, 모든 시스템이 트랜잭션을 실패로 처리하도록 보장. 이를 통해 데이터의 일관성 유지 가능
- 분산 트랜잭션의 주요 개념
- 트랜잭션
- DB 상태를 변환하는 작업의 단위, ACID(원자성, 일관성, 고립성, 지속성)를 보장
- 원자성 (Atomicity) : 트랜잭션은 전부 성공하거나 전부 실패하여, 부분적인 작업 수행이 없는 것을 보장
- 일관성 (Consistency) : 트랜잭션이 완료된 후에도 DB는 모든 무결성 제약 조건을 유지해야 함
- 격리성 (Isolation) : 동시에 실행되는 트랜잭션이 서로 간섭하지 않도록 보장
- 지속성 (Durability) : 트랜잭션이 성공적으로 완료된 후의 결과는 시스템 장애가 발생해도 영구적으로 유지됨
- DB 상태를 변환하는 작업의 단위, ACID(원자성, 일관성, 고립성, 지속성)를 보장
- 분산 트랜잭션
- 여러 분산된 데이터 소스에 걸쳐 트랜잭션을 수행하는 작업
- ex) 여러 마이크로 서비스 or DB에서 데이터를 동시에 업데이트하는 경우
- 여러 분산된 데이터 소스에 걸쳐 트랜잭션을 수행하는 작업
- 2PC (Two-Phase Commit)
- 분산 트랜잭션을 관리하는 프로토콜, 준비(Prepare)단계와 커밋(Commit)단계로 나누어 트랜잭션을 처리
- 준비 단계(Prepare Phase) : 각 참여 노드는 트랜잭션 준비 상태를 확인하고, 준비 완료를 마스터 노드에 알림
- 커밋 단계(Commit Phase) : 마스터 노드는 모든 참여 노드가 준비되었음을 확인하고, 트랜잭션을 커밋하도록 지시. 준비가 완료되지 않은 노드가 있다면 트랜잭션 롤백
- 분산 트랜잭션을 관리하는 프로토콜, 준비(Prepare)단계와 커밋(Commit)단계로 나누어 트랜잭션을 처리
- 사가 패턴(SAGA Pattern)
- 트랜잭션을 여러 단계로 나누어 처리하고, 각 단계가 독립적으로 커밋됨. 실패시 보상 트랜잭션을 실행하여 상태를 롤백
- 예시
- 주문 생성 : 사용자가 주문을 생성
- 결제 처리 : 결제 서비스가 주문 결제를 처리
- 재고 감소 : 재고 서비스가 주문된 상품의 재고를 감소시킴
- 각 단계가 성공적으로 완료되면 다음 단계로 넘어가고, 실패하면 이전 단계에서 수행된 작업을 취소
- 예시
- 트랜잭션을 여러 단계로 나누어 처리하고, 각 단계가 독립적으로 커밋됨. 실패시 보상 트랜잭션을 실행하여 상태를 롤백
- 이벤트 소싱(Event Sourcing)
- 상태 변화를 이벤트로 기록하고, 해당 이벤트를 재생하여 현재 상태를 유지. 이를통해 분산 트랜잭션의 일관성 유지 가능
- 트랜잭션
- 분산 트랜잭션의 장점
- 데이터 일관성 보장
- 분산된 여러 데이터소스에 걸쳐 일관된 데이터 상태를 유지할 수 있음. 모든 트랜잭션이 성공적으로 완료되거나 모두 실패하도록 보장
- 확장성
- 여러 시스템이 독립적으로 동작하면서도, 필요한 경우 협력하여 일관된 상태를 유지할 수 있음. 이를 통해 시스템의 확장성을 높일 수 있음
- 신뢰성
- 트랜잭션의 ACID 속성을 분산 환경에서도 유지할 수 있어, 시스템의 신뢰성을 높임
