1238. Contact
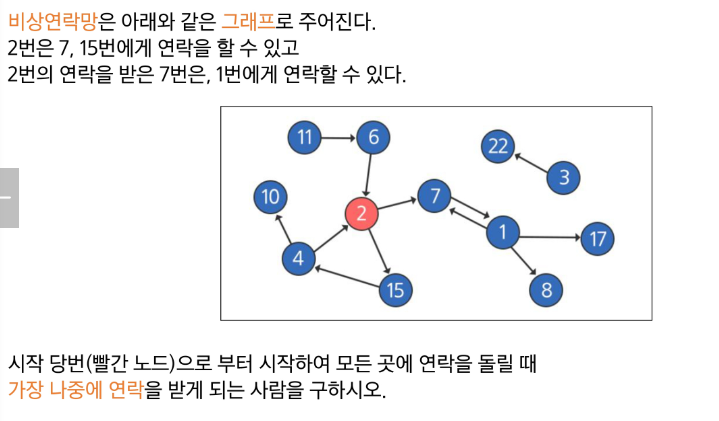
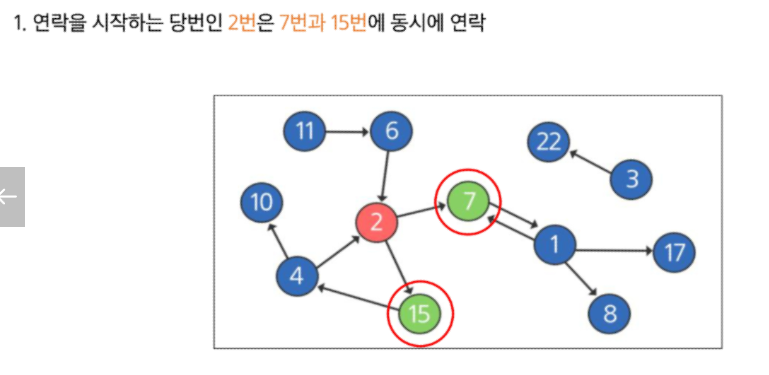
한번 실행 → 노드에서 연락할 수 있는 다른 노드가 동시에 연락 (BFS)
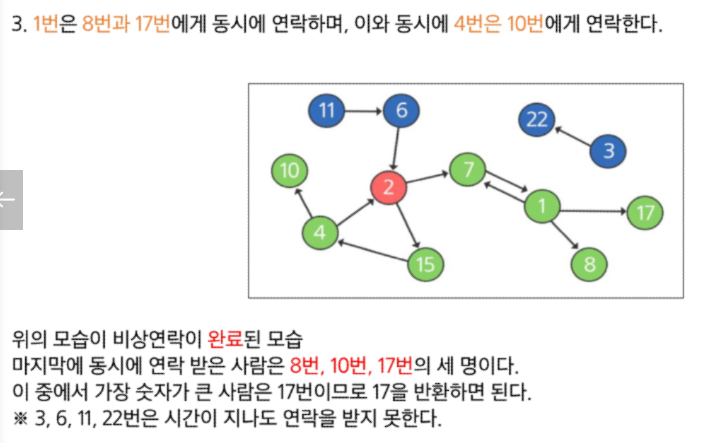
-
N번 만에 해당 노드를 탐색했다. (level, depth)
-
마지막 level에서 숫자가 가장 큰 노드를 골라야 함
-
flood fill
시간 복잡도, 공간 복잡도 계산
BFS 시간 복잡도
- 계산하는 방법 : 얼마나 방문할 수 있을까?
→ 노드의 수(V)가 최대 100개
→ 간선의 수 (E) = 0 (V+E) (인접 리스트 기준)
def bfs(start):
q = [start]
visited = [0] * 101
visited[start] = 1
max_number = start # 가장 깊은 depth의 가장 큰 수
max_depth = 1 # 마지막에 저장한 위치 저장 (가장 깊은 depth)
while q:
now = q.pop(0)
# 갈 수 있는 곳들
for to in graph[now]:
# 이미 방문했다면 pass
if visited[to]:
