Subquery: 하나의 쿼리 안에 또다른 쿼리가 있는 것을 의미
쿼리문 안에 들어가있는 쿼리문
가장 안에 있는 쿼리부터 실행함
-
kakaopay로 결제한 유저들의 정보 보기(users + orders 테이블)
1) inner join으로 보기
select u.user_id, u.name, u.email from users u
inner join orders o on u.user_id = o.user_id
where o.payment_method = 'kakaopay'2) subquery(Where에 들어가는 Subquery)
select user_id, name, email from users u
where user_id in (
select user_id from orders o
where payment_method = 'kakaopay'
)Where에 들어가는 Subquery
- 전체 유저의 포인트의 평균보다 큰 유저들의 데이터 추출
select * from point_users pu
where point > (
select round(avg(point),1)
from point_users pu
)- 이씨 성을 가진 유저의 포인트의 평균보다 큰 유저들의 데이터 추출
select * from point_users pu
where point > (
select avg(point) from point_users pu
inner join users u on pu.user_id = u.user_id
where u.name = '이**'
)Select에 들어가는 Subquery
- user_id별 평균 like 구하기
select c.checkin_id,
c.user_id,
c.likes,
(
select avg(likes) from checkins
where user_id = c.user_id
) as avg_likes_user
from checkins cselect가 될 때마다 하나하나씩 다 subquery가 실행됨
출력화면

- checkins 테이블에 course_id별 평균 likes수 필드 우측에 붙여보기
select c.checkin_id, c.course_id, c.user_id, c.likes,
(
select avg(likes) from checkins
where course_id = c.course_id
) as course_avg
from checkins c- checkins 테이블에 과목명별 평균 likes수 필드 우측에 붙여보기
select c.checkin_id, c2.title, c.user_id, c.likes,
(
select round(avg(likes),1) from checkins
where course_id = c.course_id
) as course_avg
from checkins c
inner join courses c2 on c.course_id = c2.course_id From에 들어가는 Subquery
-
유저별 포인트와 좋아요 평균값 구하기
1) 유저 별 좋아요 평균
select user_id, round(avg(likes),1) as avg_likes from checkins
group by user_id 2) 유저 별 포인트
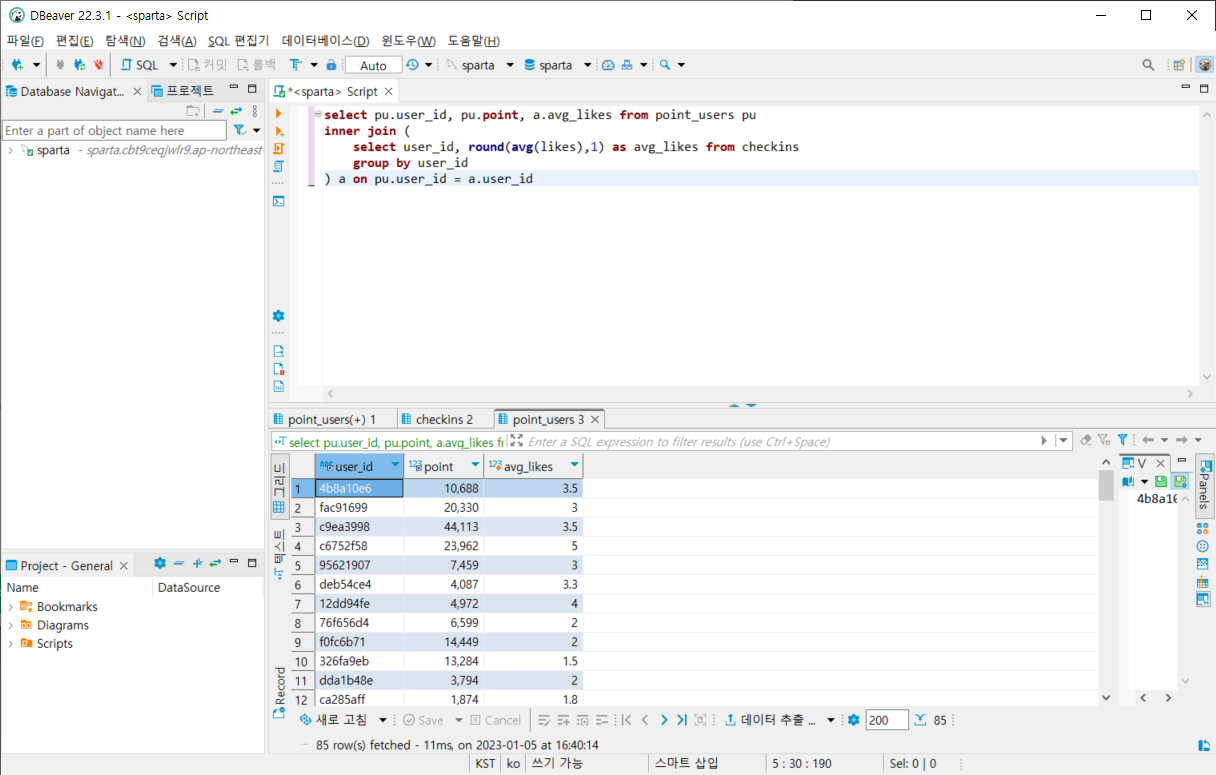
select pu.user_id, pu.point, a.avg_likes from point_users pu1)에서 구한 유저별 좋아요 평균(a라고 칭함)을 inner join 하면서 유저별 포인트, 좋아요 평균을 확인할 수 있다.