- 복구 가능성
- 트랜잭션 실패 시 롤백 메커니즘을 통해 상태를 복구할 수 있음
- 데이터 일관성 보장
- 분산 트랜잭션의 단점
- 복잡성 증가
- 구현하고 관리하는 것이 복잡함. 여러 시스템간의 트랜잭션 동기화와 데이터 일관성 유지하는 것은 어려운 작업
- 성능 저하
- 2PC와 같은 패턴을 사용할 경우, 트랜잭션의 준비와 커밋 단계에서 지연이 발생해 시스템 성능을 저하시킬 수 있음
- 네트워크 오버헤드
- 여러 시스템 간의 통신이 필요하므로 네트워크 오버헤드가 증가함. 트랜잭션의 처리 속도를 저하시킬 수 있음
- 복구의 어려움
- 트랜잭션 실패 시, 모든 시스템에서 일관된 상태로 롤백하는 것이 어려울 수 있음. 특히, 부분적으로 실패한 트랜잭션을 처리하는 데 어려움이 있을 수 있음
- 복잡성 증가
데이터 일관성 유지 방안 - 이벤트 소싱
- 데이터 상태 변화를 이벤트로 기록하고, 해당 이벤트들을 순차적으로 재생하여 현재 상태를 파악하는 방안
- 데이터 변경 자체가 아닌 변경 이벤트를 저장
- 복잡한 비즈니스 로직을 다루는 시스템에서 데이터 일관성과 추적 가능성을 높이는 데 유용
- 복잡성이 증가할 수 있으므로, 시스템의 요구사항에 따라 신중하게 적용해야 함
- 이벤트 소싱의 주요 개념
- 이벤트
- 데이터의 상태 변화를 나타내는 기록.
- ex) 주문생성, 결제완료, 주문취소 등
- 데이터의 상태 변화를 나타내는 기록.
- 이벤트 스토어
- 이벤트를 저장하는 저장소. 이벤트를 순서대로 저장하는 스토리지. 이벤트의 불변성과 순차성을 보장
- 애그리게이트(Aggregate)
- 관련된 이벤트를 모아 현재 상태를 재현할 수 있는 엔티티. 도메인 모델의 일부분으로, 이벤트를 적용하여 상태를 변화시킴
- 커맨드
- 애그리게이트에 특정 동작을 지시하는 명령. 이벤트를 생성하는 트리거 역할
- 프로젝션
- 이벤트를 읽기 모델로 변환하여 조회 성능을 최적화하는 방식. 이벤트를 기반으로 읽기 전용 DB를 업데이트
- 이벤트
- 이벤트 소싱의 장점
- 데이터 변경 이력 추적
- 모든 상태 변화를 이벤트로 기록하므로, 데이터 변경 이력을 완벽하게 추적할 수 있음. 감사와 디버깅에 유용
- 복구 및 재생
- 이벤트를 재생하여 시스템의 현재 상태를 복구할 수 있음. 데이터 손실이나 시스템 장애 시 유용
- CQRS와의 자연스러운 통합
- 이벤트 소싱은 CQRS와 잘 어울림. 명령과 조회를 분리하여 성능과 확장성을 최적화할 수 있음
- 데이터 변경 이력 추적
- 이벤트 소싱의 단점
- 복잡성 증가
- 시스템 설계와 구현의 복잡성이 증가. 이벤트 모델링과 이벤트 스토어 관리가 필요
- 읽기 성능
- 이벤트를 재생하여 현재 상태를 계산해야 하므로, 읽기 성능이 저하될 수 있음. 이를 해결하기 위해 프로젝션과 CQRS를 활용
- 복잡성 증가
데이터 일관성 유지 방안 - CQRS
- 명령(Command)와 조회(Query)의 책임을 분리하는 소프트웨어 디자인 패턴
- 읽기 작업과 쓰기 작업을 서로 다른 모델로 분리하여, 각 작업에 최적화된 구조를 사용할 수 있도록 함