continue
# 현재 방문 = 이전 방문 + 1 번만에 왔다!
visited[to] = visited[now] + 1
# depth가 더 깊어졌네? ==> max_number 초기화
# depth는 같은데 숫자가 더 크네? ==> 초기화
if max_depth < visited[to] or (max_depth == visited[to] and max_number < to):
max_depth = visited[to]
max_number = to
q.append(to)
return max_number
for tc in range(1, 11):
N, start = map(int, input().split()) # 노드 수와 스타트 지점
input_graph = list(map(int, input().split()))
graph = [[] for _ in range(101)]
for i in range(0, N, 2):
s = input_graph[i]
e = input_graph[i+1]
graph[s].append(e)
r = bfs(start)
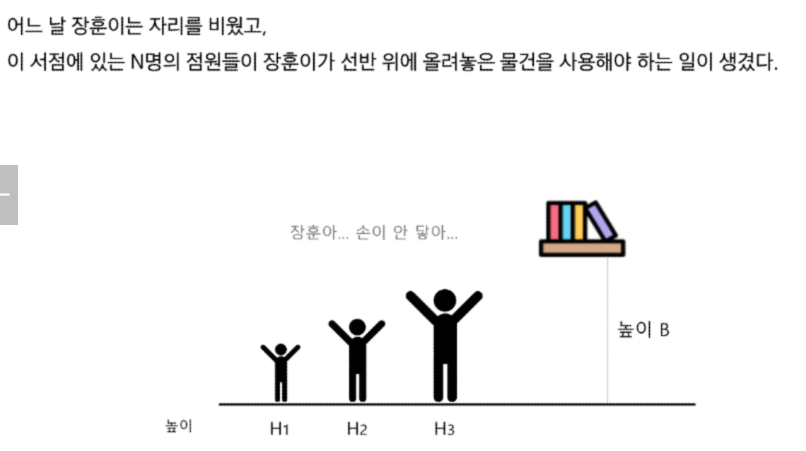
print(f'#{tc} {r}')장훈이의 높은 선반
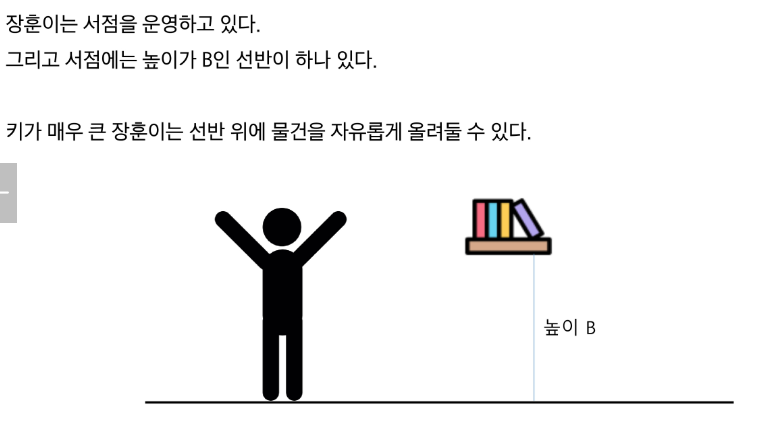
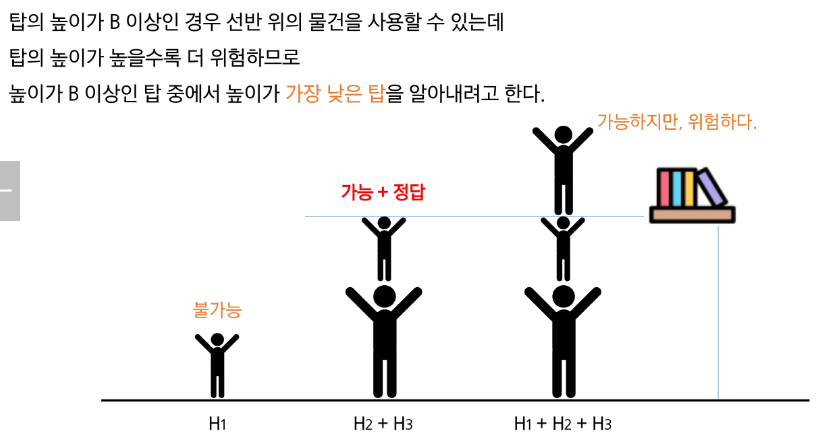
선반 높이 B
B 보다 작아서, 탑을 쌓을거야!
