백준 2304 java : 구현
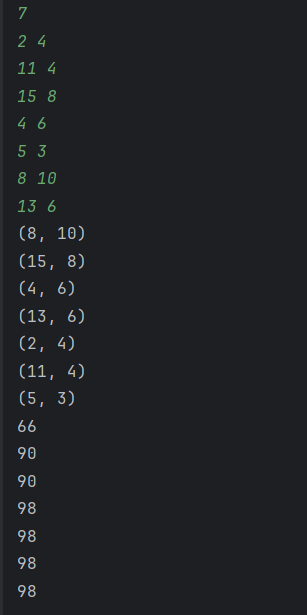
왜 정렬을 사용했는가?
정렬을 사용해 높이순으로 정렬하고 나면, 투포인터를 제어해서 left, right 값을 바꾸며 단방향 연산이 가능하다고 생각했다. 배열 이외의 자료구조도 필요 없어 메모리도 아낄 수 있다고 생각한다.
왜 시간과 메모리가 더 소모되는가?
당연히 Scanner 클래스를 사용해서 그렇다. Scanner가 사용하기 편해서 계속 사용 중이긴 한데, 입력 종료 조건이 없는 경우, 입력 횟수가 많은 경우에서는 시간, 메모리 낭비가 심하다.
import java.util.*;
public class bj2304 {
static class Pole {
int location;
int height;
public Pole(int location, int height) {
this.location = location;
this.height = height;
}
}
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N;
static Pole[] poles;
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputData();
System.out.println(findAnswer());
sc.close();
}
public static void inputData() {
N = sc.nextInt();
poles = new Pole[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int L = sc.nextInt();
int H = sc.nextInt();
poles[i] = new Pole(L, H);
}
// 위치 기준으로 정렬
Arrays.sort(poles, (a, b) -> {
if (b.height != a.height) {
return b.height - a.height; // 높이 기준 내림차순
} else {
return a.location - b.location; // 높이가 같다면 위치 기준 오름차순
}
});
for(Pole temp : poles){
System.out.println("(" + temp.location + ", " + temp.height + ")");
}
}
public static int findAnswer() {
int answer = 0;
int tallestL = poles[0].location, tallestH = poles[0].height;
int left = tallestL, right = tallestL;
int areaSum = tallestH;
int i;
int nextL, nextH;
for(i = 1; i < N; i++){
nextL = poles[i].location;
nextH = poles[i].height;
if(nextL < left){ // 현재 left보다 더 왼쪽에 있다면
areaSum += nextH * (left - nextL);
left = nextL;
}
else if(nextL > right){ // 현재 right보다 더 오른쪽에 있다면
areaSum += nextH * (nextL - right);
right = nextL;
}
//만약 이미 칠해진 영역 안쪽이면, 계산 필요 없음
System.out.println(areaSum);
}
answer = areaSum;
return answer;
}
}
BufferedReader 사용
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class bj2304 {
static class Pole {
int location;
int height;
public Pole(int location, int height) {
this.location = location;
this.height = height;
}
}
static int N;
static Pole[] poles;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
inputData();
System.out.println(findAnswer());
}
public static void inputData() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
poles = new Pole[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int L = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int H = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
poles[i] = new Pole(L, H);
}
// 높이 내림차순, 위치 오름차순 정렬
Arrays.sort(poles, (a, b) -> {
if (b.height != a.height) {
return b.height - a.height;
} else {
return a.location - b.location;
}
});
// for(Pole temp : poles){
// System.out.println("(" + temp.location + ", " + temp.height + ")");
// }
}
public static int findAnswer() {
int tallestL = poles[0].location, tallestH = poles[0].height;
int left = tallestL, right = tallestL;
int areaSum = tallestH;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
int nextL = poles[i].location;
int nextH = poles[i].height;
if (nextL < left) {
areaSum += nextH * (left - nextL);
left = nextL;
} else if (nextL > right) {
areaSum += nextH * (nextL - right);
right = nextL;
}
// System.out.println(areaSum);
}
return areaSum;
}
}