- CQRS의 주요 개념
- 명령
- 데이터를 변경하는 작업. DB에 쓰기 작업을 수행
- 명령 모델은 데이터의 상태 변경을 담당. 복잡한 비즈니스 로직을 포함할 수 있으며, 데이터 무결성을 보장하기 위해 트랜잭션을 사용
- 조회
- 데이터를 조회하는 작업. DB에 대해 읽기 작업을 수행
- 읽기 전용 DB 혹은 캐시를 사용하여 빠른 응답을 제공. 단순한 데이터 조회를 위한 최적화된 구조를 가질 수 있음
- 명령
- CQRS의 장점
- 성능 향상
- 읽기와 쓰기를 분리하여 각 작업에 최적화된 데이터 저장소와 인프라를 사용할 수 있음. 예를 들어, 조회 성능을 높이기 위해 읽기 전용 DB를 사용하거나, 캐시를 활용할 수 있음
- 확장성
- 읽기와 쓰기를 독립적으로 확장할 수 있음. 예를 들어, 읽기 요청이 많은 경우, 조회 모델을 수평적으로 확장하여 부하를 분산시킬 수 있음
- 유지보수성
- 비즈니스 로직이 명령 모델에 집중되므로, 상태 변경 로직 관리가 쉽고, 읽기 모델은 단순화되어 유지보수하기 용이함
- 데이터 일관성
- CQRS는 이벤트 소싱과 잘 어울림. 이벤트 소싱을 통해 데이터 상태 변경을 이벤트로 기록하고, 이벤트를 재생하여 현재 상태를 유지할 수 있음. 이를 통해 데이터 일관성 보장 가능
- 성능 향상
- CQRS의 단점
- 복잡성 증가
- 시스템 설계와 구현의 복잡성이 증가. 명령 모델과 조회 모델을 각각 설계하고 관리해야 함
- 데이터 동기화
- 명령 모델과 조회 모델 간의 데이터 동기화 필요. 즉, 추가적인 구현과 관리가 필요
- 복잡성 증가
모니터링과 로깅
- 대규모 시스템에서 모니터링과 로깅은 시스템의 안정성과 성능을 유지하는 데 필수적인 역할을 함
- 모니터링과 로깅의 주요 목표
- 시스템 안정성 유지
- 성능 최적화
- 문제 예방 및 대응
모니터링
- App, DB, 캐시 등 각 컴포넌트의 성능을 모니터링
- Prometheus, Grafana 같은 도구 존재
- 시스템의 주요 지표(TPS, 응답 시간, 에러율 등)을 모니터링하고, 이상 징후를 감지하면 알림을 받게 환경 구성 가능
- 모니터링을 활용하면 시스템의 상태를 실시간으로 파악하고, 문제 발생 시 빠르게 대응 가능. 또한, 모니터링 데이터를 기반으로 시스템 성능을 분석하고, 최적화할 수 있음
- 모니터링의 장점
- 실시간 상태 파악
- 시스템의 주요 지표를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있음. 이를 통해 시스템의 현재 상태 파악하고, 이상 징후를 빠르게 감지할 수 있음
- 자동 알림
- 특정 임계치를 초과하는 경우 자동으로 알림을 받을 수 있게 설정 가능. 이를 통해 잠재적인 문제를 조기에 발견하고 대응할 수 있음
- 성능 분석
- 데이터를 기반으로 시스템의 성능을 분석할 수 있음.
- 병목 지점 파악
- 시스템의 병목 지점을 파악하고, 이를 최적화하여 전체 성능을 향상시킬 수 있음
- 사전 예방
- 실시간 모니터링을 통해 문제가 발생하기 전에 예방 조치를 취할 수 있음.