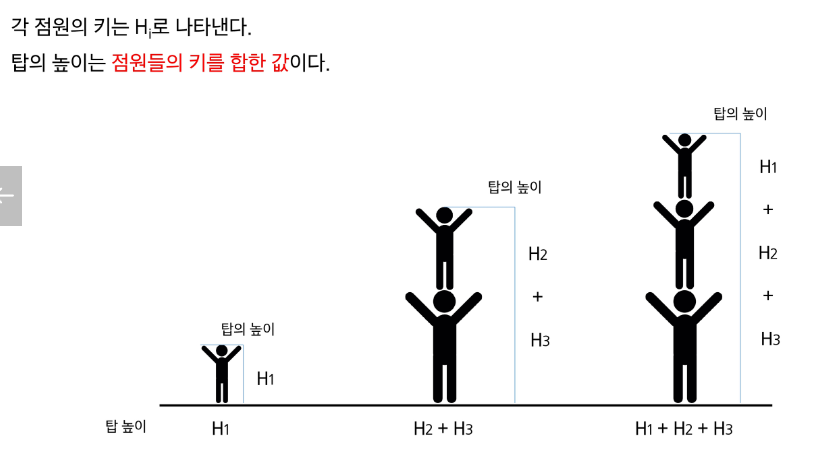
탑의 높이 : 점원들의 키(H)의 합
경우의 수를 모두 보면 될까??
def dfs(cnt, sum_height):
global ans
# 기저조건
# 1. 키의 합이 B 이상이면 종료
# → 현재까지 쌓은 탑의 높이
if sum_height >= B:
# 제일 높이가 낮은 탑이 정답
# 최소 탑의 높이는 재귀호출함수들이 '동시에' 사용함 → 전역변수로 사용
ans = min(ans, sum_height)
return
# 2. 모든 점원이 탑을 쌓는데 고려가 되었다면
# → 현재까지 쌓은 점원의 수
if cnt == N:
return
# 재귀 호출
# 쌓는다
dfs(cnt+1, sum_height + arr[cnt])
# 안쌓는다
dfs(cnt+1, sum_height)
T = int(input())
for tc in range(1, T+1):
N, B = map(int, input().split())
arr = list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = int(1e9)
dfs(0, 0)
print(f'#{tc} {abs(ans - B)}')격자판의 숫자 이어 붙이기

재귀함수 활용!
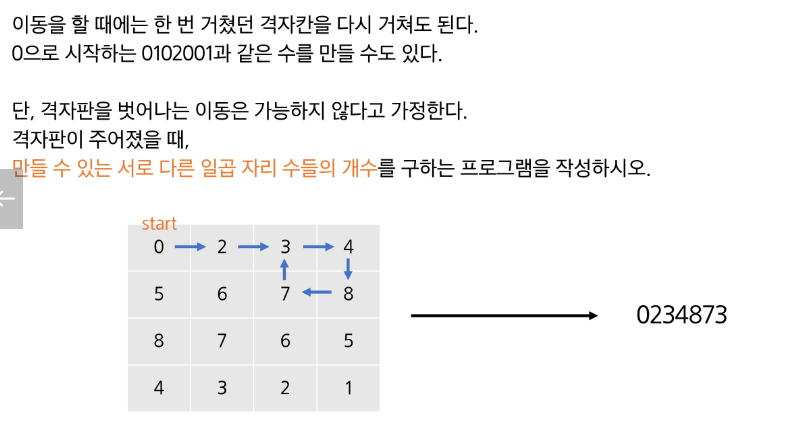
만들 수 있는 서로 다른 일곱 자리 수들의 개수
-
7자리 숫자 생성
-
중복 제거 (set, dictionary 활용)
dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
def dfs(y, x, path):
# 기저 조건 : 7자리면 끝
if len(path) == 7:
# 현재까지의 경로를 저장
result.add(path)
return
for i in range(4):
new_y = y + dy[i]
new_x = x + dx[i]
# 범위 밖으로 넘어가면 pass
if new_y < 0 or new_y >= 4 or new_x < 0 or new_x >= 4:
continue
dfs(new_y, new_x, path + maps[new_y][new_x])
T = int(input())
for test_case in range(1, T + 1):
# 격자판 저장
# 갈 때 마다 경로를 더하기 위해서 문자열로 저장
maps = [input().split() for _ in range(4)]
# 중복을 제거하기 위해 set 사용
result = set()
# 시작 지점
for i in range(4):
for j in range(4):
dfs(i, j, maps[i][j])
print(f'#{test_case} {len(result)}')수영장