select pu.user_id, pu.point, a.avg_likes from point_users pu
inner join (
select user_id, round(avg(likes),1) as avg_likes from checkins
group by user_id
) a on pu.user_id = a.user_id출력화면
- course_id별 유저의 체크인 개수
select course_id, count(distinct(user_id)) as cnt_checkins from checkins
group by course_id- course_id별 인원
select course_id, count(*) as cnt_total from orders
group by course_id- course_id별 like 개수에 전체 인원을 붙이기
select a.course_id, b.cnt_checkins, a.cnt_total from
(
select course_id, count(*) as cnt_total from orders
group by course_id
) a
inner join (
select course_id, count(distinct(user_id)) as cnt_checkins from checkins
group by course_id
) b
on a.course_id = b.course_id- 비율 추가
select a.course_id, b.cnt_checkins, a.cnt_total, (b.cnt_checkins/a.cnt_total) as ratio from
(
select course_id, count(*) as cnt_total from orders
group by course_id
) a
inner join (
select course_id, count(distinct(user_id)) as cnt_checkins from checkins
group by course_id
) b
on a.course_id = b.course_id- 코스 제목 추가
select c.title,
a.cnt_checkins,
b.cnt_total,
(a.cnt_checkins/b.cnt_total) as ratio
from
(
select course_id, count(distinct(user_id)) as cnt_checkins from checkins
group by course_id
) a
inner join
(
select course_id, count(*) as cnt_total from orders
group by course_id
) b on a.course_id = b.course_id
inner join courses c on a.course_id = c.course_idwith절
위의 6번 예제를 with절 이용해보자
with table1 as (
select course_id, count(distinct(user_id)) as cnt_checkins from checkins
group by course_id
), table2 as (
select course_id, count(*) as cnt_total from orders
group by course_id
)
select c.title,
a.cnt_checkins,
b.cnt_total,
(a.cnt_checkins/b.cnt_total) as ratio