- 신속한 대응
- 문제가 발생했을 때 빠르게 감지하고 대응할 수 있어, 시스템의 다운타임 최소화 가능
- 실시간 상태 파악
로깅
- App의 주요 이벤트를 로깅하여 문제 발생 시 원인을 추적할 수 있음
- 로그는 Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana(ELK 스택) 등을 사용하여 수집, 저장, 분석할 수 있음
- 시스템의 모든 중요한 이벤트를 기록하므로, 문제 발생 시 정확한 원인을 파악하는 데 큰 도움이 됨
- 로깅의 장점
- 이벤트 추적
- 시스템에서 발생하는 모든 중요한 이벤트를 기록해서 문제가 발생했을 때 원인을 추적하고 분석하는 데 도움이 됨
- 디버깅 및 오류 해결
- 로그 분석을 통해 오류의 원인을 파악하고, 이를 기반으로 문제 해결 가능
- 패턴 분석
- 데이터를 분석하여 사용자의 행동 패턴이나 시스템의 성능 패턴을 이해할 수 있음
- 장기적 최적화
- 데이터를 장기적으로 분석하여 시스템의 성능 저하 원인을 찾아내고, 지속적인 최적화를 진행할 수 있음
- 원인 분석
- 문제 발생 후 로그를 분석하여 정확한 원인을 파악할 수 있음. 재발 방지에 도움이 됨
- 법적 및 규제 요구 사항 준수
- 많은 산업에서는 로그 데이터를 보관하고 분석하는 것이 법적 및 규제 요구 사항을 준수하는 데 필수적임. 이는 감사 및 규제 대응에 중요한 역할을 함
- 이벤트 추적
테스트와 배포
- 대규모 시스템에서 테스트와 배포는 중요한 요소
- 시스템이 정상적으로 동작하는 지 확인하고, 문제 발생 시 빠르게 대응할 수 있어야 함
테스트
- 단위 테스트
- 시스템의 개별 구성 요소를 테스트하여 각 부분이 예상대로 동작하는 지 확인
- JUnit, TestNG와 같은 도구를 사용하여 자동화된 단위 테스트를 작성하고 실행
- 개발 초기 단계에서 발생할 수 있는 결함을 조기에 발견하고 수정하는 데 유용
- 통합 테스트
- 여러 구성 요소와 함께 동작하는지를 테스트함. 이는 개별 구성 요소들이 올바르게 상호 작용하는지를 검증
- Spring Boot에서는 @SpringBootTest 어노테이션을 사용하여 통합 테스트를 작성할 수 있음
- 통합 테스트는 시스템의 다양한 부분들이 함께 올바르게 동작하는지를 확인하여, 인터페이스간 문제를 발견하는 데 유용
- 부하 테스트
- 시스템이 높은 트래픽 상황에도 안정적으로 동작하는지를 테스트
- Apache JMeter와 같은 도구를 사용하여 다양한 부하 시나리오를 설정하고 테스트를 수행
- 시스템의 성능 한계를 파악하고, 병목 지점을 찾아 최적화할 수 있음
- 회귀 테스트
- 새로운 코드 변경이 기존 기능에 영향을 미치지 않는지 확인
- 기존 테스트 케이스를 자동화하여 주기적으로 실행함으로써, 코드 변경으로 인한 결함을 방지할 수 있음
- 지속적인 코드 변경에도 시스템의 안정성을 유지하는 데 중요함
- 사용자 수용 테스트
- 실제 사용자 환경에서 시스템을 테스트하여, 사용자가 요구하는 기능이 모두 제대로 동작하는 지 확인
- 사용자 피드백을 반영하여 시스템을 최종 조정하여, 배포 준비를 완료
- 시스템이 실제 운영 환경에서 기대대로 동작하는지 확인하는 단계
배포
- 지속적인 통합
- 개발자가 변경한 코드를 자주, 자동으로 빌드하고 테스트하여, 코드 변경 시점에서 발생할 수 있는 문제를 조기에 발견하고 해결함
- Jenkins, GitLab CI 등과 같은 도구를 사용하여 CI 파이프라인 설정
- 코드 통합을 빠르고 효율적으로 수행하여 개발 주기를 단축시키고, 코드 품질을 높임
- 지속적인 배포
- CI 파이프라인을 통해 검증된 코드를 자동으로 Prod 환경에 배포
- Argo CD와 같은 도구를 사용하여 CD 파이프라인을 설정
- CD는 코드 변경 사항을 빠르고 안전하게 Prod 환경에 적용하여, 새로운 기능을 신속하게 제공 가능
- Canary 배포
- 새 버전을 전체 시스템에 배포하기 전에, 일부 사용자에게만 배포하여 문제 없는지 확인
- 문제가 발생할 경우 롤백
- 리스크를 최소화 하며, 새로운 기능을 단계적으로 도입할 수 있는 방법
- 블루-그린 배포