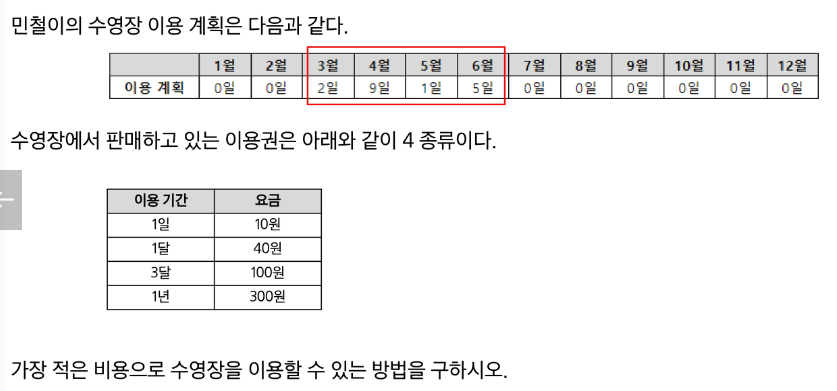
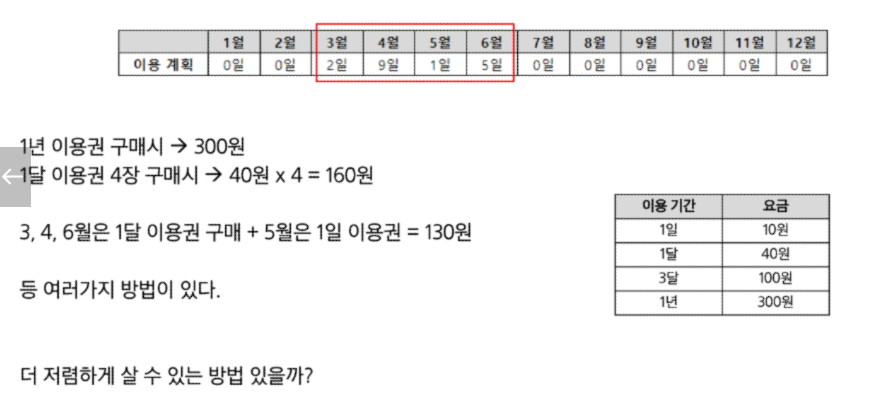
def dfs(month, sum_cost):
global ans
# 기저조건
# 1. 12월까지 다 봤네? 종료
if month > 12:
# 최소 비용
ans = min(ans, sum_cost)
return
# 2. 이미 최솟값을 넘어갔네? 종료
if sum_cost > ans:
return
# 모두 1일권으로 구매
dfs(month + 1, sum_cost + (days[month] * cost[0]))
# 1달권 구매
dfs(month + 1, sum_cost + cost[1])
# 3달권 구매
dfs(month + 3, sum_cost + cost[2])
# 1년권 구매
dfs(month + 12, sum_cost + cost[3])
T = int(input())
for tc in range(T):
cost = list(map(int, input().split()))
# 1부터 쓸래 ( 맨 앞에 0을 넣음)
days = [0] + list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = int(1e9)
dfs(1, 0)
print(f'#{tc+1} {ans}')
DP로 풀이
# 이 문제가 왜 DP로도 해결이 가능할까?
# 1. 작은 문제로 분할할 수 있어야 한다.
# - 전체의 합 = 각 달까지의 최소들이 쌓여서 완성
# - 각 달까지의 최소 비용 문제로 분할 가능
# 2. 뒤의 결과를 구할 때, 앞에서 구했던 결과가 바뀌면 안된다.
T = int(input())
for tc in range(T):
cost = list(map(int, input().split()))
days = [0] + list(map(int, input().split()))
ans = int(1e9)
# DP 배열
plans = [0] * 13
# 1~12월까지 반복
for i in range(1, 13):
# 현재 달의 최소 비용 계산
# 이전 달 + 1일권 구입 / 이전 달 + 1달권 구입 /3달전 + 3달권 구입 그 중에서 최소
plans[i] = min(plans[i-1] + (days[i] * cost[0]), plans[i-1] + cost[1])
plans[i] = min(plans[i], plans[i-3] + cost[2])
if i >= 3:
plans[i] = min(plans[i], plans[i-3] + cost[2])
# 12월까지의 계산 결과 or 1년권
min_cost = min(plans[12], cost[3])
print(f'#{tc+1} {min_cost}')