from table1 a
inner join table2 b on a.course_id = b.course_id
inner join courses c on a.course_id = c.course_id실전 SQL 문법
- 문자열 데이터 활용
1) 쪼개기
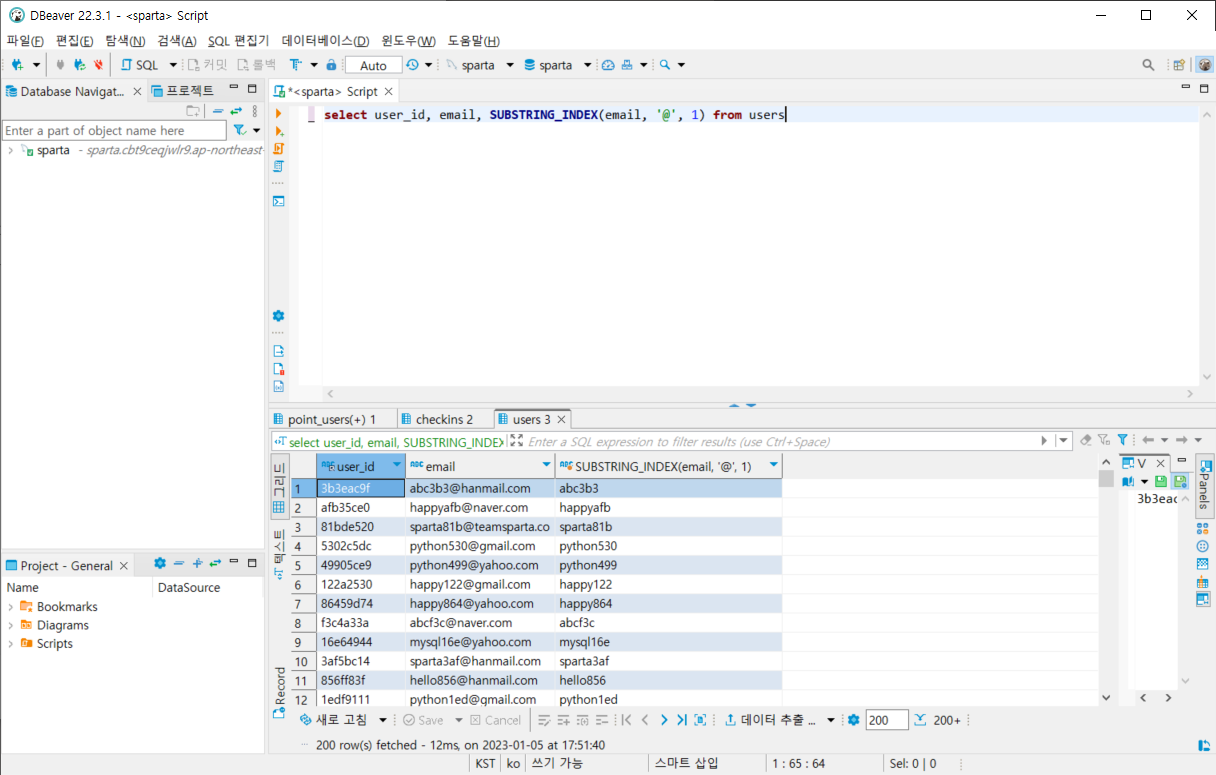
이메일에서 아이디만 가져오기
select user_id, email, SUBSTRING_INDEX(email, '@', 1) from users출력화면
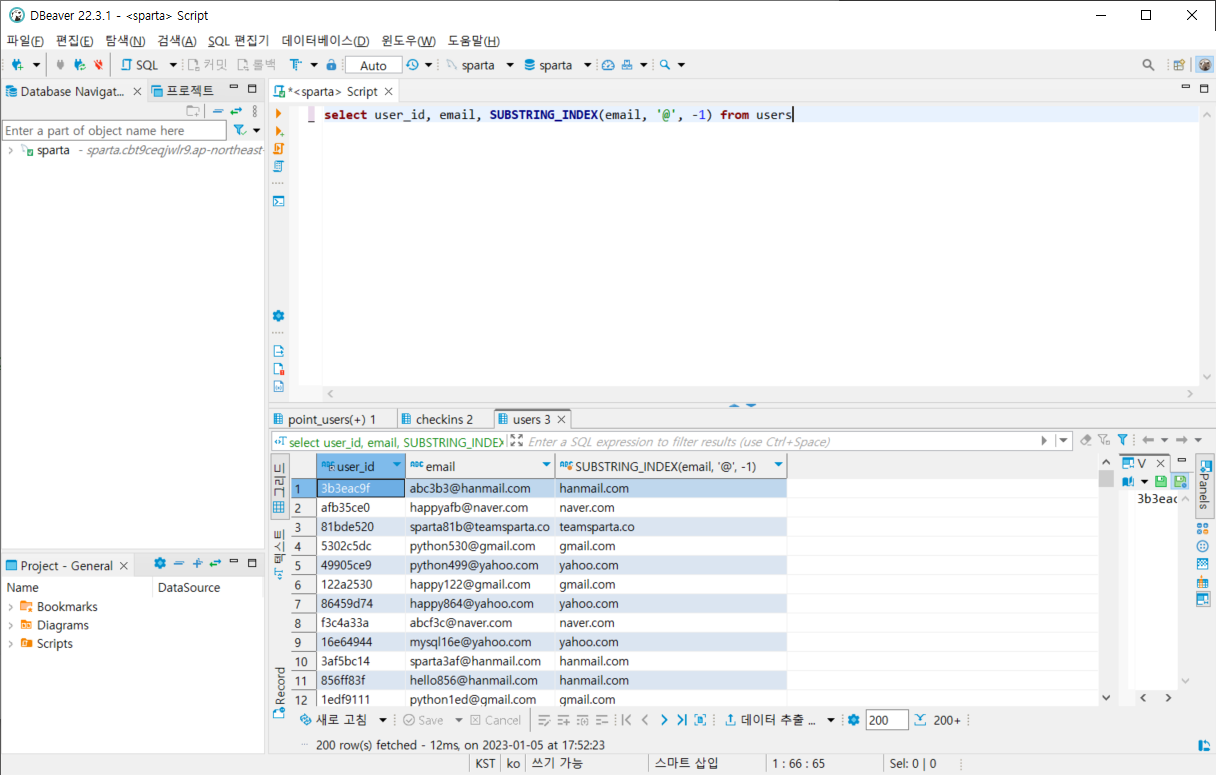
이메일에서 도메인만 가져오기
select user_id, email, SUBSTRING_INDEX(email, '@', -1) from users출력화면
2) 문자열 일부 출력
일자만 출력
substring(문자열, 시작포인트, 시작포인트부터 출력되는 문자 개수)
select order_no, created_at, substring(created_at,1,10) as date from orders출력화면
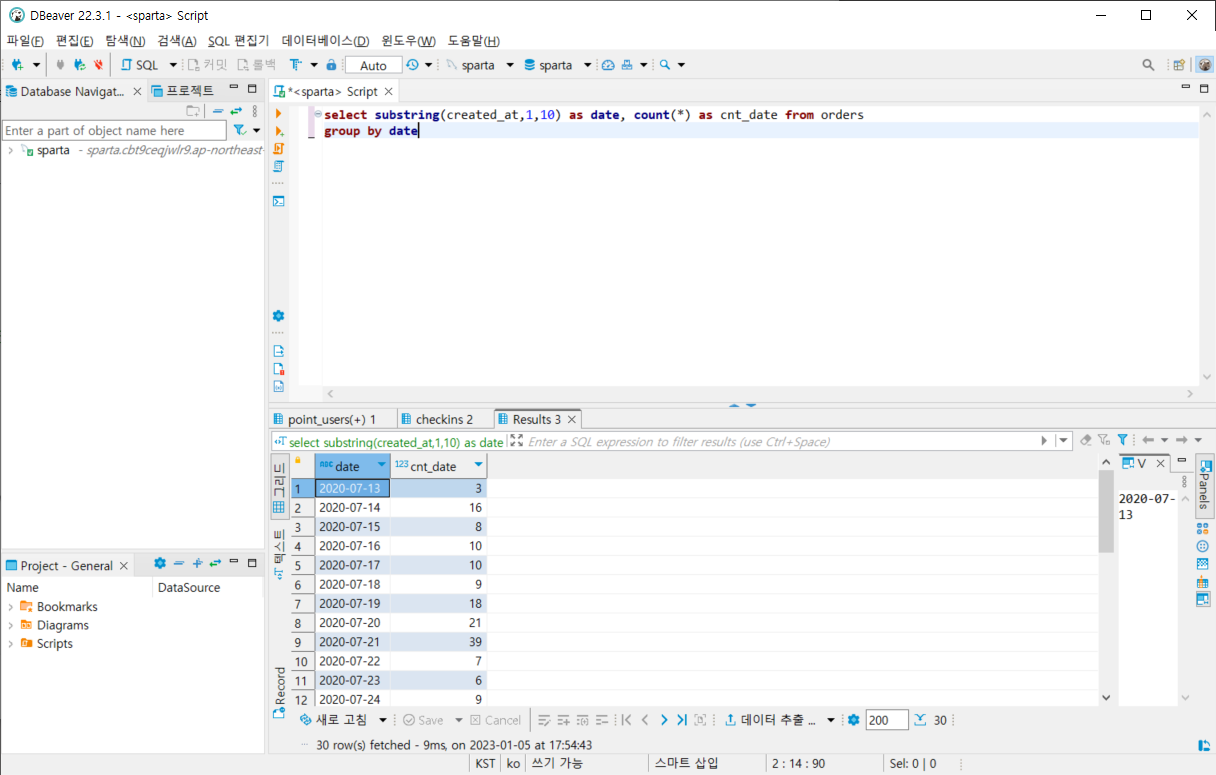
3) 일별로 주문 건수 출력
select substring(created_at,1,10) as date, count(*) as cnt_date from orders
group by date출력화면
- CASE문
경우에 따라 원하는 값을 새 필드에 출력
포인트 보유액에 따라 다르게 표시
select pu.point_user_id, pu.point,
(case when pu.point > 10000 then '잘 하고 있어요!'