- 두 개의 환경(블루, 그린)을 사용하여 하나는 현재 운영 중인 환경이고, 다른 하나는 새로운 버전을 배포하는 환경으로 사용
- 새 버전을 그린에 배포한 후, 모든 트래픽을 그린 환경으로 전환. 문제가 발생하면 블루 환경으로 빠르게 롤백 가능
- 블루-그린 배포는 무중단 배포를 가능하게 하며, 배포 실패 시 신속한 복구를 제공
- 롤링 배포
- 새로운 버전을 점진적으로 배포하여, 각 서버를 순차적으로 업데이트
- 시스템 가동 시간을 유지하며 점진적으로 새로운 버전 도입 가능
- 대규모 시스템에서 무중단 배포를 구현하는 데 유용
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ란
- RabbitMQ는 메시지 브로커. 데이터(Message)를 송신자(Producer)로부터 수신자(Consumer)에게 전달하는 중간 매개체 역할
- 메시지를 큐(Queue)에 저장하고, 필요할 때 적절한 수신자에게 전달
RabbitMQ의 역할
- 비동기 처리 : 데이터를 비동기적으로 처리하여 시스템의 응답성을 높임
- 부하 분산 : 여러 소비자에게 메시지를 분산시켜 시스템의 부하를 균형있게 분산함
- 내결함성 : 메시지를 안전하게 저장하여 시스템 장애 시 데이터 손실을 방지
RabbitMQ의 장단점
- 장점
- 신뢰성
- 메시지 지속성 : 메시지를 디스크에 저장하여 시스템 장애 발생 시에도 메시지가 손실되지 않도록 함
- 확인 메커니즘 : 메시지가 성공적으로 소비자에게 전달되었는지 확인하는 ACK(Acknowledgment)메터니즘 지원
- 유연성
- 다양한 메시지 패턴 : 여러가지 메시지 전달 패턴(단일 소비자, 다중 소비자, 라운드 로빈, 팬아웃, 주제 기반 등)을 지원
- 프로토콜 지원 : 기본적으로 AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)를 사용하지만, STOMP, MQTT등 다양한 프로토콜 지원
- 확장성
- 클러스터링 : RabbitMQ는 클러스터링을 통해 여러 노드로 구성된 환경에서 높은 가용성과 부하 분산을 제공
- 분산 아키텍처 : 페더레이션(Federation) 및 미러링된 노드(Mirrored Nodes)를 통해 분산된 메시징 시스템을 구축할 수 있음
- 관리 및 모니터링
- 관리 인터페이스 : 웹 기반 관리 인터페이스를 통해 큐, 익스체인지, 바인딩 등을 쉽게 관리할 수 있음
- 플러그인 시스템 : 다양한 플러그인을 통해 기능을 확장할 수 있음
- ex) 관리 플러그인, 모니터링 플러그인 등
- 성능
- 높은 처리량 : 적절히 구성된 RabbitMQ는 높은 메시지 처리량을 제공하여 대규모 App에서도 효과적으로 사용할 수 있음
- 신뢰성
- 단점
- 설정 및 운영 복잡성
- 복잡한 설정 : 초기 설정이 다소 복잡할 수 있으며, 클러스터링 및 분산 환경에서는 더욱 많은 설정이 필요
- 운영 관리 : 대규모 환경에서 RabbitMQ를 운영하고 관리하는 데 있어서 추가적인 노력이 필요함
- 성능 문제
- 메시지 브로커 오버헤드 : 모든 메시지를 중앙 브로커를 통해 전달하기 때문에, 높은 트래픽 상황에서는 브로커의 오버헤드가 발생할 수 있음
- 대규모 메시지 처리 : 대규모의 메시지를 처리할 때 성능 저하가 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 경우 적절한 클러스터링 및 최적화 필요
- 운영 비용
- 리소스 소비 : RabbitMQ는 메모리와 CPU 자원을 많이 소비할 수 있어, 충분한 리소스를 제공해야 원활하게 운영될 수 있음
- 모니터링 및 유지보수 : 지속적인 모니터링과 유지보수가 필요하며, 이를 위해 인력과 비용이 발생할 수 있음
- 제한된 메시지 크기
- 메시지 크기 제한 : RabbitMQ는 매우 큰 메시지 처리에 제한이 있을 수 있으며, 대용량 파일 전송에는 적합하지 않을 수 있음
- 러닝 커브
- 학습 필요성 : RabbitMQ의 개념과 설정을 이해하는 데 시간이 걸릴 수 있음
- 설정 및 운영 복잡성
RabbitMQ의 기본 구성 요소
- 메시지(Message)
- 메시지는 RabbitMQ를 통해 전달되는 데이터 단위.
- ex) 사용자 등록 정보, 주문 내역 등
- 메시지는 RabbitMQ를 통해 전달되는 데이터 단위.
- 프로듀서(Producer)
- 메시지를 생성하고 RabbitMQ에 보내는 역할.
- ex) Web App이 사용자 등록 정보를 RabbitMQ에 보내는 경우
- 메시지를 생성하고 RabbitMQ에 보내는 역할.
- 큐(Queue)
- 메시지를 저장하는 장소. 메시지는 큐에 저장되었다가 소비자에게 전달됨
- 컨슈머(Consumer)
- 큐에서 메시지를 가져와 처리하는 역할.
- ex) 이메일 발송 서비스가 큐에서 사용자 등록 정보를 가져와 환영 이메일을 보내는 경우
- 큐에서 메시지를 가져와 처리하는 역할.
- 익스체인지(Exchange)
- 메시지를 적절한 큐로 라우팅하는 역할. 프로듀서는 메시지를 직접 큐에 보내지 않고, 익스체인지에 보내며, 익스체인지는 적절한 큐로 메시지를 전달
RabbitMQ와 AMQP
- RabbitMQ는 AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)를 사용
- AMQP는 메시지 브로커를 위한 프로토콜. 메시지의 생성, 전송 큐잉, 라우팅 등을 표준화하여 메시지브로커가 상호 운용될 수 있게 함
AMQP의 주요 개념
- 메시지 : 데이터 전송 단위
- 큐 : 메시지를 저장하고 전달하는 구조
- 익스체인지 : 메시지를 큐로 라우팅하는 역할
- 바인딩 : 익스체인지와 큐를 연결하는 설정. 바인딩을 통해 메시지가 어느 큐로 전달될지 정의
Exchange 유형
- 다양한 방식으로 메시지를 라우팅할 수 있으며, 주로 메시지의 라우팅 키와 바인딩 키 또는 패턴을 기반으로 작동
- Direct Exchange
- 라우팅 키가 정확히 일치하는 큐로 메시지를 전달
- Topic Exchange
- 라우팅 키의 패턴을 사용하여 메시지를 라우팅. 패턴에는 와일드카드와 #(0개 이상의 단어) 가 사용됨
- ex) 라우팅 키가 quick.orange.rabbit인 메시지는 바인딩 키가 .orange.인 큐로 전달됨
- 라우팅 키의 패턴을 사용하여 메시지를 라우팅. 패턴에는 와일드카드와 #(0개 이상의 단어) 가 사용됨
- Fanout Exchange
- 라우팅 키를 무시하고 교환기에 바인딩된 모든 큐로 메시지를 브로드캐스트함
- 모든 바인딩된 큐로 메시지가 전달됨
- Headers Exchange
- 라우팅 키 대신 메시지의 헤더를 기반으로 메시지를 라우팅
- 헤더 값과 바인딩된 헤더 값이 일치하는 큐로 메시지를 전달함
RabbitMQ 사용 실습
Market 서비스를 만들어보는 실습
Order(Producer) - Product(Consumer) 2개, Payment(Consumer) 1개
-
RabbitMQ 설치 ( 컨테이너 )
docker run -d --name rabbitmq -p5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 --restart=unless-stopped rabbitmq:management -
Producer 프로젝트 생성(Order)
- Order Project
- 의존성
- Spring Web
- Lombok
- Spring for RabbitMQ
- application.yml
spring: application: name: order rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 stream: username: guest message: exchange: market queue: product : market.product payment : market.payment - OrderApplicationQueueConfig
@Configuration public class OrderApplicationQueueConfig { @Value("${message.exchange}") private String exchange; @Value("${message.queue.product}") private String queueProduct; @Value("${message.queue.payment}") private String queuePayment; @Bean public TopicExchange exchange() { return new TopicExchange(exchange); } @Bean public Queue queueProduct() { return new Queue(queueProduct); } @Bean public Queue queuePayment() { return new Queue(queuePayment); } @Bean public Binding bindingProduct() { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueProduct()).to(exchange()).with(queueProduct); } @Bean public Binding bindingPayment() { return BindingBuilder.bind(queuePayment()).to(exchange()).with(queuePayment); } } - OrderController