else '조금 더 달려주세요!' end) as msg
from point_users pu;출력화면

with table1 as (
select pu.user_id, pu.point,
(case when pu.point > 10000 then '1만 이상'
when pu.point > 5000 then '5천 이상'
else '5천 미만' end) as lv
from point_users pu
)
select a.lv, count(*) as cnt from table1 a
group by a.lvSQL문법 복습
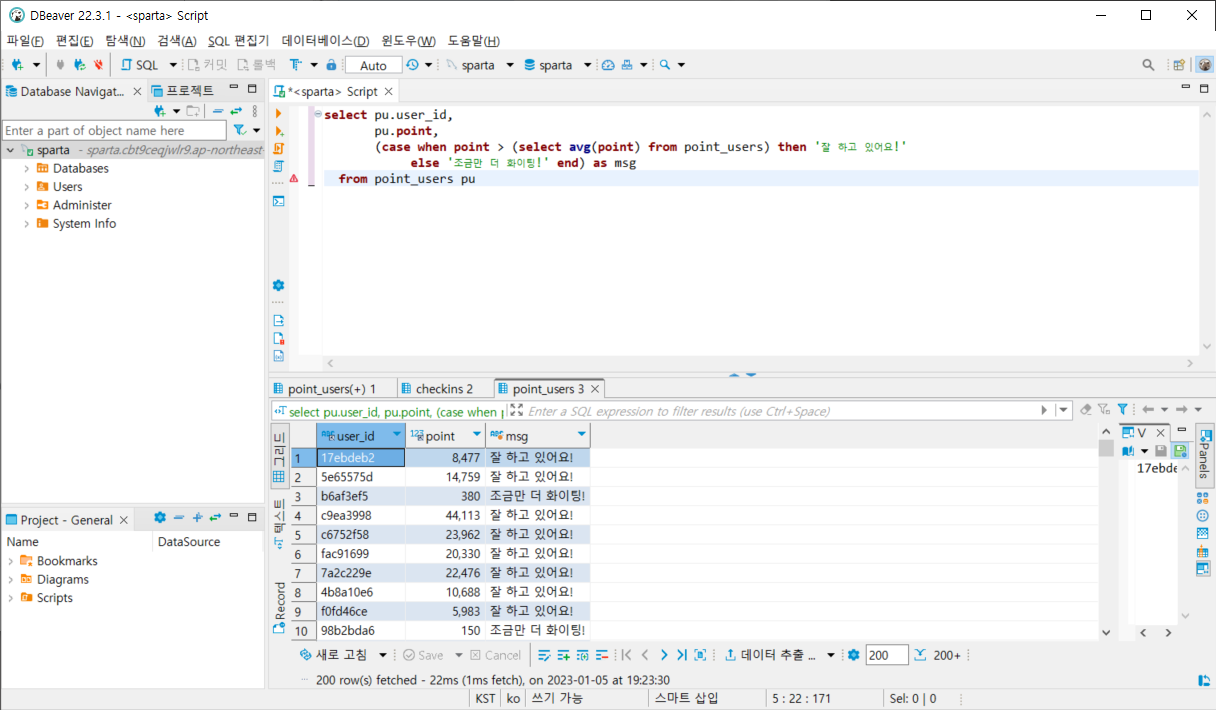
평균대비 포인트에 따라 다르게 출력
select pu.user_id,
pu.point,
(case when point > (select avg(point) from point_users) then '잘 하고 있어요!'
else '조금만 더 화이팅!' end) as msg
from point_users pu출력화면