@RestController @RequiredArgsConstructor public class OrderController { private final OrderService orderService; @GetMapping("/order/{id}") public String order(@PathVariable String id) { orderService.createOrder(id); return "Order complete"; } } - OrderService
@Service @RequiredArgsConstructor public class OrderService { @Value("${message.queue.product}") private String productQueue; @Value("${message.queue.payment}") private String paymentQueue; private final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; public void createOrder(String orderId) { rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(productQueue, orderId); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(paymentQueue, orderId); } }
- 의존성
- Order Project
-
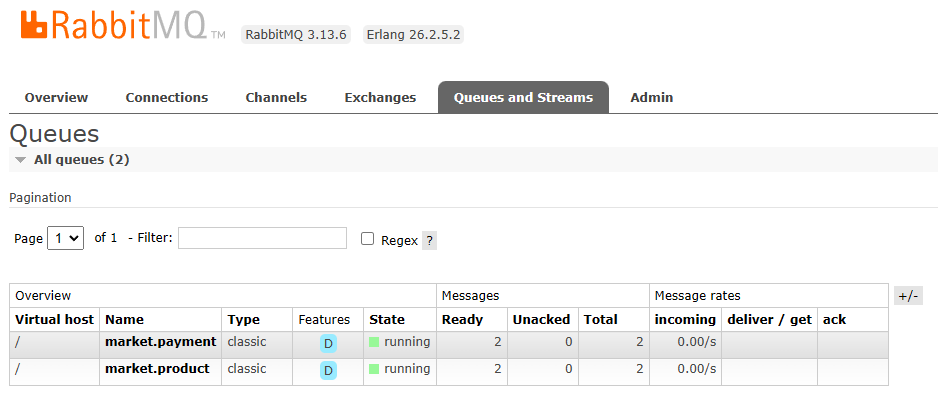
Producer 실행 후 확인
- localhost:8080/order/1 호출
- localhost:15672로 RabbitMQ 접속 ( ID : guest / PW : guest )
- 결과
-
Consumer 프로젝트 생성
- Payment Project
- 의존성
- Lombok
- Spring for RabbitMQ
- application.yml
spring: application: name: payment rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 stream: username: guest password: guest message: queue: payment : market.payment - PaymentEndpoint
@Slf4j @Component public class PaymentEndpoint { @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String appName; @RabbitListener(queues = "${message.queue.payment}") public void receiveMessage(String orderId) { log.info("receive orderId:{}, appName : {}", orderId, appName); } }
- 의존성
- Product Project
- 의존성
- Lombok
- Spring for RabbitMQ
- application.yml
spring: application: name: product rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 stream: username: guest password: guest message: queue: product : market.product - ProductEndpoint
@Slf4j @Component public class ProductEndpoint { @Value("${spring.application.name}") private String appName; @RabbitListener(queues = "${message.queue.product}") public void receiveMessage(String orderId) { log.info("receive orderId:{}, appName : {}", orderId, appName); } }
- 의존성
- Payment Project
-
전체 실행 후 확인
- localhost:8080/order/1 호출
- Payment Project
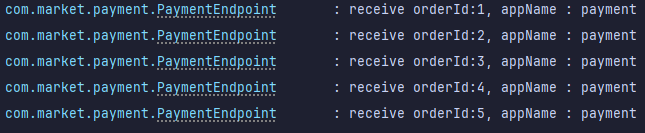
- Product Project 1
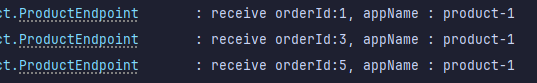
- Product Project 2